Via Francigena
The Via Francigena (Italian: [ˈviːa franˈtʃiːdʒena]) is an ancient road and pilgrimage route running from the cathedral city of Canterbury in England, through France and Switzerland, to Rome[1] and then to Apulia, Italy, where there were ports of embarkation for the Holy Land.[2] It was known in Italy as the "Via Francigena" ("the road that comes from France") or the "Via Romea Francigena" ("the road to Rome that comes from France").[3] In medieval times it was an important road and pilgrimage route for those wishing to visit the Holy See and the tombs of the apostles Peter and Paul.
History of the pilgrimage to Rome

In the Middle Ages, Via Francigena was the major pilgrimage route to Rome from the north. The route was first documented as the "Lombard Way", and was first called the Iter Francorum (the "Frankish Route") in the Itinerarium sancti Willibaldi of 725, a record of the travels of Willibald, bishop of Eichstätt in Bavaria. It was Via Francigena-Francisca in Italy and Burgundy, the Chemin des Anglois in the Frankish Kingdom (after the evangelisation of England in 607) and also the Chemin Romieu, the road to Rome. The name Via Francigena is first mentioned in the Actum Clusio, a parchment of 876 in the Abbey of San Salvatore at Monte Amiata (Tuscany).[4]

At the end of the 10th century Sigeric, the Archbishop of Canterbury, used the Via Francigena to and from Rome in order to receive his pallium;[5] he recorded his route and his stops on the return journey,[6] but nothing in the document suggests that the route was then new, nor if he made the journey by foot or on horseback.
Later itineraries to Rome include the Leiðarvísir og borgarskipan of the Icelandic traveller Nikolás Bergsson (in 1154) and the one from Philip Augustus of France (in 1191).[7] Two somewhat differing maps of the route appear in manuscripts of Matthew Paris, Historia Anglorum, from the 13th century.

The Welsh king Rhodri Mawr in 880 and his grandson Hywel Dda in 945 are both known to have visited Rome towards the end of their lives, but it is not known whether they went by land or by sea via the Straits of Gibraltar. The Benedictine William of St-Thierry used the roads towards Rome on several occasions at the end of the 11th century. The return journey by sea was likely to be easier, thanks to the prevailing south-westerly winds, but tacking down to the Mediterranean would have made a very long journey indeed.
The Via Francigena was not a single road, like a Roman road, paved with stone blocks and provided at intervals with a change of horses for official travellers. Rather, it comprised several possible routes that changed over the centuries as trade and pilgrimage waxed and waned. Depending on the time of year, the political situation, and the relative popularity of the shrines of the saints situated along the route, travellers may have used any of three or four crossings of the Alps and the Apennines. The Lombards financed the maintenance and security of the section of road through their territories as a trading route to the north from Rome, avoiding enemy-held cities such as Florence. Unlike Roman roads, the Via Francigena did not connect cities but relied more on abbeys.

Sigeric's itinerary
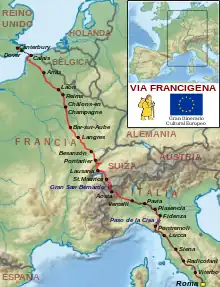
In around 990, Archbishop Sigeric journeyed from Canterbury to Rome and back, but only documented his itinerary on the return journey,[8] taken in 80 stages averaging about 20 km (12 mi) a day, for a total of some 1,700 km (1,100 mi).[9]
Modern pilgrims from England would follow Sigeric's route in the reverse order, and so would set off from the zero milestone in the South Porch of Canterbury Cathedral. Pilgrim passports are available from The Beaney Museum in Canterbury or from the information office of the Cathedral. Canons based at Canterbury Cathedral can also be arranged to offer blessings to pilgrims setting off on the journey.[10] Modern pilgrims would then follow the route, walking out of Canterbury via St Martin's Church, Canterbury, which is the oldest church in England still in use as a Church. Heading onwards, pilgrims pick up the first stamp in their pilgrim passport at to the village church of St. Mary's in Patrixbourne. It is possible to "Champ" and stay by arrangement at St. Mary's.[11] Heading on towards the English coast, pilgrims would travel through the Kentish villages of Womenswold and Woolage Green before arriving in Shepherdswell which is the end of the first stage (of 79 stages). The second stage continues to Dover via the Waldershare Park Estate and then joins the old Roman Road at Studdal outside Dover, to walk into the town. Pilgrims then cross the Channel to Sumeran (now called Sombres), landing at the village of Wissant. The route continues through Guînes (Sigeric's Gisne), Thérouanne (Teranburh), Bruay (Bruaei), and Arras (Atherats), before continuing on to Reims, Châlons-sur-Marne, Bar-sur-Aube, Langres, Champlitte, Besançon, Pontarlier, Lausanne and Saint-Maurice. From Saint-Maurice, the route traverses the Great St. Bernard Pass to Aosta and then to Ivrea, Vercelli, Pavia, Fidenza, Pontremoli, Filattiera, Aulla, Luni, Lucca, San Gimignano, Poggibonsi, Siena, San Quirico d'Orcia, Bolsena, Viterbo, Sutri, and finally Rome.
| No. | Stages as described by Sigeric | Today's stages of the Via Francigena | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Place names per Sigeric | Current place names | Start – End | Distances in km | ||
| Across the English Channel | |||||
| 1 | LXXX | Sumeran | Sombre (part of Wissant) | Calais – Wissant | 19.7 |
| 2 | LXXIX | stage missing | |||
| 3 | LXXVIII | Gisne | Guînes | Wissant – Guînes | 20.2 |
| 4 | LXXVII | Teranburh | Thérouanne | Guînes – Licques | 15.7 |
| Licques – Wisques | 23.9 | ||||
| Wisques – Thérouanne | 13.2 | ||||
| 5 | LXXVI | Bruwaei | Bruay-la-Buissière | Thérouanne – Auchy-au-Bois | 15.1 |
| Auchy-au-Bois – Bruay-la-Buissière | 19.0 | ||||
| 6 | LXXV | Atherats | Arras | Bruay-la-Buissière – Arras | 33.6 |
| 7 | LXXIV | Duin | Doingt | Arras – Bapaume | 26.2 |
| Bapaume – Péronne | 25.3 | ||||
| Peronne – Doingt | 3.0 | ||||
| 8 | LXXIII | Martinwaeth | Seraucourt-le-Grand | Doingt – Seraucourt-le-Grand | 29.2 |
| 9 | LXXII | Mundlothuin | Laon | Seraucourt-le-Grand – Tergnier | 17.0 |
| Tergnier – Laon | 33.0 | ||||
| 10 | LXXI | Corbunei | Corbeny | Laon – Bouconville-Vauclair | 18.6 |
| Bouconville-Vauclair – Corbeny | 4.5 | ||||
| 11 | LXX | Rems | Reims | Corbeny – Hermonville | 20.1 |
| Hermonville – Reims | 16.3 | ||||
| 12 | LXIX | Chateluns | Châlons-en-Champagne | Reims – Trépail | 28.1 |
| Trépail – Châlons-en-Champagne | 25.8 | ||||
| 13 | LXVIII | Funtaine | Fontaine sur Coole | Châlons-en-Champagne – Coole | 27.0 |
| 14 | LXVII | Domaniant | Donnement | Coole – Donnement | 25.7 |
| 15 | LXVI | Breone | Brienne-le-Château | Donnement – Brienne le Château | 17.8 |
| 16 | LXV | Bar | Bar-sur-Aube | Brienne-le-Château – Bar-sur-Aube | 26.9 |
| 17 | LXIV | Blaecuile | Blessonville | Bar-sur-Aube – Châteauvillain (near Blessonville) | 32.9 |
| 18 | LXIII | Oisma | Humes-Jorquenay | Châteauvillain – Langres (near Humes-Jorquenay) | 40.9 |
| 19 | LXII | Grenant | Grenant | Langres – Coublanc (near Grenant) | 27.0 |
| 20 | LXI | Sefui | Seveux | Coublanc – Dampierre-sur-Salon | 27.7 |
| Dampierre-sur-Salon – Savoyeux (near Seveux) | 5.5 | ||||
| 21 | LX | Cuscei | Cussey-sur-l'Ognon | Savoyeux – Gy | 20.6 |
| Gy – Cussey-sur-l'Ognon | 16.4 | ||||
| 22 | LIX | Bysiceon | Besançon | Cussey-sur-l'Ognon – Besançon | 17.0 |
| 23 | LVIII | Nos | Nods | Besançon – Étalans | 27.0 |
| Étalans – Chasnans (near Nods) | 9.8 | ||||
| 24 | LVII | Punterlin | Pontarlier | Chasnans – Ouhans | 18.0 |
| Ouhans – Pontarlier | 17.0 | ||||
| 25 | LVI | Antifern | Yverdon-les-Bains | Pontarlier – Orbe | 40.2 |
| 26 | LV | Urba | Orbe | ||
| 27 | LIV | Losanna | Lausanne | Orbe – Lausanne | 32.0 |
| 28 | LIII | Vivaec | Vevey | Lausanne – Cully | 12.9[12] |
| Cully – Vevey | 11.3 | ||||
| 29 | LII | Burbulei | Aigle | Vevey – Montreux | 8.4 |
| Montreux – Villeneuve | 5.9 | ||||
| Villeneuve – Aigle | 12.7 | ||||
| 30 | LI | Sce Maurici | Saint-Maurice | Aigle – Saint-Maurice | 18.0 |
| 31 | L | Ursiores | Orsières | Saint-Maurice – Martigny | 17.0 |
| Martigny – Orsières | 18.5 | ||||
| 32 | XLIX | Petrecastel | Bourg-Saint-Pierre | Orsières – Bourg-Saint-Pierre | 15.4 |
| 33 | XLVIII | Sce Remei | Saint-Rhémy-en-Bosses | Bourg-Saint-Pierre – Great St Bernard Hospice | 13.8 |
| Great St Bernard Hospice – Saint-Rhémy-en-Bosses | 6.3 | ||||
| 34 | XLVII | Agusta | Aosta | Saint-Rhémy-en-Bosses – Aosta | 25.6 |
| 35 | XLVI | Publei | (Pontey ?) Pont-Saint-Martin | Aosta – Nus | 15.9 |
| Nus – Saint-Vincent | 22.3 | ||||
| Saint-Vincent – Arnad | 22.4 | ||||
| Arnad – Pont-Saint-Martin | 15.9 | ||||
| 36 | XLV | Everi | Ivrea | Pont-Saint-Martin – Ivrea | 25.2 |
| 37 | XLIV | Sca Agatha | Santhià | Ivrea – Viverone | 21.4 |
| Viverone – Santhià | 16.2 | ||||
| 38 | XLIII | Vercel | Vercelli | Santhià – Vercelli | 28.6 |
| 39 | XLII | Tremel | Tromello | Vercelli – Robbio | 19.7 |
| Robbio – Mortara | 14.2 | ||||
| Mortara – Tromello | 18.1 | ||||
| 40 | XLI | Pamphica | Pavia | Tromello – Gropello Cairoli | 13.5 |
| Gropello Cairoli – Pavia | 18.1 | ||||
| 41 | XL | Sce Cristine | Santa Cristina e Bissone | Pavia – Santa Cristina e Bissone | 27.4 |
| 42 | XXXIX | Sce Andrea | Corte San Andrea | Santa Cristina e Bissone – Piacenza (crossing the Po) | 38.2 |
| 43 | XXXVIII | Placentia | Piacenza | ||
| 44 | XXXVII | Floricum | Fiorenzuola d'Arda | Piacenza – Fiorenzuola d'Arda | 26.4 |
| 45 | XXXVI | Sce Domnine | Fidenza (up till 1927 called Borgo San Donino) | Fiorenzuola d'Arda – Fidenza | 22.3 |
| 46 | XXXV | Metane | Costamezzana (Medesano) | Fidenza – Costamezzana | 10.8 |
| 47 | XXXIV | Philemangenur | Fornovo di Taro (or Felegara) | Costamezzana – Medesano | 9.7 |
| Medesano – Fornovo di Taro | 9.2 | ||||
| 48 | XXXIII | Sce Moderanne | Berceto | Fornovo di Taro – Cassio di Terenzo | 19.8 |
| Cassio di Terenzo – Berceto | 10.4 | ||||
| 49 | XXXII | Sce Benedicte | Montelungo | Berceto – Pontremoli | 29.4 |
| 50 | XXXI | Puntremel | Pontremoli | ||
| 51 | XXX | Aguilla | Aulla | Pontremoli – Villafranca in Lunigiana | 19.1 |
| Villafranca in Lunigiana – Aulla | 15.3 | ||||
| 52 | XXIX | Sce Stephane | Santo Stefano di Magra | Aulla – Sarzana | 16.3 |
| 53 | XXVIII | Luna | Luni | Sarzana – Luni | 12.7 |
| 54 | XXVII | Campmaior | Pieve di Camaiore | Luni – Massa | 14.8 |
| Massa – Pietrasanta | 15.8 | ||||
| Pietrasanta – Camaiore | 8.2 | ||||
| 55 | XXVI | Luca | Lucca | Camaiore – Lucca | 24.2 |
| 56 | XXV | Forcri | Porcari | Lucca – Porcari | 10.6 |
| 57 | XXIII | Aqua Nigra | Ponte a Cappiano. Part of Fucecchio | Porcari – Ponte a Cappiano | 19.7 |
| 58 | XXIII | Arne Blanca | Fucecchio | Ponte a Cappiano – Fucecchio | 4.9 |
| 59 | XXII | Sce Dionisii | San Genesio near San Miniato | Fucecchio – San Miniato Alto | 7.6 |
| 60 | XXI | Sce Peter Currant | Coiano. Today part of Castelfiorentino | San Miniato Alto – Coiano | 12.1 |
| 61 | XX | Sce Maria Glan | Santa Maria a Chianni near Gambassi Terme | Coiano – Gambassi Terme | 12.2 |
| 62 | XIX | Sce Gemiane | San Gimignano | Gambassi Terme – San Gimignano | 14.5 |
| 63 | XVIII | Sce Martin in Fosse | San Martino Fosci (Molino d'Aiano. Part of Colle di Val d'Elsa) | San Gimignano – Badia a Isola | 20.5/25.5 |
| 64 | XVII | Aelse | Gracciano (Pieve d'Elsa. Part of Colle di Val d'Elsa) | ||
| 65 | XVI | Burgenove | Badia a Isola. Part of Monteriggioni | ||
| 66 | XV | Seocine | Siena | Badia a Isola – Monteriggioni | 3.5 |
| Monteriggioni – Siena | 20.5 | ||||
| 67 | XIV | Arbia | Ponte d'Arbia. Part of Monteroni d'Arbia | Siena – Monteroni d'Arbia | 17.9 |
| Monteroni d'Arbia – Ponte d'Arbia | 9.8 | ||||
| 68 | XIII | Turreiner | Torrenieri (Part of Montalcino) | Ponte d'Arbia – Buonconvento | 5.7 |
| Buonconvento – Torrenieri | 13.5 | ||||
| 69 | XII | Sce Quiric | San Quirico d'Orcia | Torrenieri – San Quirico d'Orcia | 7.4 |
| 70 | XI | Abricula | Briccole di Sotto | San Quirico d'Orcia – Bagno Vignoni | 5.3 |
| Bagno Vignoni – Radicofani | 27.4 | ||||
| 71 | X | Sce Petir in Pail | San Pietro in Paglia (Voltole) | Radicofani – Ponte a Rigo | 10.7 |
| 72 | IX | Aquapendente | Acquapendente | Ponte a Rigo – Acquapendente | 13.8 |
| 73 | VIII | Sca Cristina | Bolsena | Acquapendente – Bolsena | 20.2 |
| 74 | VII | Sce Flaviane | Montefiascone | Bolsena – Montefiascone | 18 |
| 75 | VI | Sce Valentine | Viterbo (Bullicame) | Montefiascone – Viterbo | 18.7 |
| 76 | V | Furcari | Vetralla (Forcassi) | Viterbo – Vetralla | 17.9 |
| 77 | IlIl | Suteria | Sutri | Vetralla – Sutri | 22.1 |
| 78 | III | Bacane | Baccano (Campagnano di Roma) | Sutri – Campagnano di Roma | 22.3 |
| 79 | II | Johannis VIIII | San Giovanni in Nono (La Storta) | Campagnano di Roma – La Storta | 25.6 |
| 80 | I | Urbs Roma | Roma | La Storta – Rome | 14.8 |
The final stretch towards the Apulian ports

From Rome, the path followed for a long stretch the Via Appia or the parallel Via Latina up to Benevento. From that town Via Traiana was taken up the Campanian Apennines and Daunian Mountains, where Crepacore castle stood, a fortress held by the Knights of Jerusalem in order to guarantee the safety of pilgrims along the mountain stretch.[13] The road, therefore, reached Troia, in the high plain of Tavoliere delle Puglie (where Via Francigena is attested since 1024),[2] and then continued towards Bari, Brindisi and Otranto, the main ports of embarkation for the Holy Land.
Today
Today some pilgrims still follow in Sigeric's ancient footsteps and travel on foot, on horseback or by bicycle on the Via Francigena, although there are far fewer pilgrims on this route than on the Way of St. James pilgrims' route to Santiago de Compostela in Spain.[14] Roughly 50,000 pilgrims were estimated to have walked the Via Francigena in 2022.[15] In 2011, James Saward-Anderson and Maxwell Hannah ran the entire route for Water Aid.[16] They completed the route unassisted in 58 days.
Accommodation
Due to the scarcity of dedicated pilgrims' accommodation along the Via Francigena, pilgrims often camp out rather than stay in hotels or pensions. However, increasingly in Italy, some monasteries and religious houses offer dedicated pilgrim accommodation. These are called spedali and — like the refugios found on the Way of St. James in France and Spain — they offer cheap and simple dormitory-style accommodation. Spedali accept pilgrims who bear a valid credenziale (pilgrim's passport), usually for one night only. Some places offer meals as well. In Kent, local churches often encourage pilgrims to "Champ" (camp in a church) and some of the churches along the Via Francigena have contacts on their website to allow pilgrims to arrange this. There is an accommodation list online which regularly updated and published by the Confraternity of Pilgrims to Rome [18]
As of 2016, the old guest houses dedicated to pilgrims were not reconditioned by tourist operators, due to the lack of economic return.[19]
The state and path of the route
Only a few decades ago, interest in the Via Francigena was limited to scholars. This began to change in recent years when many who, after travelling the Way of St. James in Spain, wanted to make the pilgrimage to Rome on foot as well. In Italy, this gave birth to a network of lovers of the Via Francigena, who with paint and brush, began to mark its trails and paths. These people were joined by religious and local government agencies who also tried to recover the original route. Where possible today's route follows the ancient one but sometimes it deviates from the historical path in favour of paths and roads with low traffic. The potential for the tourist trade in Italy has been recognised but this has also led some to gain unfair economic advantage by diverting the path so that it passes next to their business, thus increasing footfall.[20]

In England, the Via Francigena starts at the southern portico of Canterbury’s cathedral where the milestone zero of the route is located.[21] The route passes through part of the county of Kent, from Canterbury to the ferries at Dover.
In France, the Via Francigena (given the Grande Randonnée designation 'GR145') goes through the régions Hauts-de-France, Grand-Est and Bourgogne-Franche-Comté before reaching the Swiss border.
In Switzerland, the Via Francigena (with the route designation '70') goes through the cantons of Vaud and Valais.
In Italy the Via Francigena goes through the Regione of Valle d'Aosta, Piedmont, Lombardy, Emilia-Romagna, Tuscany, and finally about halfway through Lazio to Rome.
Walkers could choose to walk along the EuroVelo EV5 cycling route which bears the name 'Via Francigena'. However, this EuroVelo route varies substantially from Sigeric's route and the one given by the Via Francigena Association.
In 1994 the Via Francigena was designated a Cultural Route,[19] and in 2004 a Major Cultural Route.
In November 2009, the Italian government launched a project to recover the Italian leg of it. The object of the plan is to recover the entire route (disjointed parts of which are already signposted) "not only in spiritual and religious terms but also in terms of the environment, architecture, culture, history, wine and cuisine and sport." The initiative was promoted by the Region of Tuscany, which hosts 400 km (250 mi) of the Via, and which presented a plan detailing the low environmental impact infrastructures to be created. The plan will be shared with other local authorities located along the route as an encouragement to carry out similar recovery work.[22] Tuscany has also announced cooperation with the Opera Romana Pellegrinaggi (ORP), the Vatican’s organisation for encouraging pilgrimages.
The final stretch, from Rome to the Apulian ports of embarkation for Jerusalem, has been renamed Via Francigena nel Sud (in Italian "Via Francigena in the South (Italy)") or else Vie Francigene del Sud ("The Francigena Ways to the South").[23]
Gallery
- Stages along the Via Francigena
 Canterbury Cathedral, the starting point of the Via Francigena.
Canterbury Cathedral, the starting point of the Via Francigena. Crossroads of the Via Francigena (designated in France as the Grande Randonnée route GR145) and the GR654 in the département of Marne, northern France.
Crossroads of the Via Francigena (designated in France as the Grande Randonnée route GR145) and the GR654 in the département of Marne, northern France. The Great St. Bernard Pass in high summer.
The Great St. Bernard Pass in high summer. Column built by the Compagnia di Sigerico at Soprarivo, Calendasco. An identical one stands in the village of Corte Sant'Andrea, Lombardy.
Column built by the Compagnia di Sigerico at Soprarivo, Calendasco. An identical one stands in the village of Corte Sant'Andrea, Lombardy. Sigeric's station no. XXX in Aulla, Tuscany.
Sigeric's station no. XXX in Aulla, Tuscany. The Cisa Pass between Tuscany & Emilia-Romagna.
The Cisa Pass between Tuscany & Emilia-Romagna. Mediaeval Italian manuscript depicting the Castle of Tentennano on the Via Francigena.
Mediaeval Italian manuscript depicting the Castle of Tentennano on the Via Francigena. St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican City in Rome holds one of the destinations of the pilgrimage, the tomb of St. Peter the Apostle.
St. Peter's Basilica in the Vatican City in Rome holds one of the destinations of the pilgrimage, the tomb of St. Peter the Apostle. Via Francigena along Southern Apennines, near Ariano Irpino, on the final route connecting Rome and the Apulian ports of embarkation for the Holy Land.
Via Francigena along Southern Apennines, near Ariano Irpino, on the final route connecting Rome and the Apulian ports of embarkation for the Holy Land. A steep section of the Via Francigena in Settimo Vittone, Piedmont.
A steep section of the Via Francigena in Settimo Vittone, Piedmont.
See also
- Way of St. James
- Valdorcia
- Ponte della Maddalena – a river crossing en route.
- Order of the Holy Sepulchre – The Order of the Holy Sepulchre was one such order of Pilgrimage providing Hospices on the Vía. (The road to Jerusalem lay through Rome, as it still does for the intrepid.)
- EV5 Via Romea Francigena, a long-distance cycling route also running from London to Brindisi.
- CoEur devotional path
References
- Stanford, Peter (28 March 2021). "Secular pilgrims: why ancient trails still pack a spiritual punch". The Observer.
- Renato Stopani (1992). Centro Studi Romei (ed.). "La via Appia Traiana nel Medioevo" [Via Appia Traiana in the Middle Age] (PDF). Vie Francigene del Sud (in Italian). p. 4.
- Valle d'Aosta Aosta Valley: Gran San Bernardo – La Via Francigena
- Via Francigena: history (PDF) Archived July 19, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- Hindley, Geoffrey A Brief History of the Anglo-Saxons: The beginnings of the English nation (New York: Carroll & Graf) 2006:294–295.
- The transcript, formerly in the Cottonian Library, is now in the British Library (Cotton Tiberius B.v., folios 34 and 35; On-line map of Sigeric's route
- Nikolás is noted in F. P. Magoun, Jr., "The Italian Itinerary of Philip II (Philippe-Auguste) in the Year 1191", Speculum 17.3 (July 1942:367–376) p. 367 note 2.
- Ortenberg "Anglo-Saxon Church and the Papacy" English Church and the Papacy in the Middle Ages p. 49
- Via Francigena – 03 |Augnet
- "Pilgrimage".
- "St Mary's".
- Distances given by Ingrid Retterath: Via Francigena von Lausanne nach Rom. Outdoor guide Bd. 201. Conrad Stein Verlag 2011.
- "San Vito". Commune of Faeto (in Italian).
- http://www.francigena.ch/newsite/upload/Chinn_horse_06.pdf
- "The Via Francigena 2022 in numbers". 19 January 2023.
- "Epic run from Canterbury to Rome follows pilgrimage". BBC.
- www.viefrancigene.it
- https://pilgrimstorome.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2018/01/CPRViaFrancigenaAccommodationList.pdf/
- Locarno, Guido (2016). "The Camino de Santiago de Compostela (Spain) and The Via Francigena (Italy): a comparison between two important historic pilgrimage routes in Europe" (pdf). International Journal of Religious Tourism and International Journal and Pilgrimage. 7 (7 – (article 7)): 52–53. doi:10.21427/D7Z30X. ISBN 9781472107596. ISSN 2009-7379. OCLC 8539036575. S2CID 54827830. Archived from the original on February 12, 2020.
- it:Via Francigena
- "The Via Francigena in England", viefrancigene.org
- 128-page PDF in Italian, with plans and pictures
- "The Francigena Ways to the South". Vie Francigene del Sud.
Sources
- Kerschbaum & Gattinger, Via Francigena – DVD- Documentary of a modern pilgrimage to Rome, ISBN 3-200-00500-9, Verlag EUROVIA, Vienna 2005
- Trezzini, La Via Francigena. Vademecum dal Gran San Bernardo a Roma La Via Francigena. Vademecum dal Gran San Bernardo a Roma (Association Via Francigena) 2000
- Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. San Pellegrino sulle Via Francigene. Ed. Gangemi Cod. ISBN 88-492-1607-6
- Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Topofrancigena da Canterbury a Roma (2004–2007) Ed. Ass. int. Via Francigena
- Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Guide-Vademecum da Canterbury a Roma. Ed.2002–03
- Adelaide Trezzini-AIVF. Dormifrancigena da Canterbury a Roma.2006 + 2007 Ed. Ass. int. Via Francigena
External links
- Via Francigena on URCamino
- Canterbury City Council local info on the route through the UK
- BBC News– Epic run from Canterbury to Rome follows pilgrimage
- (in French) The GR145 Via Francigena in the Champagne-Ardenne region of France
- Italian Ministry of Cultural and Heritage Multiple language site of the official route in Italy including roadbooks, GPS and maps
- La Via Francigena website for Italy (in Italian & English)
- The Via Francigena in Southern Italy, from Rome to Apulia (English version)
Via Francigena associations
- (in Spanish) Asociación de la vía Francígena en España
- Association Internationale Via Francigena Active since 1997 promoting cultural and tourist awareness of the Via Francigena to Roma
- Confraternity of Pilgrims to Rome United Kingdom pilgrim association providing information on the Via Francigena
- European Association of Vie Francigene Information on the route through Italy
- (in Dutch) Dutch Association Dutch Association of pilgrims walking or cycling to Rome
- Via Francigena Association in Switzerland
- (in German) EUROVIA Austrian pilgrim Association supporting pilgrims to Rome (German/English/Italian)
- Camminando sulla Via Francigena. The Italian Community of pilgrims 3.0 (choose your language)
Related routes
- (in Italian) La Francigena in Garfagnana Route between Aulla and Lucca through the Garfagnana in Italy (in Italian)
- Via Francigena di San Francesco Route from Roma to Rieti.
- (in Italian) Via Francigena Appia Pedemontana Route from Roma to Formia
