North Macedonia under the Ottoman Empire
North Macedonia was part of the Ottoman Empire for over five hundred years, from the late 14th century to the Treaty of Bucharest (1913).[1] Before its conquest, this area was divided between various Serbian feudal principalities. Later, it became part of the Ottoman province or Eyalet of Rumelia. The name Rumelia (Turkish: Rumeli) means "Land of the Romans" in Turkish, referring to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Turks from the Byzantine Empire.[1]
History
Conquests
In the Battle of Maritsa of 1371, the King of Lordship of Prilep Vukašin Mrnjavčević and his brother Jovan Uglješa led 70,000 men against the Ottomans. Despite having smaller numbers, the Ottomans managed to kill Vukašin and his brother and win the Battle of Maritsa.[2]
After the battle, most of Serbia broke into smaller principalities. One of those principalities is known as the Kingdom of Prilep, led by Vukašin's son Marko.[3] Like most regional rulers in the Macedonian region, Marko accepted vassalage under Sultan Murad I to preserve his position.
The Battle of Kosovo of 1389 sealed the fate of the region of Macedonia for the next 500 years. While both armies lost leaders and large numbers of soldiers, the Ottomans could easily assemble another army just as large while the locals could not.
Marko died alongside Konstantin Dragaš at the Battle of Rovine in 1395 and the territory of his realm became the Sanjak of Ohrid.[4][5]
All of Vardar Macedonia was under Ottoman control by the early of the 15th century, with Skopje falling under Turkish rule on January 19, 1392.[6][7] Aside from conflict with Skanderbeg's forces, in which areas of western part of the region of Macedonia became a battleground of Ottoman–Albanian war for more than 20 years (1444–1467), the Ottoman Empire ultimately succeeded in taking the region, incorporating it into Rumelia Eyalet.[8]
Rumelia Eyalet
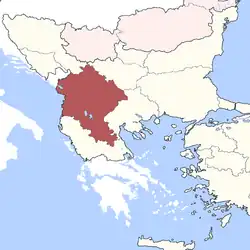
From its foundation, the province of Rumelia encompassed the entirety of the Ottoman Empire's European possessions. The first capital of Rumelia was probably Edirne (Adrianople), which was also, until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, the Ottomans' capital city. In the 18th century, Monastir (present day Bitola) emerged as an alternate residence of the governor, and in 1836, it officially became the capital of the eyalet. At about the same time, the Tanzimat reforms, aimed at modernizing the Empire, split off the new eyalets of Üsküb, Yanya and Selanik and reduced the Rumelia Eyalet to a few provinces around Monastir. The rump eyalet survived until 1867, when, as part of the transition to the more uniform vilayet system, it became part of the Salonica Vilayet.[9][10]
The reduced Rumelia Eyalet, centred at Manastir, encompassed also the sanjaks of Iskenderiyye (Scutari), Ohri (Ohrid) and Kesrye (Kastoria). In 1855, according to the French traveller A. Viquesnel, it comprised the sanjaks of Iskenderiyye, with 7 kazas or sub-provinces, Ohri with 8 kazas, Kesrye with 8 kazas and the pasha-sanjak of Manastir with 11 kazas.[11]
Vilayets
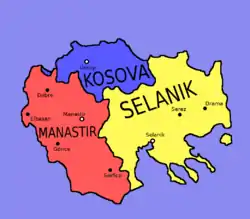
After administrative reform in 1860s, the Ottoman Empire was divided into vilayets which were subdivided into sanjaks.
Kosovo Vilayet
The northern part of the Macedonian region was included in the Kosovo Vilayet. Sanjaks located in this vilayet that contained territory now within the Republic of North Macedonia were:
- Sanjak of Üsküp, which included the kazas of Üsküp (Skopje), Kumanova (Kumanovo), İştip (Štip), Karatova (Kratovo), Planka (Kriva Palanka), Radovişte (Radoviš) and Koçana (Kočani).
- Sanjak of Prizren, which included the kaza of Kalkandelen (Tetovo).
Monastir Vilayet
The southwestern part of the region was located in the Monastir vilayet. Sanjaks located in this vilayet that contained territory now within the Republic of North Macedonia were:
- Sanjak of Monastir, which included the kazas of Monastir (Bitola), Ohri (Ohrid) and Pirlepe (Prilep)
- Sanjak of Dibra, which included the kazas of Debar and Kırçova (Kičevo)
Salonika Vilayet
The southeastern part of the region was located in the Salonika vilayet. Sanjaks located in this vilayet that contained territory now within the Republic of North Macedonia were:
- Sanjak of Selanik, which included the following kazas: Tikveş (Kavadarci), Usturumca (Strumica), Köprülü (Veles)), Toyran (Dojran) and Gevgili (Gevgelija)
1881/82 Ottoman General Census
Ottoman censuses did not count ethnic groups, but rather millets, and increasingly from the 1870s onwards, ethnoconfessional groups. Thus, "Muslims" in the 1881/82 Census covered all adherents of Islam, regardless if they were ethnic Turks, Slavs, Albanians, Romani, etc. "Greeks" referred to all Greeks and to any Vlachs, Albanians and Slavs, who considered themselves to be Greek (or Serbian). "Bulgarians"comprised only those (Christian) Slavs, who considered themselves Bulgarians.
Thus, according to the Ottoman General Census of 1881/82, the population of the kazas currently falling within the borders of the Republic of North Macedonia is divided into the following ethnoconfessional grou[s:[12]
| Kaza1 | Bulgarians | Muslims | Greeks | Miscellaneous2 | Kaza total | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | Number | % | |||||||
| Köprülü | 32,843 | 64.0 | 18,093 | 35.2 | 420 | 0.8 | 0 | - | 51,356 | 100% | ||||||
| Tikveş | 21,319 | 51.3 | 19,909 | 47.8 | 260 | 0.6 | 32 | 0.1 | 41,520 | 100 | ||||||
| Gevgili | 5,784 | 14.9 | 17,063 | 44.0 | 14,558 | 37.5 | 1,402 | 3.6 | 38,807 | 100 | ||||||
| Toyran | 5,605 | 20.6 | 19,423 | 58.2 | 1,591 | 5.9 | 551 | 2.0 | 27,170 | 100 | ||||||
| Usturumca | 2,974 | 9.0 | 15,760 | 47.7 | 13,726 | 41.6 | 564 | 1.7 | 33,024 | 100 | ||||||
| Selanik Vilayet Subtotal | 68,525 | 35.7 | 90,248 | 47.0 | 30,555 | 15.9 | 2,549 | 1.3 | 191,877 | 100 | ||||||
| Üsküp | 22,497 | 32.1 | 40,256 | 57.3 | 6,655 | 9.5 | 762 | 1.1 | 70,170 | 100 | ||||||
| Karatova | 19,618 | 81.8 | 4,332 | 18.1 | 33 | 0.1 | 0 | - | 23,985 | 100 | ||||||
| Kumanova | 29,478 | 70.5 | 12,268 | 29.3 | 87 | 0.2 | 8 | 0.0 | 41,841 | 100 | ||||||
| Planka | 18,196 | 88.1 | 2,078 | 10.1 | 388 | 1.8 | 0 | - | 20,662 | 100 | ||||||
| İştip | 17,575 | 41.6 | 24,166 | 57.2 | 0 | - | 515 | 1.2 | 42,251 | 100 | ||||||
| Kaçana | 33,120 | 59.7 | 22,239 | 40.1 | 83 | 0.2 | 0 | - | 55,442 | 100 | ||||||
| Radovişte | 7,364 | 41.0 | 10,519 | 58.5 | 0 | - | 97 | 0.5 | 17,980 | 100 | ||||||
| Kalkandelen | 9,830 | 22.4 | 29,212 | 66.3 | 4,990 | 11.3 | 0 | - | 44,032 | 100 | ||||||
| Kosova Vilayet Subtotal | 157,678 | 49.8 | 145,070 | 45.9 | 12,236 | 3.9 | 1,382 | 0.4 | 316,363 | 100 | ||||||
| Monastir | 61,494 | 44.7 | 30,517 | 22.2 | 41,077 | 29.9 | 4,365 | 3.2 | 137,453 | 100 | ||||||
| Ohri | 33,306 | 63.2 | 16,360 | 31.0 | 3,049 | 5.8 | 0 | - | 52,685 | 100 | ||||||
| Pirlepe | 43,763 | 73.8 | 14,270 | 24.0 | 1,248 | 2.1 | 42 | 0.1 | 59,327 | 100 | ||||||
| Kirçova | 20,879 | 60.1 | 13,282 | 38.8 | 64 | 0.2 | 4 | 0.0 | 34,229 | 100 | ||||||
| Monastir Vilayet Subtotal | 159,442 | 56.2 | 74,429 | 26.2 | 45,438 | 16.0 | 4,411 | 1.6 | 283,694 | 100 | ||||||
| NORTH MACEDONIA borders | 385,645 | 48.7 | 309,747 | 39.1 | 88,229 | 11.1 | 8,342 | 1.1 | 791,963 | 100 | ||||||
1 The kaza of Dibra did not participate in the census. 2 The "Miscellaneous" category includes, among other things, Jews—numbering 4,274 in Monastir, 724 in Üsküp, 573 in Usturumca, 515 in İştip, 167 in Toyran, etc.; Greek Catholic (Uniate) Bulgarians—numbering 1,402 in Gevgili, 376 in Toyran. etc.; Protestants—numbering 97 in Radovişte, and so on. | ||||||||||||||||
Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars consisted of two wars that occurred in 1912 and 1913. The first began on 8 October 1912 when the nations of the Balkan League, who had large parts of their ethnic populations under Ottoman rule, attacked the Ottoman Empire. It lasted seven months with the Balkan League nations coming up victorious, ending 500 years of Ottoman rule in the Balkans.[13]
Vardar Macedonian cities under Ottoman rule

During the Ottoman rule of the Balkans, cities experienced many changes with regards to the demographic makeup of their population and the look of their cityscapes. With laws that prohibited Christian buildings from being higher than Islamic ones, the skylines of cities like Üsküp (Skopje) and Manastır (Bitola) were dominated by minarets.[14]
Ottoman traveller Evliya Çelebi visited the city of Manastır in 1661. He wrote that of the seven mosques in the city at the time, six were built in the 16th century. Most of the mosques constructed on the territory of today's Republic of North Macedonia were square in shape with a three-domed portico and a minaret on the building's right side.[15]
 Ottoman Manastır (Bitola) in the 1800s
Ottoman Manastır (Bitola) in the 1800s Pirlepe (Prilep) at the end of the 19th century
Pirlepe (Prilep) at the end of the 19th century Minarets in the Ottoman Üsküp (Skopje) skyline
Minarets in the Ottoman Üsküp (Skopje) skyline Ottoman İştip (Štip)
Ottoman İştip (Štip)
See also
References
- Encyclopædia Britannica – Rumelia at Encyclopædia Britannica.com
- Sedlar, Jean W., East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000-1500, (University of Washington Press, 1994), 385.
- The last centuries of Byzantium, (1261-1453) by Donald MacGillivray Nicol
- Stojanovski, Aleksandar (1989), Makedonija vo turskoto srednovekovie : od krajot na XIV--početokot na XVIII vek (in Macedonian), Skopje: Kultura, p. 49, OCLC 21875410, retrieved 24 December 2011,
ОХРИДСКИ САНЏАК (Liva i Ohri): Овој санџак исто така е еден од најстарите санџаци во Румелискиот беглербеглак. Се смета дека бил создаден по загинувањето на крал Марко (1395),..
- Šabanović, Hazim (1959), Bosanski pašaluk : postanak i upravna podjela (in Croatian), Sarajevo: Oslobođenje, p. 20, OCLC 10236383, retrieved 26 December 2011,
Poslije pogibije kralja Marka i Konstantina Dejanovića na Rovinama (1394) pretvorene su njihove oblasti u turske sandžake, Ćustelndilski i Ohridski.
- "Macedonia :: The Ottoman Empire". Britannica. 2010. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
- "A brief account of the history of Skopje". skopje.mk. 2010. Archived from the original on February 25, 2009. Retrieved August 25, 2010.
A monk at the Saint Theodor Monastery on Mt. Vodno briefly recorded the date of the town's capture by the Turks: "In the 69th year (1392) the Turks took Skopje on the 6th day of the month (January 19, 1392 according to the new calendar).
- Marinus Barletius: Historia de vita et gestis Scanderbegi Epirotarum principis
- Ursinus, M. (1991). "Manāstir". The Encyclopedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume VI: Mahk–Mid. Leiden and New York: BRILL. pp. 371–372. ISBN 90-04-08112-7.
- Birken, Andreas (1976). Die Provinzen des Osmanischen Reiches. Beihefte zum Tübinger Atlas des Vorderen Orients (in German). Vol. 13. Reichert. pp. 50, 52. ISBN 9783920153568.
- Viquesnel, Auguste (1868). Voyage dans la Turquie d'Europe: description physique et géologique de la Thrace (in French). Vol. Tome Premier. Paris: Arthus Betrand. pp. 107, 114–115.
- Karpat, K.H. (1985). Ottoman population, 1830-1914: demographic and social characteristics. Madison, Wis: University of Wisconsin Pres. p. 134-135, 140-141, 144-145.
- "Balkan Wars". Britannica. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
- "The Church of St Spas - Skopje". National Tourism Portal of Macedonia. July 2005. Archived from the original on May 27, 2011. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
...half of it was constructed underground, due to the 17th century edict of the Turkish Sultan that prohibited Christian structures from being higher than mosques.
- "The Sixteenth Century Mosques of Bitola / Toli Manastır1" (PDF). Kalamus. c. 2010. Retrieved August 27, 2010.
