Warsaw–Vienna railway
The Warsaw-Vienna Railway (Polish: Kolej Warszawsko-Wiedeńska, German: Warschau-Wiener Eisenbahn) was a railway system which operated since 1845 in Congress Poland, then part of the Russian Empire. The main component of its network was a line 327.6 km in length from Warsaw to the border station at Maczki in Sosnowiec with the Austrian Empire, and since 1867 the Austro-Hungarian Empire. There the line reached the Austrian railway network, offering connections to Vienna (hence the name of the line) and beyond. It was the first railway line built in Congress Poland and the second in the Russian Empire, after a short stretch of 27 km between Tsarskoye Selo and Saint Petersburg (Saint Petersburg - Tsarskoe Selo Railway) which opened in 1837.[1] The line used the standard European gauge (1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in)), as opposed to all other railways in the Russian Empire which used the broad gauge (1,524 mm or 5 ft), hence it formed a system physically separated from other Imperial Russian railways.

History
Ownership

The first concrete plan to build a railway between Warsaw and the southern border of the Congress Poland was submitted to Bank Polski (Polish Bank) by a consortium led by Henryk Łubieński in January 1835. Three years later, in 1838 Towarzystwo Akcyjne Drogi Żelaznej Warszawsko-Wiedeńskiej (Warsaw-Vienna Rail Road Company Ltd) was established and granted a licence to build the railway. Arguments between proponents of horse and steam traction lasted many years, and only in 1840, the latter was chosen when the building work started. The company went bankrupt in 1843 and was taken over by the state. In 1857 the line was leased to a private company (also called Towarzystwo Akcyjne Drogi Żelaznej Warszawsko-Wiedeńskiej) for 75 years, however, it was re-nationalized in 1912, with a compensation paid to the shareholders (mostly Belgians and Germans).
Permanent way
The first stretch of the line, from Warsaw to Grodzisk Mazowiecki (30 km), opened on 14 June 1845, and was extended to Skierniewice with a branch to Łowicz on 15 October 1845. Trains reached Częstochowa in 1846, Ząbkowice in 1847 and the Austrian border on 1 April 1848. There were 27 stations on the line.
Initially, the line was single, but from the outset, the earthworks were prepared for a second track, which was gradually added to the whole route between 1872 and 1881.
The terminal border station lay close to Szczakowa Station of the Kraków and Upper Silesia railway (Kolej Krakowsko-Górnośląska / Krakau-Oberschlesische Bahn). This line indirectly, via the two Prussian lines of the Upper Silesian Railway (Oberschlesische Bahn) and William's Railway (Wilhelmsbahn) was joined to the Austrian Northern Railway (in Bohumin), which reached the Prussian border from Vienna. An entirely Austrian communication was not available before 1856, when the Austrian Eastern National Railway, predecessor of the Kraków and Upper Silesia Railway, closed the gap with a branch from Trzebinia to Czechowice-Dziedzice.
Stations

- The Warsaw terminus (Vienna Station, Polish: Dworzec Wiedeński), designed by Enrico Marconi, opened in 1845 and remained in use for over 75 years. The building, facing Aleje Jerozolimskie, was 166 meters long and 18 meters wide, with the three-story central part, flanked by two 25 meter towers. The western tower housed an optical telegraph station on the top floor, the eastern one had a clock.
- Marconi designed also the southern terminus of the line, in Granica, on a much more modest scale.
Rolling stock

The first five locomotives were purchased from John Cockerill's factory in Seraing. Later on, additional engines were obtained from Borsig and other West European factories. From 1901 locomotives were Russian-built, but different from common Russian stock.[1]
Route
Main line: Warszawa - Grodzisk Mazowiecki - Skierniewice - Koluszki - Piotrków Trybunalski - Radomsko - Częstochowa - Zawiercie - Ząbkowice Będzińskie - Strzemieszyce Południowe - Granica (border with Austria)
Branch lines:
- Skierniewice - Łowicz
- Ząbkowice - Sosnowiec
- Koluszki - Łódź-Fabryczna
The railway forms the present day PKP rail line 1 from Warszawa Zachodnia to Katowice railway station, which runs along the original route from Warsaw up to Ząbkowice in present-day Dąbrowa Górnicza, however on the initial stretch between Warszawa Zachodnia and Grodzisk Mazowiecki the line runs on an additional pair of tracks added during the second half of the 20th century, while the tracks running along the original trail form a separate line, designated PKP rail line 447, serving local traffic. In Dąbrowa Górnicza the PKP rail line 1 diverges along the original branch line to Sosnowiec and a short final segments to Katowice follows the route of the Upper Silesian Railway,[2] while the end of the main line to Szczakowa forms PKP rail line 133 from Dąbrowa Górnicza Ząbkowice to Kraków Główny, together with the Kraków and Upper Silesia railway.[3]
The branch line from Skierniewice to Łowicz forms the present day PKP rail line 11[4] and the branch from Koluszki to Łódź Fabryczna - PKP rail line 17.
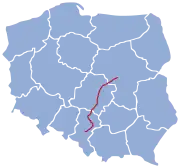 PKP line 1
PKP line 1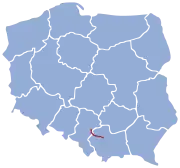 PKP line 133
PKP line 133 PKP line 11
PKP line 11 PKP line 17
PKP line 17
The significance of the line as the main connection with southern Poland has decreased following the construction of the Central Rail Line in the 1970s, as well as the 1930s Coal Trunk Line providing a direct connection between Upper Silesian Industrial Area and the Baltic Sea coast while the PKP rail line 8 offers an alternative connection between Warsaw and Kraków, however the line still remains one of Poland's main trunk lines.
See also
References
- Rakov, V.A.: Lokomotivy otechestvennyh zheleznyh dorog 1845-1955, Moscow 1995, ISBN 5-277-00821-7, p.10
- "Linia 1 Warszawa Zachodnia - Katowice".
- "Linia 133 Dąbrowa Górnicza Ząbkowice - Kraków Główny".
- "11 Skierniewice - Łowicz Główny".
External links
- Stawarz, Andrzej (ed.) (1990). Gdy do Grodziska ruszył parochód. Tow. Przyjaciół Grodziska Mazowieckiego.
{{cite book}}:|first=has generic name (help)