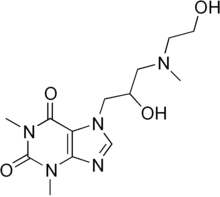
Xanthinol
Xanthinol is a drug prepared from theophylline used as a vasodilator.[1][2] It is most often used as the salt with niacin (nicotinic acid), known as xanthinol nicotinate.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C13H21N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 311.342 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- JA 38020588, Yokoyama M, Kawano S, "3-(Theophyllyl-7)-1-(N-methyl-N-hydroxyethyl)amino-2-propanol.", published 1963
- Morton IK, Hall JM (1999). Concise dictionary of pharmacological agents : properties and synonyms. Boston: Kluwer Academic. p. 294. ISBN 978-0-7514-0499-9.
- "Xanthinol niacinate]". cancerweb.ncl.ac.uk.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.