United Nations geoscheme for Oceania
The following is an alphabetical list of subregions in the United Nations geoscheme for Oceania, created by the United Nations Statistics Division (UNSD).[1]
Oceania
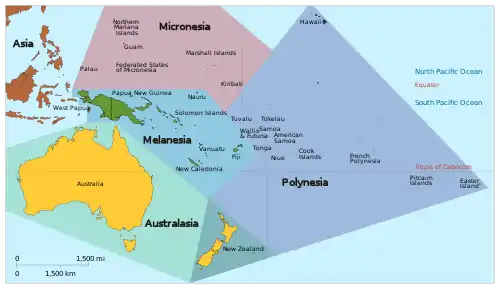
UN geoscheme subregions of Oceania
| Area | 8,525,989 km2 (3,291,903 sq mi) |
|---|---|
| Population | 41,570,842 (2018, 6th) |
| Demonym | Oceanian |
| Countries | 14 (sovereign) 2 (associated) |
| Dependencies | 21 |
| Time Zones | UTC+14 (Kiribati) to UTC-11 (American Samoa and Niue) (West to East) |
| Largest Cities |
UN Subregions

Oceania with its sovereign and dependent islands within the subregions Melanesia, Micronesia, Polynesia and Australasia
The United Nations geoscheme subdivides the region into Australia and New Zealand, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. The UNSD notes that "the assignment of countries or areas to specific groupings is for statistical convenience and does not imply any assumption regarding political or other affiliation of countries or territories".[1]
| Subregion | Country/Territory and capital city[note 1] |
|---|---|
| Australia and New Zealand | Capital: Canberra |
Capital: Flying Fish Cove | |
Capital: West Island | |
Capital: Wellington | |
Capital: Kingston | |
| Melanesia | Capital: Suva |
Capital: Nouméa | |
Capital: Port Moresby | |
Capital: Honiara | |
Capital: Port Vila | |
| Micronesia | Capital: Hagåtña |
Capital: South Tarawa | |
Capital: Majuro | |
Capital: Palikir | |
Capital: Yaren (unofficial, seat of parliament) | |
Capital: Saipan | |
Capital: Ngerulmud | |
Capital: Washington, D.C. (administrative centre) | |
| Polynesia | Capital: Pago Pago |
Capital: Avarua | |
Capital: Pape'ete | |
Capital: Alofi | |
Capital: Adamstown | |
Capital: Apia | |
Capital: Fakaofo | |
Capital: Nukuʻalofa | |
Capital: Funafuti | |
Capital: Mata-Utu |
See also
Notes
- Subregions and countries/territories as per the United Nations geoscheme.
- The United Nations geoscheme has included the United States Minor Outlying Islands in Micronesia despite most of its islands are located in Polynesia geographically. Wake Island is the only island in the territory located in Micronesia. Navassa Island in the Caribbean Sea has been excluded from this territory by the UN geoscheme. This disputed island has not been included in the Caribbean subregion either.[2]
References
- United Nations Statistics Division – Standard Country and Area Codes Classifications
- UNSD M49 Standard – Recent changes (see Note 11)
- CIA (2010-07-15). "Cook Islands at the CIA's page". CIA. Retrieved 2015-06-23.
- CIA (2010-07-15). "Niue at the CIA's page". CIA. Retrieved 2015-06-23.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.