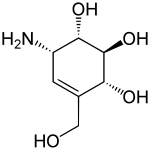
Valienamine
Valienamine is a C-7 aminocyclitol found as a substructure of pseudooligosaccharides such as the antidiabetic drug acarbose[1] and the antibiotic validamycin. It can be found in Actinoplanes species.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1S,2S,4R,6S)-6-Amino-4-(hydroxymethyl)cyclohex-4-ene-1,2,3-triol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H13NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 175.184 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
It is an intermediate formed by microbial degradation of validamycins.[3]
References
- Laube, Heiner (March 2002). "Acarbose An Update of Its Therapeutic Use in Diabetes Treatment". Clinical Drug Investigation. 22 (3): 141–156. doi:10.2165/00044011-200222030-00001.
- Zhang CS, Stratmann A, Block O, et al. (June 2002). "Biosynthesis of the C(7)-cyclitol moiety of acarbose in Actinoplanes species SE50/110. 7-O-phosphorylation of the initial cyclitol precursor leads to proposal of a new biosynthetic pathway". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (25): 22853–62. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202375200. PMID 11937512.
- CID 193758 from PubChem
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.