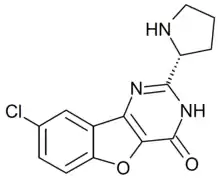
XL-413
XL-413 is a drug which acts as a selective inhibitor of the enzyme cell division cycle 7-related protein kinase (CDC7). It is being researched for the treatment of some forms of cancer, and also has applications in genetic engineering.[1][2][3][4]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEBI | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C14H12ClN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 289.71 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- Koltun ES, Tsuhako AL, Brown DS, Aay N, Arcalas A, Chan V, et al. (June 2012). "Discovery of XL413, a potent and selective CDC7 inhibitor". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 22 (11): 3727–31. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2012.04.024. PMID 22560567.
- Sasi NK, Tiwari K, Soon FF, Bonte D, Wang T, Melcher K, et al. (2014). "The potent Cdc7-Dbf4 (DDK) kinase inhibitor XL413 has limited activity in many cancer cell lines and discovery of potential new DDK inhibitor scaffolds". PLOS ONE. 9 (11): e113300. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...9k3300S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0113300. PMC 4239038. PMID 25412417.
- Jin S, Ma H, Yang W, Ju H, Wang L, Zhang Z (June 2018). "Cell division cycle 7 is a potential therapeutic target in oral squamous cell carcinoma and is regulated by E2F1". Journal of Molecular Medicine. 96 (6): 513–525. doi:10.1007/s00109-018-1636-7. PMID 29713760. S2CID 14036264.
- Wienert B, Nguyen DN, Guenther A, Feng SJ, Locke MN, Wyman SK, et al. (April 2020). "Timed inhibition of CDC7 increases CRISPR-Cas9 mediated templated repair". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 2109. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.2109W. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15845-1. PMC 7193628. PMID 32355159.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.