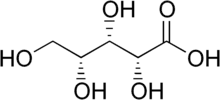
Xylonic acid
Xylonic acid is a sugar acid that can be obtained by oxidation of the hemiacetal/aldehyde group of xylose.[1][2][3] The C-2 epimer is known as lyxonic acid.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(2R,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentanoic acid | |
| Other names
Xylonate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C 5H 10O 6 | |
| Molar mass | 166.13 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
References
- PubChem. "L-Xylonic acid". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- "D-Xylonic acid | C5H10O6 | ChemSpider". www.chemspider.com. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
- "XYLONIC ACID | Sigma-Aldrich". www.sigmaaldrich.com. Retrieved 2019-06-02.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.