Walls of Avignon
The walls of Avignon (French: Les Remparts d'Avignon) are a series of defensive stone walls that surround the city of Avignon in the south of France. They were originally built in the 14th century during the Avignon papacy and have been continually rebuilt and repaired throughout their subsequent history.
| Walls of Avignon | |
|---|---|
 Walls between the Porte de L'Oulle and the Porte du Rhône | |
| Location | Avignon, Vaucluse, France |
| Coordinates | 43°56′53″N 4°48′25″E |
| Built | 14th century |
| Owner | Centre des monuments nationaux |
| Official name | Remparts et leurs abords |
| Designated | 1906, 1914, 1915, 1933, 1937 |
| Reference no. | PA00081943 |
 Location in France | |
The walls replaced an earlier double set of defensive walls that had been completed in the first two decades of the 13th century. During the Albigensian Crusade the town sided with the Count of Toulouse, Raymond VII but in 1226, after a three-month siege by Louis VIII of France, Avignon capitulated and was forced to dismantle the walls and fill in the moats. Beginning in around 1231, the defences were rebuilt. Although these early walls have not survived, their path is preserved in the street plan of the city.
In 1309 Pope Clement V moved to Avignon and under the papacy the town expanded outside the limits of the earlier city walls. From the 1350s during the Hundred Years' War the town became vulnerable to pillage by marauding bands of mercenaries and in 1357 under Innocent VI, the fifth Avignon pope, work began on the construction of a new set of city walls to enclose the expanded town. The walls took nearly 20 years to complete.
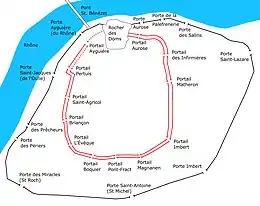
The walls stretch for 4.3 km (2.7 mi) and enclose an area of 150 ha (370 acres). There were originally twelve gates controlling access to the city but this number was reduced to seven when the fortifications were modified between 1481 and 1487. There are now 15 vehicular entrances and 11 pedestrian entrances.
Early fortifications
Historians had assumed that during the Roman period Avignon would have been defended by a wall,[1] but this is now considered unlikely.[2] A large amount of rescue archaeology has taken place in Avignon since the 1960s, especially around the Place de l'Horloge. This has revealed many details of the Roman town but no evidence has been found for a defensive wall.[2]
In late antiquity a rudimentary wall was erected by reusing material from Roman monuments. It was centred on the Rocher des Doms and enclosed a much smaller area than the Roman town.[3][4] This wall is mentioned by the Gallo-Roman historian Gregory of Tours when describing the siege of the town by the Frankish king, Clovis I, in around 500 AD.[4][5]
13th century double walls
In the 12th century the town enjoyed a degree of independence and became very prosperous. A bridge was built across the Rhône, the Pont Saint-Bénézet whose construction is traditionally dated to between 1177 and 1185.[6] There are no surviving records of when the first city wall was built but historians have suggested dates between 1060[7][8] and 1176.[3]
In the first two decades of the 13th century the town added a second wall with a second moat outside the earlier wall. The two walls were parallel and separated by around 30 m (33 yd). Built into the outer wall were a series semi-circular towers. Access to the town was provided by twelve pairs of gates, each pair consisting of a gate in the inner wall and another in the outer.[lower-alpha 1] Water for the moats came from the Sorgue through the Canal de Vaucluse. After 1229, additional water was also provided from the Durance by the Canal de l'Hôpital (La Durançole). The double walls extended around a perimeter of approximately 3 km (1.9 mi) and enclosed an area of around 45 ha (110 acres).[10]
During the Albigensian Crusade the town sided with the Count of Toulouse, Raymond VII. In 1226 the French king, Louis VIII, descended the Rhône valley with a papal legate and a large army en route to a new campaign against the Albigensians. Avignon refused to open its gates but after a siege lasting three months (10 June until 12 September) the city was forced by famine to capitulate. One of the conditions imposed on the town was the dismantling of the city walls.[11] The town rebuilt the defences between 1234 and 1237, presumably on the same plan,[12] but in 1251 Avignon lost its independence when the two younger brothers of King Louis IX, Alphonse of Poitiers and Charles of Anjou (Charles I of Naples) took back control and appointed a viguier (magistrate) to administer the town.[13]

The only surviving piece of the 13th century fortifications is a small fragment of the outer wall at the junction of rue Joseph-Vernet with rue Saint-Charles.[14] Much of the path of the double defence is preserved in the city plan as modern streets follow what was once the gap between the two city walls. Working clockwise from the northeast the walls followed the rue des Trois-Colombes, the rue Campane, the rue Paul-Saïn, the rue Philonarde, the rue des Lices, the rue Henri-Farbe, the rue Joseph-Vernet and the rue Grande-Fusterie.[10] The path of early walls in northwest corner of the town near the Pont Saint-Bénézet is obscure due to the subsequent changes to the fortifications in this important area.[15]
The pairs of arched gateways were retained long after the double set of walls had been demolished and are depicted on 16th and 17th century maps of the town.[1] Many of the old gates were removed in the 18th century but the Portail de Pertuis was not demolished until 1847. The appearance of these gates is unknown as they are not depicted on any print or lithograph.[16] The names of some gates have survived in the modern street names: rue Portail Biensen, rue du Portail Magnanen, rue Portail Matheron and Planet du Portail Peint.[1][lower-alpha 2]
Water from the Sorgue joined the outer moat near the Portail Imbert, flowed around the walls to the Portail l'Êveque and then flowed away to join the Rhône. With the development of the town the moat was vaulted over although the river remained visible along the rue des Teinturiers. In the covered section of the moat, which now serves as a main sewer, the external surfaces of the 13th century walls are clearly visible as are the lower portions the semi-circular towers. The towers average 6.2 m (20 ft) in diameter and are spaced about 34 m (37 yd) apart. The façades of the buildings on the south side of the rue des Lice, rue Henri Fabre and rue Joseph Vernet are aligned with the remains of the outer city wall below ground.[19]
Avignon papacy and the 14th century city walls


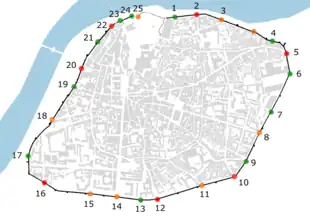
1. Poterne Banasterie 2. Porte de la Ligne
3. Porte Saint-Joseph 4. Poterne Saint-Lazare
5. Porte Saint-Lazare 6. Porte de l'Université
7. Poterne Chabran 8. Porte Thiers
9. Poterne des Teinturiers 10. Porte Limbert
11. Portail Magnanen 12. Porte Saint-Michel
13. Poterne Monclar 14. Porte de la République
15. Porte Saint-Charles 16. Porte Saint-Roch
17. Poterne Raspail 18. Porte Saint-Dominique
19. Poterne de l'Oratoire 20. Porte de l'Oulle
21. Poterne Georges Pompidou 22. Porte du Rhône
23. Le Châtelet 24. Tour Polygonale
25. Porte du Rocher
Pope Clement V moved the papacy from Rome to Avignon in 1309.[21] This led to a large expansion of the town so that the free space within the double walls was soon exhausted. Church officials began building outside the old walls,[22] joining the mendicant orders that had established monasteries outside the city gates in the previous century.[23] The residents of these new suburbs lacked the protection provided by the walls but were exempt from paying the city taxes.[22]
In 1348 Pope Clement VI purchased the town of Avignon from Joanna I of Naples, the Queen of Naples and Countess of Provence, for 80,000 gold florins.[24] Prompted by the threat from the bands of marauding mercenaries (free companies) that were roaming elsewhere in France, sometime between 1355 and 1357 Pope Innocent VI decided to protect the expanded town with a new set of walls.[25] The walls were to enclose a large lozenge shaped area that included the Chapelle Notre-Dame-des-Miracles in the southwest that had been founded by the second Avignon pope John XXII and the Hôpital Sainte-Marthe to the east that had recently been founded by the legal expert Bernard Rascas and his wife.[26][lower-alpha 3] The area of the town would increase by more than three-fold to 151.7 ha (375 acres).[28] The pope may have initially provided small sums for the project but from January 1358 the construction costs were paid for by a tax (gabelle) on wine brought into the town. Additional taxes were introduced on salt and general merchandise in 1363.[29] The papacy also lent money to the town to allow the work to proceed more rapidly.[30]
While work on the wall was progressing the town came under attack from unemployed mercenaries whose numbers increased when a truce in the Hundred Years' War was agreed in Bordeaux between the English and French forces in March 1357. In 1358 Pope Innocent VI bought off a group of mercenaries led by Arnaud de Cervole (known as the Archpriest) with a ransom of 1,000 gold florins.[31]
The new suburbs were protected with temporary wooden structures while the stone walls were being built.[32][33][34] Limestone for the walls and towers came from a quarry on the other side of the Rhône above Villeneuve-lès-Avignon, wood came from Savoy, lime for the mortar came from Villeneuve-lès-Avignon and sand came from islands in the Rhône.[35] By 1372 the new walls were sufficiently advanced to protect the town against a band of mercenaries en route to Italy.[36][34] Work continued and in 1381 the merlons near the Dominican monastery (Porte des Prêcheurs) were rebuilt.[20]
The walls extended for a length of 4.33 km (2.69 mi) and included 12 gates, 36 large towers and around 50 small towers with blind arches.[37] No wall was required for a stretch of 270 metres (300 yd) at the north of the town which was protected by the steep sides of the Rocher des Doms.[38] Except for a section near the Rhône between the Porte Saint-Jacques and the Rocher des Doms the walls were surrounded by a moat which was supplied with water from the Sorgue and the Durance.[39] Each of the gates included a drawbridge, a portcullis and a pair of heavy wooden doors.[20] The walls were crowned with a battlement which protected a walkway (chemin de ronde). The towers had tiled roofs and may have originally been fitted with wooded hoarding which were later replaced with stone.[40]
15th century modifications
During the western schism (1378 to 1417) that followed the Avignon papacy, Aragonese troops paid by the antipope Benedict XIII defended the papal palace complex against attacks by people from the town. The walls near the bridge were damaged and in 1410 the tower controlling access to the bridge collapsed. It was rebuilt in 1414.[41][20] Between 1479 and 1488 the walls were repaired and remodelled with the reduction in the number of gates from twelve to seven. The work was initiated by the papal legate Archbishop Giuliano della Rovere who subsequently became Pope Julius II.[42]
16th century and the Wars of Religion
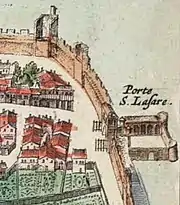
In the first half of the 16th century the crumbling towers were repaired and between 1524 and 1538 extra loopholes were pierced for the newly acquired cannons.[20] In 1561 Pope Pius IV sent his cousin, Fabrizio Serbelloni, to organise the defence of the town against the Huguenots during the French Wars of Religion (1562–1598).[43][44] The walls were repaired, and three of the gates were walled up. These were Porte Saint-Roch, Porte de l'Oulle and Porte de la Ligne. The remaining four gates were strengthened by the addition of protective fortifications (ravelins) outside the gates themselves.[45][46]
From the second half of the 17th century some of the defensive structures were dismantled. Beginning in 1661 the three gates that had been walled up during the Wars of Religion were reopened, and a few years later all the drawbridges were removed. In 1679 some of the exterior fortifications protecting the Porte de Saint Michel were transformed into a triumphal arch dedicated to Pope Innocent XI (in post 1676–1689).[45]
List of modern entrances
There are now around 25 entrances through the city walls.[47]
| Image | Gate | Notes |
|---|---|---|
 | Poterne Banasterie | Pedestrian entrance opened in the 1980s[48] |
 | Porte de la Ligne | In the 14th century there were two gates in the stretch of wall directly to the east of the Rocher des Doms: Porte Aurose and Porte de la Palefrenerie. Porte Aurose was located near the position of the modern Poterne Banasterie. At an early date, perhaps at the end of the 14th century, Porte Aurose was closed. Porte de la Palefrenerie became known as Porte de la Ligne. In 1755–1757 the Porte de la Ligne was moved and rebuilt in the classical style by Jean-Pierre Franque in its present position at the end of rue Palaphanerie.[49][50][lower-alpha 4][lower-alpha 5] The gate was restored in 2003.[51] |
 | Porte Saint-Joseph | Tower opened in 1965. Referred to as the "tour de la Navigation", it was purchased by the town from the French state in 1826 and until 1851 housed the office controlling navigation on the Rhône.[58] |
 | Poterne Saint-Lazare | Pedestrian entrance through small tower opened in 1974[59] |
 | Porte Saint-Lazare | One of the original 14th century entrances. A fortified avant-corps was constructed to protect the gate by Antoine Carteron in 1488. This was replaced in 1568 during the Wars of Religion by a ravelin.[52] The gate was restored and a second entrance created in 1882. At the same time the remains of the ravelin were demolished.[60] |
 | Porte de l'Université | Tower opened in 1962 to allow access to the Hôpital Sainte-Marthe. Avignon University now occupies the former site of the hospital.[61] |
 | Poterne Chabran | Tower opened in 1903 to allow easy access to the town from the army barracks outside the walls, the Caserne Chabran. The Caserne Chabran is now occupied by the Préfecture de Vaucluse.[62] |
 | Porte Thiers | Gap created in 1879, enlarged in 1908[63] |
 | Poterne des Teinturiers | Passageway opened in 1995. The tower, La Pyramide, contains sluices that control the flow of water from the Sorgue to within the city walls.[64][lower-alpha 6] |
 | Porte Limbert | 14th century gate demolished in 1896 to allow more space for an electric tramline. A ravelin, constructed to protect the gate at the end of the 16th century, was demolished in 1760.[66] |
 | Portail Magnanen | Gap opened in 1902[67] |
 | Porte Saint-Michel | Original 14th century name was Porte Saint-Antoine. In 1595 during the Wars of Religion a ravelin was constructed outside the gate. In 1679 the gate of the ravelin was converted into a triumphal arch.[68] This arch was demolished when Eugène Viollet-le-Duc rebuilt the gate in 1868. Damaged by American bombs in World War II the gate was restored in 1951.[69] |
 | Poterne Monclar | Two small lateral openings created in the tower in 1972.[70] |
 | Porte de la République | Gap opened in 1855 to allow access to the railway station. In 1863 Viollet-le-Duc removed two old towers in the existing walls and built a fantasy tower on either side of the gap.[71] |
 | Porte Saint-Charles | Gap opened in 1902[72] |
 | Porte Saint-Roch | The original 14th century name was Portail des Miracles. It later became Porte de Champfleury. Closed during the Wars of Religion (1562–1598), it was reopened in 1661.[68] The gate was restored in 1742 and then rebuilt by Viollet-le-Duc in 1865.[73] |
 | Poterne Raspail | Entrance through a small tower opened in 1972[74] |
 | Porte Saint-Dominique | Gap opened in 1839, enlarged in 1953. This is close to the site of an original 14th century gate, the Porte des Prêcheurs or Porte des Dominicains, that was walled-up at the end of the 14th century.[75] |
 | Poterne de l'Oratoire | Pedestrian entrance opened in the 1980s.[76] |
 | Porte de l'Oulle | The original 14th century name was Porte Sainte-Jacques, it later became Porte du Limas. The gate was walled up during the Wars of Religion,[68] and opened again in 1663. Rebuilt by Jean-Baptiste Péru in 1785–1786 20 metres north of the original position, it was demolished in 1900.[77] Oulle or Oulo is a "cooking pot" in the Provençal dialect. They were sold in a nearby market.[78][76] |
 | Poterne Georges Pompidou | Pedestrian entrance opened in the 1980s[79] |
 | Porte du Rhône | This was one of the 14th century entrances. Its original name was Ayguière or Eyguière.[lower-alpha 7] During the Wars of Religion the gate was protected by a ravelin. It was rebuilt in a classical style by Jean-Pierre Franque in 1761.[82] |
.jpg.webp) | Le Châtelet | The gatehouse controlled access to the town from the bridge. A tower constructed in 1368 was replaced by a larger tower in 1380. During the Western Schism Aragonese troops paid by the antipope Benedict XIII defended the papal palaces and bridge tower against attacks by people from the town. The bridge tower collapsed in 1410 during this conflict and was rebuilt in 1414. The bartizans at the corners were added in 1490.[41] |
 | Tour Polygonale | Pedestrian entrance through a tower that was built at the end of the 15th century. The tower is also referred to Tour des Chiens and confusingly as Tour Octogonale although there are eleven sides at the base and ten at the top.[83] |
 | Porte du Rocher | Pair of tunnels for vehicles through the rock that were opened in 1974. They provide access to La Place Ferruce and an underground car park.[38] |
See also
Notes
- For four of the twelve entrances the surviving manuscripts only ever mention a single gate. These are: Portail Pertuis, Portail Saint-Agricol, Portail l'Évêque, and Portail Aurose.[9]
- Portail Peint was another name for the old Portail Imbert.[17][18]
- The site of the hospital is now occupied by Avignon University.[27]
- The positions of the 13th century gates and towers between the Rocher des Doms and the Porte Saint-Lazare are not well documented.[51] Joseph Girard in his 1958 book Évocation du Vieil Avignon suggests that the Porte de la Palefrenerie was remove in the 15th century and that the Porte Aurose remained in use. In Girard's narrative in the 18th century the Porte Aurose, then referred to as Porte de la Ligne, was moved from its original position at the end of rue Banasterie to its present position at the end of rue Palapharneri.[52] This account conflicts with evidence from 17th century plans and pictures that show an entrance to the town at a position well away from the Rocher des Doms.[51] A complication is that there was a gate with the same name in the earlier 13th century walls, the Portail Aurose, that was not demolished until 1738.[53][54]
- The name Aurose is derived from Provençal dialect Auro meaning "wind".[55] The mistral could be particularly violent at this northern edge of the town.[1] The word ligne is derived from the Provençal ligno or legno meaning "wood" or more specifically "firewood". The gate gave access to the Quai de la Ligne where wood was brought.[56][57]
- In the 14th century this tower was given the name "Tour Saint-Esprit". It later became "Tour du Bourreau" and "Tour du Moulin des Mort".[65]
- The spelling of the original name varied: Ayguière, Eyguière, Aiguière etc.[80] Aigo means "water" in the Provençal dialect.[81]
References
- Girard 1958, p. 26.
- Carru 1999, p. 111.
- Gagnière et al. 1979, p. 107.
- Carru 1999, p. 112.
- Grégoire 1836, pp. 224.
- Girard 1958, pp. 24–25.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 13.
- Rolland 1989, p. 175.
- Rolland 1989, p. 178.
- Girard 1958, pp. 27–28.
- Girard 1958, pp. 32–33.
- Gagnière et al. 1979, p. 1049.
- Girard 1958, p. 33.
- Girard 1958, p. 26 Fn 1.
- Rolland 1989, p. 186.
- Rolland 1989, pp. 185–186.
- Girard 1958, p. 312.
- Pansier 1911, p. 313.
- Rolland 1989, pp. 187–190.
- Girard 1958, p. 343.
- Girard 1958, p. 37.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 16.
- Girard 1958, p. 34.
- Girard 1958, p. 41.
- Hayez 1978, p. 203.
- Hayez 1978, p. 204.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 16 Fn 25.
- Girard 1958, pp. 28, 52.
- Hayez 1978, pp. 196–199.
- Hayez 1978, pp. 201.
- Girard 1958, p. 42.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 19.
- Hayez 1978, pp. 203–204.
- Girard 1958, p. 342.
- Hayez 1978, pp. 213–215.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 20.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 22.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 107.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 122-123.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 72.
- Pansier 1930.
- Girard 1958, pp. 342–343.
- Girard 1958, p. 75.
- Gagnière et al. 1979, p. 344.
- Girard 1958, p. 344.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 26.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 112.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 105.
- Clap & Huet 2005, pp. 104, 119.
- Breton, Alain (1997). "La Porte de la Ligne". Annuaire de la Société des Amis du Palais des Papes. 74: 51–58.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 119.
- Girard 1958, pp. 343–344.
- Rolland 1989, p. 185.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 104.
- Mistral 1879a, p. 182.
- Mistral 1879b, p. 215.
- Girard 1958, p. 343 Fn 2.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 102.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 99.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 118.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 96.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 94.
- Clap & Huet 2005, pp. 93, 112.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 91.
- Clap & Huet 2005, pp. 22 Fn 52, 91.
- Clap & Huet 2005, pp. 90, 117.
- Clap & Huet 2005, pp. 89, 112.
- Girard 1958, pp. 342–344.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 116.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 85.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 84.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 83.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 115.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 79.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 74.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 71.
- Clap & Huet 2005, pp. 71, 114.
- Mistral 1879b, p. 436.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 69.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 21 Fn 45.
- Mistral 1879a, p. 57.
- Clap & Huet 2005, pp. 67, 113.
- Clap & Huet 2005, p. 108.
Sources
- Carru, Dominique (1999). "Le Rhône à Avignon: données archéologiques". Gallia (in French). 56: 109–120. doi:10.3406/galia.1999.3248.
- Clap, Sylvestre; Huet, Oliver (2005). Les Remparts d'Avignon (in French). Avignon: Benezet. ISBN 2-9522-367-1-2.
- Gagnière, Sylvain; et al. (1979). Histoire d'Avignon (in French). Aix-en-Provence, France: Édisud. ISBN 2-85744-056-1.
- Gagnière, Sylvain; Granier, Jean (1978). Images du Vieil Avignon : 126 documents anciens choisis et commentés (in French). Avignon: Rullière-Libeccio. OCLC 919032410.
- Girard, Joseph (1958). Évocation du Vieil Avignon (in French). Paris: Les Éditions de Minuit. OCLC 5391399.
- Grégoire, George Florence (1836). Histoire Ecclésiastique des Francs (in Latin and French). Vol. 1. J. Guadet, translator. Paris: J. Renouard.
- Hayez, Anne-Marie (1978). "Travaux à l'enceinte d'Avignon sous les pontificats d'Urbain V et de Grégoire XI". La Guerre et la paix, frontières et violences au Moyen âge: Actes du 101e Congrès National des Sociétés Savantes, Lille, 1976 (in French). Paris: Secrétariat d'Etat aux Universités. Comité des Travaux Historiques et Scientifiques. pp. 193–223. ISBN 978-2-7177-1430-2.
- Maureau, Alain (1994). "Les remparts d'Avignon au XIXe siècle". Provence Historique (in French). 44 (176): 211–223.
- Mistral, Frédéric (1879a). Lou Trésor dou Félibrige ou Dictionnaire provençal-français (in French and Occitan). Vol. 1: A-F. Aix-en-Provence: J. Remondet-Aubin.
- Mistral, Frédéric (1879b). Lou Trésor dou Félibrige ou Dictionnaire provençal-français (in French and Occitan). Vol. 2: G-Z. Aix-en-Provence: J. Remondet-Aubin.
- Pansier, Pierre (1910). "Les rues d'Avignon au Moyen Âge". Mémoires de l'Académie de Vaucluse. 2nd series (in French). 10: 41–74, 147–200, 209–244.
- Pansier, Pierre (1911). "Les rues d'Avignon au Moyen Âge (suite)". Mémoires de l'Académie de Vaucluse. 2nd series (in French). 11: 89–101, 281–322, 355–405.
- Pansier, Pierre (1930). "La Tour du Pont d'Avignon" (PDF). Annales d'Avignon et du Comtat Venaissin (in French). 16: 5–19.
- Rolland, Franck (1989). "Un mur oublié : le rempart du XIIIe siècle à Avignon". Archéologie Médiévale (in French). 19: 173–208. doi:10.3406/arcme.1989.955.
- Rollo-Koster, Joëlle (2015). Avignon and Its Papacy, 1309–1417: Popes, Institutions, and Society. Lanham, Maryland: Rowman and Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-4422-1532-0.
- Taupin, Jean-Louis (1971). "Les murs d'Avignon". Les Monuments Historiques de la France (in French). 17 (2–3): 141–186.
Further reading
- Hayez, Anne-Marie (1979). "Les gabelles d'Avignon d'Innocent VI à Grégoire XI". Études sur la fiscalité au Moyen Âge: Actes du 102e Congrès National des Sociétés Savantes, Limoges, 1977 (in French). Paris: Bibliotèque Nationale. pp. 171–206. ISBN 978-2-7177-1478-4.
- Hayez, Anne-Marie (2002). "La défense d'Avignon au temps des papes". In Le Blévec, Daniel (ed.). Défendre la ville dans les pays de la Méditerranée occidentale au Moyen âge : Actes de la Journée d'Études du 6 mars 1999 (in French). Montpellier: Centre Historique de Recherches et d'Etudes sur la Méditerranée Médiévale Occidentale, Université Paul-Valéry Montpellier III. pp. 63–101. ISBN 978-2-84269-524-8.
- Michel, Robert (1910). "La constructions des remparts d'Avignon au XIVe siècle". Congrès Archéologique de France (in French). Vol. 2. Paris: Derache. pp. 341–360.
- Michel, Robert (1910). "La défense d'Avignon sous Urbain V et Grégorie XI". Mélanges de l'école française de Rome (in French). 30: 129–154.
- Zerner-Chardavoine, Monique (1988). "Le siège d'Avignon par Louis VIII (10 juin – 10 septembre 1226)". Avignon au Moyen Age : textes et documents. Archives du Sud (in French). Avignon: Aubanel. pp. 43–52. ISBN 978-2-7006-0132-9.