Zhucheng
Zhucheng (simplified Chinese: 诸城; traditional Chinese: 諸城; pinyin: Zhūchéng) is a county-level city in the southeast of Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It is under the administration of Weifang city and had at the 2010 census a population of 1,086,222 even though its built-up (or metro) area is much smaller.
Zhucheng
诸城市 Chucheng | |
|---|---|
 The China Tyrannosaurus Rex Hall in Zhucheng | |
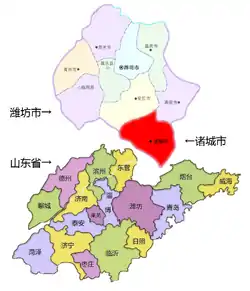 Location of Zhucheng (red) within Weifang City, and location of Weifang City within Shandong province | |
 Zhucheng Location in Shandong | |
| Coordinates: 36°00′N 119°25′E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Shandong |
| Prefecture-level city | Weifang |
| Area | |
| • Total | 2,183 km2 (843 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 66 m (215 ft) |
| Population (2018) | |
| • Total | 1,109,000 |
| • Density | 510/km2 (1,300/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard Time) |
| Postal code | 262200 |
| Area code | 0536 |
| Website | www |
History
Zhucheng was originally known as Langya (琅琊). It was from here that Emperor Qin Shi Huang sent Xu Fu to sail towards Japan in 210 BC, in pursuit of the elixir of youth.
Song dynasty
During the Song Dynasty, Zhucheng was known as Dongwu. Major figures who hailed from the area during the Song Dynasty include painter Zhang Zeduan, Zhao Tingzhi, and Zhao Mingcheng.
Ming dynasty
Wan Zhen'er, a famous concubine to Hongzhi Emperor, was born in Zhucheng.
Qing dynasty
Major Qing dynasty figures from Zhucheng include Liu Tongxun, Liu Yong, and Dou Guangnai.
People's Republic of China
A number of Mao-era figures hailed from Zhucheng, including Mao Zedong's last wife and leader of the Gang of Four, Jiang Qing, as well as Kang Sheng. Zhao Shucong, former vice-governor of Anhui province, is a native of Zhucheng.[1]
On January 31, 2021, the Zhucheng city government reported that a number of residents in Shunwang Subdistrict experienced symptoms of gas poisoning due to illegal discharge of chemical waste in the city.[2] On February 2, city authorities detained 16 suspects, and stated that the discharge had killed 4 people, and poisoned at least 37.[2]
Administration
Zhucheng was upgraded to a county-level city in 1987 and is administered as a provincial-level economic development district,[3] and had jurisdiction over 3 subdistricts and 10 towns.[4]
Subdistricts
The city's 3 subdistricts are Mizhou Subdistrict, Longdu Subdistrict, and Shunwang Subdistrict.[4]
Towns
The city's 10 towns are Zhigou, Jiayue, Shiqiaozi, Xiangzhou, Changcheng, Baichihe, Xinxing, Linjiacun, Huanghua, and Taolin.[4]
Former divisions
Former Towns are merged to others include Lübiao (吕标镇), Wanjiazhuang (万家庄镇), Qiankou (箭口镇), Mengtuan (孟疃镇), Mazhuang (马庄镇), Chenggezhuang (程戈庄镇), Jiutai (九台镇), Guojiatun (郭家屯镇), Zhujie (朱解镇), Haogezhuang (郝戈庄镇) and Wadian (瓦店镇). Wadian has been merged into Linjia Village and is now Wadian community.
Former Townships are merged to others include Taolin (桃林乡), Wujialou (吴家楼乡), Taoyuan (桃园乡), Shihetou (石河头乡), Shimen (石门乡), and Shandongtou (山东头乡).
Climate
| Climate data for Zhucheng (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1981–2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 16.9 (62.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
29.5 (85.1) |
34.6 (94.3) |
36.1 (97.0) |
39.6 (103.3) |
40.3 (104.5) |
35.9 (96.6) |
37.7 (99.9) |
34.1 (93.4) |
26.9 (80.4) |
19.7 (67.5) |
40.3 (104.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 3.7 (38.7) |
7.0 (44.6) |
13.1 (55.6) |
19.8 (67.6) |
25.4 (77.7) |
28.8 (83.8) |
30.6 (87.1) |
29.8 (85.6) |
26.6 (79.9) |
20.8 (69.4) |
13.0 (55.4) |
5.8 (42.4) |
18.7 (65.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −1.3 (29.7) |
1.5 (34.7) |
6.9 (44.4) |
13.6 (56.5) |
19.3 (66.7) |
23.1 (73.6) |
26.0 (78.8) |
25.3 (77.5) |
21.2 (70.2) |
15.1 (59.2) |
7.8 (46.0) |
1.0 (33.8) |
13.3 (55.9) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −5.0 (23.0) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
2.3 (36.1) |
8.6 (47.5) |
14.3 (57.7) |
18.7 (65.7) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.0 (71.6) |
17.1 (62.8) |
10.7 (51.3) |
3.7 (38.7) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
9.2 (48.5) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −18.7 (−1.7) |
−12.5 (9.5) |
−8.4 (16.9) |
−2.7 (27.1) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
8.9 (48.0) |
15.4 (59.7) |
13.8 (56.8) |
7.2 (45.0) |
−1.5 (29.3) |
−12.0 (10.4) |
−13.1 (8.4) |
−18.7 (−1.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 10.9 (0.43) |
16.6 (0.65) |
17.8 (0.70) |
33.4 (1.31) |
60.9 (2.40) |
73.3 (2.89) |
149.6 (5.89) |
219.5 (8.64) |
69.8 (2.75) |
33.1 (1.30) |
30.0 (1.18) |
13.2 (0.52) |
728.1 (28.66) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 3.2 | 4.0 | 4.4 | 6.3 | 7.3 | 8.3 | 11.8 | 12.8 | 7.5 | 5.5 | 5.6 | 4.0 | 80.7 |
| Average snowy days | 4.3 | 3.4 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.8 | 2.5 | 12.7 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 62 | 61 | 58 | 59 | 64 | 71 | 81 | 82 | 75 | 69 | 66 | 63 | 68 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 167.3 | 170.3 | 220.8 | 237.5 | 257.2 | 222.1 | 193.9 | 196.2 | 201.8 | 199.5 | 168.5 | 166.4 | 2,401.5 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 54 | 55 | 59 | 60 | 59 | 51 | 44 | 47 | 55 | 58 | 55 | 55 | 54 |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration[5][6] | |||||||||||||
Economy
In 2005, Zhucheng had a total output value of RMB 20.8 billion and an average annual growth rate of 16%. Zhucheng is projected to continue its 16% annual growth rate and attain a total output value of RMB 43.6 billion by 2010.[7]
Economic Development Zone
The Zhucheng Industrial Park was approved by the Shandong Provincial Government in 1992. Its total area spans 25 square kilometres (9.7 sq mi). The National Highway 206 which runs through it from south to north, and the city is linked by the Jiaoxin Railway Station, which connects it to Qingdao, 60 kilometres (37 mi) east, Rizhao, 60 kilometres (37 mi) south, and Weifang city, 80 kilometres (50 mi) north.[8] As of 2001, industries based at the zone included food processing, chemicals, building materials, textiles and electromechanical products, and 2001 annual total industrial output was 2 billion yuan, with the added industrial value of 350 million yuan. For 2001, exports were US$68.92 million, and revenue was 83.17 million yuan.[8]
Transportation
Zhucheng is about an hour's drive from Qingdao city.
Dinosaur city
Zhucheng has been an important site for dinosaur excavation since 1960. The local community is known to use calcium rich fossils for traditional village remedies used to treat muscle cramps and other minor ailments.[9] The world's largest hadrosaurid fossil was found in Zhucheng in the 1980s and is on display in the local museum.[10] Scientists have collected more than 50 metric tons (55 short tons) of fossils since 1960.[11] The city has also been a place for smuggling of dinosaur bones; in January 2008, Australia returned hundreds of kilograms of Chinese dinosaur fossils, including dinosaur fossil eggs. These fossils were recovered during a sting operation carried out on warehouses and cargo containers.[12][13]
The ceratopsian Zhuchengceratops (2010), sauropod Zhuchengtitan (2017) and theropod Zhuchengtyrannus (2011) have been described from deposits near and named after Zhucheng.
2008 discovery
On 31 December 2008, palaeontologists from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of Chinese Academy of Sciences announced they have unearthed 7,600 dinosaur fossils since March 2008 around Zhucheng. The latest sites to be discovered are near the towns of Longdu, Shunwang, Jiayue and Zhigou.[10] The palaeontologists believe they have found one of the biggest sites of dinosaur remains from a massive excavation pit. The fossilized bones date to the late Late Cretaceous just prior to the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.[14] The findings also include the remains of a 20 metres (66 ft) hadrosaurid, a record size for the duck-billed dinosaur.[9] A fossilized skull of a large ceratopsian was also found along with bones which belong to club-tailed ankylosaurs.[9]
According to Professor Zhao Xijin, a palaeontologist in charge of the excavations from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology, "This group of fossilised dinosaurs is currently the largest ever discovered in the world... in terms of area."[14]
Such a high concentration of fossil bones in such a small area is significant for the theories of extinction of dinosaurs. A detailed scientific journal on the fossils is expected to be published later in 2009. Excavations are currently suspended for the winter but will resume when the weather gets warmer.[14] Scientists believe a volcanic eruption may have killed the dinosaurs, and a subsequent flood carried the fossils to Zhucheng, which may have been a wetland covered in grass.[10]
The local authorities in Shandong are making plans to set up a fossil park in the area.[14]
Demographic and culture
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 1,030,658 | — |
| 2000 | 1,057,313 | +2.6% |
| 2010 est. | 1,194,800 | +13.0% |
Zhucheng is heavily industrialized and is one of the few dozen cities of China exceeding a million inhabitants. The major ethnic groups comprising the city include Han Chinese (99.7%), Manchu (0.1%), Korean (0.1%) and Hui (0.1%). The city has a Christian population of approximately of 19,000 (1.8%). Based on a census from the year 1990, the city had 523,425 males and 507,233 females with 260,678 households.[15] Zhucheng's sister city is Belleville, Ontario, Canada.[15]
References
- "China Vitae : Biography of Zhao Shucong". Chinavitae.com. Retrieved 2 January 2009.
- You, Li (2 February 2021). "Shandong Family Dies From Gas Poisoning After Illegal Dumping". Sixth Tone. Archived from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- 潍坊市-行政区划网 www.xzqh.org (in Chinese). XZQH. Retrieved 24 May 2012.
- 2020年统计用区划代码(诸城市) [2020 Statistical Division Codes (Zhucheng)] (in Chinese). National Bureau of Statistics of China. 2020. Archived from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 3 February 2021.
- 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- "Textile & Apparel — Zhucheng creates branded garments — Zhucheng — Shandong — Xinlang Sinoer — Sangsha Garment — Lanfeng Knitting". Textile.2456.com. Archived from the original on 11 January 2008. Retrieved 2 January 2009.
- "Zhucheng Economic Development Zone". 2007. Retrieved 31 December 2008.
- "Big dinosaur fossils find in China". NDTV Convergence. Press Trust of India. 31 December 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2008.
- "Chinese scientists claim discovery of earth's largest dinosaur fossil site". CBC news. 30 December 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2008.
- "Experts: Shandong dinosaur fossil field "world's largest"". chinaview.cn. Xinhua News Agency. 29 December 2008. Archived from the original on 31 December 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2008.
- "China finds 'largest dinosaur fossil site' in world". Reuters. 30 December 2008. Retrieved 31 December 2008.
- "One good fossil deserves another: China's gift to Australia", Brisbane Times, 24 May 2008
- Jackson, Steve (31 December 2008). "China finds major dinosaur site". BBC News. Retrieved 31 December 2008.
- "Zhucheng" (PDF). Asia Harvest. Retrieved 2 January 2009.