Ultrawide formats
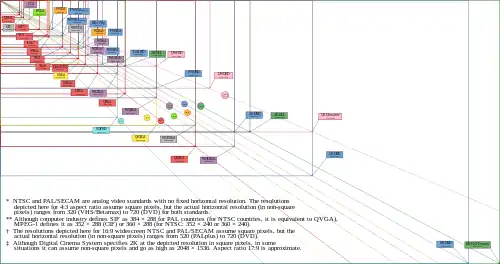
Ultrawide formats refers to photos, videos,[1] and displays[2] with aspect ratios greater than 2. There were multiple moves in history towards wider formats, including one by Disney,[3] with some of them being more successful than others.
Cameras usually capture ultra-wide photos and videos using an anamorphic format lens, which shrinks the extended horizontal field-of-view (FOV) while saving on film or disk.[4]
Historic displays
Before computer monitors became a separate product line, televisions were used as displays[5] for computers such as Timex Sinclair 1000.
4:3
4:3 was the aspect ratio used by 35 mm silent films. By having televisions match this aspect ratio, movies originally filmed in 4:3 could be satisfactorily viewed on standard-definition television (SDTV). Monitors around the turn of the century would often use resolutions like 640x480, 800x600, 1024x768 or 1200x900 in an 4:3 aspect ratio.
NTSC (480i)
National Television System Committee (NTSC) broadcasts were analogue and intended for analogue NTSC displays. The standard was developed and implemented by the NTSC in the United States in 1954. It also saw widespread international adoption by trade partners of the US. When converted to the Digital Video format, DV NTSC has a 3:2 aspect ratio, a resolution of 720x480i, and a refresh rate of 60 Hz.
PAL (576i)
Phase Alternating Line (PAL) broadcasts were analogue broadcasts meant for PAL analogue displays. The standard was developed in 1967 by the United Kingdom and Germany, and implemented in most countries. When converted to Digital Video format, DV PAL has a 5:4 resolution of 720×576i running at 50 Hz.
32:27
32:27 was originally developed for compressed video storage in cameras, meant to be displayed in anamorphic x1.5 as 16:9. 640×540i was such a 32:27 resolution running at 50 Hz and 100 Hz, meant for cameras.
Panasonic's DVCPRO HD[6] with a resolution of 1280×1080i was latest in the line of 32:27 video formats for cameras. Hitachi's 42" and 50" 1280×1080i televisions, like the P50T501, were the last line of 32:27 consumer displays.[7]
32:27 is derived from 4:3 aspect ratio.
Historic Ultrawide Cinema
Historically ultrawide movie formats have varied between ~2.35 (1678:715), ~2.39 (1024:429) and 2.4. To complicate matters further, films were also produced in following ratios: 2.55, 2.76 and 4. Developed by Rowe E. Carney Jr. and Tom F. Smith, the Smith-Carney System used a 3 camera system, with 4.6945 (1737:370) ratio, to project movies in 180°.[8] Disney even created a 6.85 ratio, using 5 projectors to display 200°. The only movie filmed in Disney's 6.85 ratio is Impressions de France.[3]
Modern displays
Widescreen revolution
15:9
16:10
16:9
Suggested by Dr. Kerns H. Powers of SMPTE in USA, the 16:9 aspect ratio was developed to unify all other aspect ratios. 16:9 was first adopted in the USA.
Around 2007, cameras and screens began to switch from 15:9 and 16:10 to 16:9 resolutions. Aspect ratio of 16:9 is currently the universal standard for 'widescreen' and High-definition television.
Univisium
Univisium is an aspect ratio of 2.00:1, created by Vittorio Storaro of ASC in the USA, to unify all other aspect ratios. It is popular on Smartphones and cheap VR displays. VR displays halve the screen into two, one for each eye. So a 2:1 VR screen would be halved into two 1:1 screens. Smartphones began moving to this aspect ratio since late 2010s with the release of Samsung Galaxy S8, advertised as 18:9.
Ultrawide Cinema
21:9 is a consumer electronics (CE) marketing term to describe the ultra-widescreen aspect ratio of 64:27 (2.370) = 1024:432 for multiples of 1080 lines. It is used for multiple anamorphic formats and DCI 1024:429 (21.482517:9), but also for ultrawide computer monitors, including 43:18 (211⁄2:9) for resolutions based on 720 lines and 12:5 (213⁄5:9) for ultrawide variants of resolutions based either on 960 pixels width or 900 lines height.
The 64:27 aspect ratio is the logical extension of the existing video aspect ratios 4:3 and 16:9. It is the third power of 4:3, whereas 16:9 of widescreen HDTV is 4:3 squared. This allows electronic scalers and optical anamorphic lenses to use an easily implementable 4:3 (1.33) scaling factor.
21:9 movies usually refers to 1024:429 ≈ 2.387, the aspect ratio of digital ultrawide cinema formats, which is often rounded up to 2.39:1 or 2.40:1
Ultrawide resolution can also be described by its height, such as "UW 1080" and "1080p ultrawide" both stands for the same 2560×1080 resolution.
| common name | aspect ratio | resolution |
|---|---|---|
| WFHD | 64∶27 | 2560×1080 |
| WFHD+ | 12∶5 | 2880×1200 |
| WQHD | 43∶18 | 3440×1440 |
| WQHD+ | 12∶5 | 3840×1600 |
| UW4K | 12∶5 | 4320×1800 |
| UW5K (WUHD) | 64∶27 | 5120×2160 |
| UW5K+ | 12∶5 | 5760×2400 |
| UW6K | 43∶18 | 6880×2880 |
| UW7K | 12∶5 | 7680×3200 |
| UW8K | 12∶5 | 8640×3600 |
| UW10K | 64∶27 | 10240×4320 |
| simple | decimal | n∶9 |
|---|---|---|
| 64∶27 | 2.370 | 211⁄3∶9 |
| 43∶18 | 2.38 | 211⁄2∶9 |
| 12∶5 | 2.40 | 213⁄5∶9 |
Ultra-Widescreen 3.6
In 2016, IMAX announced the release of films in 'Ultra-WideScreen 3.6' format,[9] with an aspect ratio of 18:5 (36:10).[10] A year later, Samsung and Phillips announced 'super ultra-wide displays', with aspect ratio of 32:9, for "iMax-style cinematic viewing".[11] Panacast developed a 32:9 webcam with three integrated cameras giving 180° view, and resolution matching upcoming 5K 32:9 monitors, 5120x1440.[12] In 2018 Q4, Dell released the U4919DW, a 5K 32:9 monitor with a resolution of 5120x1440, and Phillips announced the 499P9H with the same resolution. 32:9 Ultrawide monitors are often sold as an alternative to dual 16:9 monitor setups and for more inmersive experiences while playing videogames, and many are capable of displaying 2 16:9 inputs at the same time.
32:9 aspect ratio is derived from 16:9 being twice as large.
Super wide resolutions refers to that with aspect ratio greater than 3.
| common name | aspect ratio | resolution |
|---|---|---|
| DWXGA+ | 16∶5 | 2880×900 |
| DFHD | 32∶9 | 3840×1080 |
| DFHD+ | 16∶5 | 3840×1200 |
| SWFHD+ | 18∶5 | 4320×1200 |
| DQHD | 32∶9 | 5120×1440 |
| DQHD+ | 16∶5 | 5120×1600 |
| SWQHD+ | 18∶5 | 5760×1600 |
| 16:5 5K | 16∶5 | 5760×1800 |
| 32:9 6K | 32∶9 | 6400×1800 |
| 18:5 6K | 18∶5 | 6480×1800 |
| DUHD | 32∶9 | 7680×2160 |
| DUHD+ | 16∶5 | 7680×2400 |
| 18:5 8K | 18∶5 | 8640×2400 |
| simple | decimal |
|---|---|
| 16∶5 | 3.2 |
| 32∶9 | 3.5 |
| 18∶5 | 3.6 |
Ultra-WideScreen 3.6 video never spread, as cinemas in an even wider ScreenX 270° format were released.[13]
4:1 (36:9)
Abel Gance experimented with ultrawide formats including making a film in 4:1 (36:9). He made a rare use of Polyvision, three 35 mm 1.3 images projected side by side in Napoléon (1927 film).
Recently, Sony introduced a 19.2-metre-wide by 5.4-metre-tall commercial 16K display at NAB 2019 that is set to be released in Japan.[14][15] It is made up of 576 modules (48 by 12) each 360 pixels across, resulting in a 4:1, 17280x4320p screen.
Multi-Screen Theaters

Developed by CJ CGV in 2012, ScreenX uses three (or more) projectors to display 270° content,[13] with an unknown aspect ratio above 4. Walls on both sides of a ScreenX theatre are used as projector screens.
Developed by Barco N.V. in 2015, Barco Escape used three projectors of 2.39 ratio to display 270° content, with an aspect ratio of 7.17. The two side screens were angled at 45 degree in order to cover peripheral vision. Barco Escape shut down in February 2018.
Comparison
| Decimal value | Aspect ratio | Format name | Resolutions | Lens & Film |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.185 | 32:27 | DVCPRO HD | 640×540, 1280×1080 | 1x |
| 1.25 | 5:4 | DV PAL | 720×576, 1280×1024, 1500×1200 | 1x |
| 1.3 | 4:3 | Video Graphics Array | 640×480, 960×720, 1440×1080, 1600×1200 | SDTV |
| 1.5 | 3:2 | DV NTSC / laptops | 720×480, 1920×1280, 2160×1440, 2256×1504, 2400×1600, 3000×2000 | 1x |
| 1.6 | 8:5 | 16:10 widescreen (PC only) | 1280×800, 1440×900, 1680×1050, 1920×1200, 2560×1600, 2880×1800, 3072×1920, 3840×2400 | - |
| 1.6 | 5:3 | European Widescreen | 800×480, 1280×768 | Super 16 mm |
| 1.7 | 16:9 | Widescreen | 1920×1080, 2560×1440, 3840×2160, 7680×4320 | Anamorphic 1.5x on 32:27, HDTV |
| 1.618 | 16:10 | 16:10 Tallboy | 640×400, 960×600, 1280×800, 1440×900, 1680×1050, 1920×1200, 2560×1600, 3840×2400 | - |
| 1.85 | 37:20 | "Flat" DCI | 1998×1080, 3996×2160 | 1x |
| 1.8962 | 256:135 | "Full" DCI | 2048×1080, 4096×2160 | 1x |
| 2.0 | 2:1 | VistaVision / Univisium | 2160×1080, 2400×1200, 2880×1440, 3200×1600, 3600×1800, 3840×1920, 4320×2160, 4800×2400, 5760×2880 | VR cameras (most) |
| 2.3468531 | 1678:715[16] | Cinemascope (1950s–1970s) | analog | Anamorphic 2x on 35 mm with optical audio |
| 2.370 | 64:27 | "21:9" ultrawide | 2560×1080, 5120×2160, 7680×3240, 10240×4320 | Dashcam, Anamorphic 1.33x on 16:9, 1.25x on DCI 256:135, 2x on 32:27 |
| 2.386946 | 1024:429 | "Scope" DCI cinema format | 2048×858, 4096×1716, 8192×3432 | 1x |
| 2.38 | 43:18 | "21:9" ultrawide (PC only) | 3440×1440, 5160×2160, 6880×2880 | - |
| 2.4 | 12:5 | 24:10 ultrawide | 2880×1200, 3840×1600, 4320×1800, 5760×2400, 7680×3200 | - |
| 2.55 | 51:20 | Cinemascope 55 | analog | Anamorphic 2x on 35 mm without optical audio |
| 2.6 | 8:3 | Cinerama / 24:9 ultrawide (PC only) | 2880×1080, 3840×1440, 5120×1920, 5760×2160, 7680×2880, 10240×3840 | - |
| 2.76 | 69:25 | Ultra Panavision | analog | Anamorphic 1.25x on 70 mm |
| 3.2 | 16:5 | 32:10 super wide (PC only) | 2880×900, 3840×1200, 5120×1600, 5760×1800, 7680×2400, 10240×3200 | - |
| 3.5 | 32:9 | 32:9 super wide (PC only) | 3840×1080, 5120×1440, 7680×2160, 10240×2880 | - |
| 3.6 | 18:5 | 36:10 super wide (ultra-widescreen 3.6) | 4320×1200, 5760×1600, 6480×1800, 8640×2400 | 1x |
| 4.0 | 4:1 | Polyvision | analog / 3 images 4:3 projected side by side | 3x |
See also
References
- A History of Widescreen and Wide-Film Projection Processes
- All About Ultrawide Monitors, the Latest Trend in Gaming and Productivity
- p20, Sherlock, Daniel J. "Wide Screen Movies" Corrections, 1994–2004
- Red Camera: Anamorphic lens intro
- University of Virginia's Computer Museum
- Apple Final Cut Pro: DV Pro HD Format, Archived
- "Hitachi P50T501". Wired. 2007-10-23. Archived from the original on 2023-06-01.
- Smith-Carney System
- "Voyage of Time: The IMAX Experience in Ultra-Widescreen". IMAX.com. Dec 7, 2016. Retrieved April 27, 2018.
- Kristopher Tapley (Dec 5, 2016). "'Ultra Widescreen' Version of Terrence Malick's 'Voyage of Time' Set for Release". variety.com. Retrieved April 27, 2018.
- super ultra-wide -Samsung News
- Panacast
- Introducing Screen X, Cinema in 270 Degrees
- Waniata, Ryan (2019-04-10). "Sony's massive new MicroLED display stands 17 feet tall and packs 16K resolution". Digital Trends. Retrieved 2019-10-17.
- Dent, Steve (2019-09-13). "Sony's Crystal cinema display supports 16K, but could cost millions". Engadget. Retrieved 2019-12-18.
- "Wide Screen Apertures and Aspect Ratios". The American WideScreen Museum. October 17, 2000. Retrieved November 2, 2018.