U1A polyadenylation inhibition element (PIE)
The U1A polyadenylation inhibition element (PIE) is an RNA element which is responsible for the regulation of the length of the polyA tail of the U1A protein pre-mRNA. The PIE is located in the U1A mRNA 3' UTR. PIE adopts a U-shaped structure, with binding sites for a single U1A protein at each bend and when complexed with the two proteins it blocks activity of poly(A) polymerase (PAP), and inhibits its activity.[1][2]
| U1A polyadenylation inhibition element (PIE) | |
|---|---|
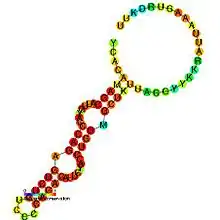 Predicted secondary structure and sequence conservation of U1A_PIE | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | U1A_PIE |
| Rfam | RF00460 |
| Other data | |
| RNA type | Cis-reg |
| Domain(s) | Eukaryota |
| SO | SO:0005836 |
| PDB structures | PDBe |
References
- Clerte C, Hall KB (October 2004). "Global and local dynamics of the U1A polyadenylation inhibition element (PIE) RNA and PIE RNA-U1A complexes". Biochemistry. 43 (42): 13404–13415. doi:10.1021/bi049117g. PMID 15491147.
- Varani L, Gunderson SI, Mattaj IW, Kay LE, Neuhaus D, Varani G (April 2000). "The NMR structure of the 38 kDa U1A protein - PIE RNA complex reveals the basis of cooperativity in regulation of polyadenylation by human U1A protein". Nature Structural Biology. 7 (4): 329–335. doi:10.1038/74101. PMID 10742179. S2CID 13432764.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.