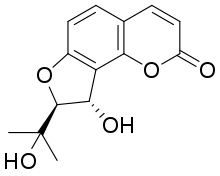
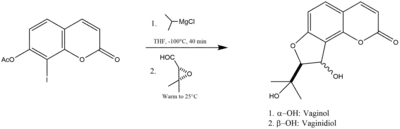Vaginol
Vaginol is a chemical compound of the furanocoumarin class. Its glucoside is apterin.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14O5 | |
| Molar mass | 262.261 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It has been prepared by the following reaction sequence:
References
- Alamgir, A.N.M. (2018). Therapeutic Use of Medicinal Plants and their Extracts: Volume 2: Phytochemistry and Bioactive Compounds. Progress in Drug Research. Springer International Publishing. p. 253. ISBN 978-3-319-92387-1. Retrieved 18 April 2019.
Coumarin glycosides contain coumarin or a derivative as aglycone, e.g., apterin is a coumarin glycoside. It is a furanocoumarin, the glucoside of vaginol. It has been isolated from the root of plants in the Apiaceae (Angelica spp. Zizia aptera ...
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.