Unified Thread Standard
The Unified Thread Standard (UTS) defines a standard thread form and series—along with allowances, tolerances, and designations—for screw threads commonly used in the United States and Canada. It is the main standard for bolts, nuts, and a wide variety of other threaded fasteners used in these countries. It has the same 60° profile as the ISO metric screw thread, but the characteristic dimensions of each UTS thread (outer diameter and pitch) were chosen as an inch fraction rather than a millimeter value. The UTS is currently controlled by ASME/ANSI in the United States.
Origins
Basic profile
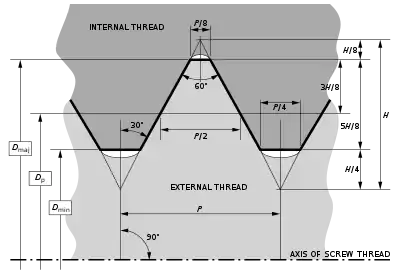
Each thread in the series is characterized by its major diameter Dmaj and its pitch, P. UTS threads consist of a symmetric V-shaped thread. In the plane of the thread axis, the flanks of the V have an angle of 60° to each other. The outermost 1⁄8 and the innermost 1⁄4 of the height H of the V-shape are cut off from the profile.
The major diameter Dmaj is the diameter of the screw measured from the outer edge of the threads. The minor diameter Dmin (also known as the root diameter) is the diameter of the screw measured from the inner edge of the threads. The major diameter may be slightly different than the shank diameter, which is the diameter of the unthreaded part of the screw. The diameters are sometimes given approximately in fractions of an inch (e.g. the major diameter of a #6 screw is 0.1380 in, approximately 9⁄64 in = 0.140625 in).
The pitch P is the distance between thread peaks. For UTS threads, which are single-start threads, it is equal to the lead, the axial distance that the screw advances during a 360° rotation. UTS threads do not usually use the pitch parameter; instead a parameter known as threads per inch (TPI) is used, which is the reciprocal of the pitch.
The relationship between the height H and the pitch P is found using the following equation where is half the included angle of the thread, in this case 30 degrees:[1]
or
In an external (male) thread (e.g., on a bolt), the major diameter Dmaj and the minor diameter Dmin define maximum dimensions of the thread. This means that the external thread must end flat at Dmaj, but can be rounded out below the minor diameter Dmin. Conversely, in an internal (female) thread (e.g., in a nut), the major and minor diameters are minimum dimensions, therefore the thread profile must end flat at Dmin but may be rounded out beyond Dmaj.
The minor diameter Dmin and effective pitch diameter Dp are derived from the major diameter and pitch as:
Designation
The standard designation for a UTS thread is a number indicating the nominal (major) diameter of the thread, followed by the pitch measured in threads per inch. For diameters smaller than 1⁄4 inch, the diameter is indicated by an integer number defined in the standard; for all other diameters, the inch figure is given.
This number pair is optionally followed by the letters UNC, UNF or UNEF (Unified) if the diameter-pitch combination is from the coarse, fine, or extra fine series, and may also be followed by a tolerance class.
Example: #6-32 UNC 2B (major diameter: 0.1380 inch, pitch: 32 tpi)
| Major diameter Dmaj (inch, mm) |
Thread density (d, threads per inch) and thread pitch (p) | Preferred cutting tap drill size | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coarse (UNC) | Fine (UNF) | Extra fine (UNEF) | |||||||||||||||
| d (TPI) | p (inch, mm) | d (TPI) | p (inch, mm) | d (TPI) | p (inch, mm) | Coarse | Fine | Extra fine | |||||||||
| #0 | 0.0600 | 1.5240 | None | 80 | 0.012500 | 0.3175 | None | 3⁄64 in | .047 | ||||||||
| #1 | 0.0730 | 1.8542 | 64 | 0.015625 | 0.3969 | 72 | 0.013888 | 0.3528 | None | #53 | .060 | #53 | .060 | ||||
| #2 | 0.0860 | 2.1844 | 56 | 0.017857 | 0.4536 | 64 | 0.015625 | 0.3969 | None | #50 | .070 | #50 | .070 | ||||
| #3 | 0.0990 | 2.5146 | 48 | 0.020833 | 0.5292 | 56 | 0.017857 | 0.4536 | None | #47 | .079 | #45 | .082 | ||||
| #4 | 0.1120 | 2.8448 | 40 | 0.025000 | 0.6350 | 48 | 0.020833 | 0.5292 | None | #43 | .089 | #42 | .094 | ||||
| #5 | 0.1250 | 3.1750 | 40 | 0.025000 | 0.6350 | 44 | 0.022727 | 0.5773 | None | #38 | .102 | #37 | .104 | ||||
| #6 | 0.1380 | 3.5052 | 32 | 0.031250 | 0.7938 | 40 | 0.025000 | 0.6350 | None | #36 | .107 | #33 | .113 | ||||
| #8 | 0.1640 | 4.1656 | 32 | 0.031250 | 0.7938 | 36 | 0.027778 | 0.7056 | None | #29 | .136 | #29 | .136 | ||||
| #10 | 0.1900 | 4.8260 | 24 | 0.041667 | 1.0583 | 32 | 0.031250 | 0.7938 | None | #25 | .150 | #21 | .159 | ||||
| #12 | 0.2160 | 5.4864 | 24 | 0.041667 | 1.0583 | 28 | 0.035714 | 0.9071 | 32 | 0.031250 | 0.7938 | #16 | .177 | #14 | .182 | 3⁄16 in | .188 |
| 1⁄4″ | 0.2500 | 6.3500 | 20 | 0.050000 | 1.2700 | 28 | 0.035714 | 0.9071 | 32 | 0.031250 | 0.7938 | #7 | .201 | #3 | .213 | 7⁄32 in | .219 |
| 5⁄16″ | 0.3125 | 7.9375 | 18 | 0.055556 | 1.4111 | 24 | 0.041667 | 1.0583 | 32 | 0.031250 | 0.7938 | F | .257 | I | .272 | 9⁄32 in | .281 |
| 3⁄8″ | 0.3750 | 9.5250 | 16 | 0.062500 | 1.5875 | 24 | 0.041667 | 1.0583 | 32 | 0.031250 | 0.7938 | 5⁄16 in | .313 | Q | .332 | 11⁄32 in | .344 |
| 7⁄16″ | 0.4375 | 11.1125 | 14 | 0.071428 | 1.8143 | 20 | 0.050000 | 1.2700 | 28 | 0.035714 | 0.9071 | U | .368 | 25⁄64 in | .391 | Y | .404 |
| 1⁄2″ | 0.5000 | 12.7000 | 13 | 0.076923 | 1.9538 | 20 | 0.050000 | 1.2700 | 28 | 0.035714 | 0.9071 | 27⁄64 in | .422 | 29⁄64 in | .453 | 15⁄32 in | .469 |
| 9⁄16″ | 0.5625 | 14.2875 | 12 | 0.083333 | 2.1167 | 18 | 0.055556 | 1.4111 | 24 | 0.041667 | 1.0583 | 31⁄64 in | .484 | 1⁄2 in | .500 | 33⁄64 in | .516 |
| 5⁄8″ | 0.6250 | 15.8750 | 11 | 0.090909 | 2.3091 | 18 | 0.055556 | 1.4111 | 24 | 0.041667 | 1.0583 | 17⁄32 in | .531 | 9⁄16 in | .563 | 37⁄64 in | .578 |
| 3⁄4″ | 0.7500 | 19.0500 | 10 | 0.100000 | 2.5400 | 16 | 0.062500 | 1.5875 | 20 | 0.050000 | 1.2700 | 21⁄32 in | .656 | 11⁄16 in | .688 | 45⁄64 in | .703 |
| 7⁄8″ | 0.8750 | 22.2250 | 9 | 0.111111 | 2.8222 | 14 | 0.071428 | 1.8143 | 20 | 0.050000 | 1.2700 | 49⁄64 in | .766 | 51⁄64 in | .797 | 53⁄64 in | .828 |
| 1″ | 1.0000 | 25.4000 | 8 | 0.125000 | 3.1750 | 12[lower-alpha 1] | 0.083333 | 2.1167 | 20 | 0.050000 | 1.2700 | 7⁄8 in | .875 | 59⁄64 in | .922 | 61⁄64 in | .953 |
| 1+1⁄8″ | 1.1250 | 28.5750 | 7 | 0.142857 | 3.6286 | 12 | 0.083333 | 2.1167 | |||||||||
| 1+1⁄4″ | 1.2500 | 31.7500 | 7 | 0.142857 | 3.6286 | 12 | 0.083333 | 2.1167 | |||||||||
| 1+3⁄8″ | 1.3750 | 34.9250 | 6 | 0.166667 | 4.2333 | 12 | 0.083333 | 2.1167 | |||||||||
| 1+1⁄2″ | 1.5000 | 38.1000 | 6 | 0.166667 | 4.2333 | 12 | 0.083333 | 2.1167 | |||||||||
| 1+3⁄4″ | 1.7500 | 44.4500 | 5 | 0.200000 | 5.0800 | ||||||||||||
| 2″ | 2.0000 | 50.8000 | 4+1⁄2 | 0.222222 | 5.6444 | ||||||||||||
| 2+1⁄4″ | 2.2500 | 57.1500 | 4+1⁄2 | 0.222222 | 5.6444 | ||||||||||||
| 2+1⁄2″ | 2.5000 | 63.5000 | 4 | 0.250000 | 6.3500 | ||||||||||||
| 2+3⁄4″ | 2.7500 | 69.8500 | 4 | 0.250000 | 6.3500 | ||||||||||||
| 3″ | 3.0000 | 76.2000 | 4 | 0.250000 | 6.3500 | ||||||||||||
| 3+1⁄4″ | 3.2500 | 82.5500 | 4 | 0.250000 | 6.3500 | ||||||||||||
| 3+1⁄2″ | 3.5000 | 88.9000 | 4 | 0.250000 | 6.3500 | ||||||||||||
| 3+3⁄4″ | 3.7500 | 95.2500 | 4 | 0.250000 | 6.3500 | ||||||||||||
| 4″ | 4.0000 | 101.6000 | 4 | 0.250000 | 6.3500 | ||||||||||||
- For many years non-standard 1-inch 14-tpi nuts and bolts have been widely used instead of standard-sized 1-inch 12-tpi fasteners; consequently 1″-14 fasteners are easier to find and less expensive than 1″-12 fasteners. After several decades 1″-14 fasteners have now come to be commonly referred to as "Standard Fine Thread" or "UNF". Though technically incorrect (the UNF standard specifies 1″-12), size 1″-14 is universally accepted as standard for fine-threaded 1-inch fasteners, and "1-inch 14-tpi NF" has become established as a "common use" term, or "a genericized brand name/standard". In other words, the 1″-12 standard has lacked effective enforcement for a long enough time (many decades) to give generic trademark–like status to 1-inch 14-tpi fasteners.
The following formula is used to calculate the major diameter of a numbered screw greater than or equal to 0: Major diameter = Screw # × 0.013 in + 0.060 in. For example, the major diameter of a #10 screw is 10 × 0.013 in + 0.060 in = 0.190 in. To calculate the major diameter of "aught" size screws count the number of extra zeroes and multiply this number by 0.013 in and subtract from 0.060 in. For example, the major diameter of a #0000 screw is 0.060 in − (3 × 0.013 in) = 0.060 in − 0.039 in = 0.021 in.
The number series of machine screws has been extended downward to include #00-90 (0.047 in = 0.060 in − 0.013 in) and #000-120 (0.034 in = 0.060 in − 2 × 0.013 in) screws;[3] however, the main standard for screws smaller than #0 is ANSI/ASME standard B1.10 Unified Miniature Screw Threads. This defines a series of metric screws named after their major diameters in millimetres, from 0.30 UNM to 1.40 UNM. Preferred sizes are 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 and 1.2 mm, with additional defined sizes halfway between.[2]: 1861 The standard thread pitch is approximately 1/4 of the major diameter. The thread form is slightly modified to increase the minor diameter, and thus the strength of screws and taps. The major diameter still extends to within 1/8H of the theoretical sharp V, but the total depth of the thread is reduced 4% from 5/8H = 5/8 cos(30°) P ≈ 0.541P to 0.52P.[2]: 1858–1859 This increases the amount of the theoretical sharp V which is cut off at the minor diameter by 10% from 0.25H to 7/8 − 0.52/cos 30° ≈ 0.27456H.
The number series of machine screws once included more odd numbers and went up to #16 or more. Standardization efforts in the late 19th and the early part of the 20th century reduced the range of sizes considerably. Now, it is less common to see machine screws larger than #14, or odd number sizes other than #1, #3 and #5. Even though #14 and #16 screws are still available, they are not as common as sizes #0 through #12.
Sometimes "special" diameter and pitch combinations (UNS) are used, for example a 0.619 in (15.7 mm) major diameter with 20 threads per inch. UNS threads are rarely used for bolts, but rather on nuts, tapped holes, and threaded ODs. Because of this UNS taps are readily available.[4][5] Most UNS threads have more threads per inch than the correlating UNF or UNEF standard; therefore they are often the strongest thread available.[6] Because of this they are often used in applications where high stresses are encountered, such as machine tool spindles[7] or automotive spindles.[8]
Gauging
A screw thread gauging system comprises a list of screw thread characteristics that must be inspected to establish the dimensional acceptability of the screw threads on a threaded product and the gauge(s) which shall be used when inspecting those characteristics.
Currently this gauging for UTS is controlled by:
- ASME/ANSI B1.2-1983 Gauges And Gauging For Unified Inch Screw Threads
- This Standard provides essential specifications and dimensions for the gauges used on Unified inch screw threads UN [unified] and UNR [external threads only] thread form, and covers the specifications and dimensions for the thread gauges and measuring equipment listed in Tables 1 and 2. The basic purpose and use of each gauge are also described.
- ASME/ANSI B1.3-2007 Screw Thread Gauging Systems for Acceptability: Inch and Metric Screw Threads (UN, UNR, UNJ, M, and MJ)
- This Standard presents screw thread gauging systems suitable for determining the acceptability of Unified [UN], UNR [external threads only], UNJ [internal and external threads], M, and MJ screw threads on externally and internally threaded products. It establishes the criteria for screw thread acceptance when a gauging system is used.
- A screw thread gauging system comprises a list of screw thread characteristics that must be inspected to establish the dimensional acceptability of the screw threads on a threaded product and the gauge(s) which shall be used when inspecting those characteristics.
- Federal Government Use. When this Standard is approved by the Department of Defense and federal agencies and is incorporated into Federal Standard-H28/20 [FED-STD-H28/20], Screw Thread Standards for Federal Services, Section 20, the use of this Standard by the federal government is subject to all the requirements and limitations of Federal Standard-H28/20 [FED-STD-H28/20].
These standards provide essential specifications and dimensions for the gauges used on Unified inch screw threads (UN, UNR, UNJ thread form) on externally and internally threaded products. It also covers the specifications and dimensions for the thread gauges and measuring equipment. The basic purpose and use of each gauge are also described. It also establishes the criteria for screw thread acceptance when a gauging system is used.
Tolerance classes
A classification system exists for ease of manufacture and interchangeability of fabricated threaded items. Most (but certainly not all) threaded items are made to a classification standard called the Unified Screw Thread Standard Series. This system is analogous to the fits used with assembled parts.
- Class 1 threads are loose fit, intended for ease of assembly or use in a dirty environment.
- Class 2 threads are free fit, and the most common. They are designed to maximize strength considering typical machine shop capability and machine practice.
- Class 3 threads are medium fit, still quite common and used for closer tolerances on high quality work.
- Class 4 threads previously designated a close fit for even tighter tolerances, but this classification is now obsolete.
- Class 5 fit is an interference thread, requiring the use of a wrench for turning. These can be seen in applications like spring shackles on an automobile.
The letter suffix "A" or "B" denotes whether the threads are external or internal, respectively. Classes 1A, 2A, 3A apply to external threads; Classes 1B, 2B, 3B apply to internal threads.[9]
Thread class refers to the acceptable range of pitch diameter for any given thread. The pitch diameter is indicated as Dp in the figure shown above. There are several methods that are used to measure the pitch diameter. The most common method used in production is by way of a go/no-go gauge.
Related standards
- ASME/ANSI B1.1 – 2019 Unified Inch Screw Threads, UN, UNR, & UNJ Thread Form
- ASME/ANSI B1.10M – 2004 Unified Miniature Screw Threads
See also
Notes
- Oberg et al. 2000, p. 1706.
- Oberg, Erik (2012). Machinery's Handbook (29th ed.). New York: Industrial Press. ISBN 978-0-8311-2900-2.
- #00-90 and #000-120 screws for sale
- McMaster-Carr, p. 2520, retrieved 28 August 2009
- McMaster-Carr, p. 2501, retrieved 28 August 2009
- Schwaller 2004, p. 55.
- Special connections, archived from the original on 18 May 2009, retrieved 28 August 2009.
- Hub components (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on 17 June 2009, retrieved 29 August 2009.
- "AFT Thread Terminology" (PDF). aftfasteners.com. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
Bibliography
- Ryffel, Henry H.; et al., eds. (1988), Machinery's Handbook (23rd ed.), New York: Industrial Press, ISBN 978-0-8311-1200-4.
- Schwaller, Anthony E. (2004), Total Automotive Technology (4th ed.), Cengage Learning, ISBN 978-1-4018-2476-1.
External links
- Unified Screw Threads with Tolerances
- Unified Coarse/Fine diameters and tap drill sizes (U.S. units)
- Unified Coarse/Fine tap drill sizes (U.S. units)
- Imperial Metric fastening size conversion charts
- International Thread Standards
- Conversion chart Whitworth/BSF/AF and metric Archived 2 May 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- Spanner Jaw Sizes Additional information and spanner jaw size table.
- Unified Screw Threads Series
- ASME B1.1-2003 Unified Inch Screw Threads, (UN and UNR Thread Form)
- Unified Inch Screw Threads