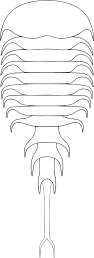
Willwerathia
Willwerathia is a genus of Devonian arthropod. It is sometimes classified as synziphosurine,[1][2] a paraphyletic group of horseshoe crab-like fossil chelicerate arthropods,[2] while some studies compare its morphology to an artiopod.[3][4] Willwerathia known only by one species, Willwerathia laticeps, discovered in deposits of the Devonian period from the Klerf Formation, in the Rhenish Slate Mountains of Germany.[1][5]
| Willwerathia Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Reconstruction of Willwerathia laticeps | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Order: | |
| Genus: | †Willwerathia Størmer, 1969 |
| Species | |
| |
Morphology

As a synziphosurine, Willwerathia is unusually large and so far the largest known synziphosurine, with largest carapace measured about 90mm in width.[1] Prosoma of Willwerathia covered by a vaulted carapace with pointed genal spines, recurved (M-shaped) ophthalmic ridges and pairs of dorsal nodes.[1] Tergites of the opisthosoma are either incomplete or disarticulated in available fossil materials, making it difficult to reveal the original number of opisthosomal segments.[1] The opisthosoma of Willwerathia most likely compose of 10 segments, each expressed by a tergite that bore a median dorsal spine and a pair of tergopleurae (lateral extensions).[1] The opisthosoma subdivided into a wider, most likely 7-segmented preabdomen and a narrower, 3-segmented postabdomen.[1] tergite of the first opisthosomal segment is reduced in length while the remaining segments possess well-developed tergites with lateral nodes and posteriorly curved tergopleurae. The final segment terminated with a short, teardrop-shaped telson.[1]
Paleoecology
Willwerathia was most likely a bottom-dwelling predator.[1] The marked articulation surfaces on each of the preabdominal segments suggest that Willwerathia capable to enroll itself in a way similar to Legrandella.[1] The environment in which Wilwerathia lived in was likely an estuarine to deltaic one, and other animals like the largest eurypterid, Jaekelopterus, are known from the same formation.[6]
Classification
Willwerathia was originally thought to be an eurypterid (sea scorpion), with additional fossils described in 1998 reveal its synziphosurine affinities.[1] In the redescription done by Anderson et al. 1998, Willwerathia had been grouped under the synziphosurine family Weinberginidae alongside Weinbergina and Legrandella,[1] a classification which is not supported by phylogenetic analysis.[2] Willwerathia was regarded as part of the monophyletic Xiphosura sensu stricto (true horseshoe crab) by Lamsdell 2013,[2][7] but further phylogenetic analysis repeatedly resolving it within a clade compose of Bunodids, Pseudoniscids and Dekatriatan (chasmataspidids, eurypterids and arachnids).[8][9][10][11] Morphology of Silurian-Devonian arthropd Maldybulakia is sometimes compared to that of Willwerathia.[4][12] However, in 2020, Lamsdell found that Willwerathia bears a strong resemblance to the Cambrian artiopod Falcatamacaris, while it does not bear resemblance to other chelicerates.[3]
References
- Anderson, Lyall I.; Poschmann, Markus; Brauckmann, Carsten (1998). "On the Emsian (Lower Devonian) arthropods of the Rhenish Slate Mountains: 2. The synziphosurine Willwerathia". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 72 (3–4): 325–336. doi:10.1007/BF02988363. ISSN 0031-0220. S2CID 128464147.
- Lamsdell, James C. (2013-01-01). "Revised systematics of Palaeozoic 'horseshoe crabs' and the myth of monophyletic Xiphosura". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 167 (1): 1–27. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2012.00874.x. ISSN 0024-4082.
- Lamsdell, James C. (2020-09-01). "A chasmataspidid affinity for the putative xiphosuran Kiaeria Størmer, 1934". PalZ. 94 (3): 449–453. doi:10.1007/s12542-019-00493-8. ISSN 1867-6812.
- Zong, Ruiwen; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Liu, Bingcai; Wang, Yi; Yin, Jiayi; Ma, Juan; Xu, Honghe (2023). Cherns, Lesley (ed.). "Silurian freshwater arthropod from northwest China". Papers in Palaeontology. 9 (2): e1488. doi:10.1002/spp2.1488. ISSN 2056-2799.
- Dunlop, J. A.; Penney, D.; Jekel, D. (2020). "A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives" (PDF). World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern. pp. 1–296.
- Poschmann, Markus; Tetlie, O. Erik (2006-12-01). "On the Emsian (Lower Devonian) arthropods of the Rhenish Slate Mountains: 5. Rare and poorly known eurypterids from Willwerath, Germany". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 80 (4): 325–343. doi:10.1007/BF02990208.
- Bicknell, Russell D. C.; Pates, Stephen (2020). "Pictorial Atlas of Fossil and Extant Horseshoe Crabs, With Focus on Xiphosurida". Frontiers in Earth Science. 8: 98. Bibcode:2020FrEaS...8...98B. doi:10.3389/feart.2020.00098. ISSN 2296-6463. S2CID 220405124.
- Selden, Paul A.; Lamsdell, James C.; Qi, Liu (2015). "An unusual euchelicerate linking horseshoe crabs and eurypterids, from the Lower Devonian (Lochkovian) of Yunnan, China". Zoologica Scripta. 44 (6): 645–652. doi:10.1111/zsc.12124. ISSN 0300-3256. S2CID 55264483.
- Lamsdell, James C.; Briggs, Derek E. G.; Liu, Huaibao P.; Witzke, Brian J.; McKay, Robert M. (2015). "A new Ordovician arthropod from the Winneshiek Lagerstätte of Iowa (USA) reveals the ground plan of eurypterids and chasmataspidids". The Science of Nature. 102 (9–10): 63. Bibcode:2015SciNa.102...63L. doi:10.1007/s00114-015-1312-5. ISSN 0028-1042. PMID 26391849. S2CID 8153035.
- Lamsdell, James C. (2016). "Horseshoe crab phylogeny and independent colonizations of fresh water: ecological invasion as a driver for morphological innovation". Palaeontology. 59 (2): 181–194. doi:10.1111/pala.12220. ISSN 1475-4983. S2CID 85553811.
- Bicknell, Russell D. C.; Lustri, Lorenzo; Brougham, Tom (2019-12-01). "Revision of "Bellinurus" carteri (Chelicerata: Xiphosura) from the Late Devonian of Pennsylvania, USA". Comptes Rendus Palevol. 18 (8): 967–976. doi:10.1016/j.crpv.2019.08.002. ISSN 1631-0683.
- Lamsdell, James C. (2013-01-01). "Revised systematics of Palaeozoic 'horseshoe crabs' and the myth of monophyletic Xiphosura". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society. 167 (1): 1–27. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2012.00874.x. ISSN 0024-4082. S2CID 82434358.