Yakovlev Yak-36
The Yakovlev Yak-36, also known as Izdeliye V, (NATO reporting name "Freehand") is a Soviet technology demonstrator for a VTOL combat aircraft.[2]
| Yak-36 | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| Yak-36 undergoing a demonstration flight before the Domodedovo Air Show in 1967 | |
| Role | Experimental VSTOL aircraft |
| National origin | Soviet Union |
| Manufacturer | OKB Yakovlev |
| First flight | 9 January 1963[1] |
| Number built | 4[2] |
Design and development
From 1960, the Yakovlev Design Bureau began work on a VTOL system, using the compact and lightweight Tumansky RU-19-300 turbojet engine, drafting a proposal for the Yak-104, a converted Yak-30 jet trainer with two vertically mounted Ru-19 engines between the inlet ducts of the standard Yak-30 powerplant. Work on the Yak-104 was terminated in favour of an aircraft with a single lift/cruise engine with rotating nozzles, similar to the Hawker Siddeley P.1127, which was nearing completion in England. Unable to find a suitable engine or convince the government to order the development of one, the Yakovlev bureau was forced to follow a different course.[2]
In response to a contract for the development of a single-seat V/STOL fighter in 1961, Yakovlev proposed a twin-engined aircraft with a large nose air intake, engines in the forward fuselage and swivelling exhaust nozzles, one for each engine on either side of the lower fuselage near the centre of gravity of the aircraft. The fighter version was not proceeded with but four technology demonstrators, (initially designated Izdeliye V) based on the fighter studies were ordered.[2]
Four prototypes were completed, one of which was used only for static testing. The second was used for takeoff and landing tests, including free hovering. The third incorporated improvements found in testing, including an improved autopilot which automatically selected optimal air flow for hover stability. This prototype crashed, but was later rebuilt. The fourth prototype crashed in February 1971 and was not rebuilt.[2]
Construction
The airframe had a semi-monocoque fuselage with bicycle-type landing gear, short cropped delta wings of 37° leading edge sweep, with 5° anhedral, attached to the fuselage in a mid position. The fuselage was substantial forward of the wing trailing edges, due to accommodating the engines, cockpit, fuel tanks and equipment bays as close to the centre of gravity as possible, tapering sharply to the swept tail surfaces with a high-set tailplane. Control of the aircraft was by conventional rudder, ailerons and elevators in normal flight and by compressed engine bleed air blown from control nozzles at the wingtips, rear fuselage tip and at the end of a long boom extending forwards from the top lip of the air intakes.[2]
Two underwing hard points could carry bombs, podded machine guns or rocket pods, but the Yak-36 had insufficient excess thrust and range for effective use as a combat aircraft.
Operational history
The first tethered hover flight took place on 9 January 1963. There were initial problems with hot gas reingestion where hot exhaust gasses are sucked back into the intakes causing poor airflow through the engines and loss of thrust. The suction effect of the exhaust on the ground (which made a higher engine power needed) and problems with control systems caused further difficulties. After modifications, the first untethered vertical flight was made on 23 June 1963, followed by the first full transition to horizontal flight on 16 September 1963.[1]
On 24 March 1966, the first complete flight was made from vertical takeoff transition to horizontal flight deceleration to vertical flight and vertical landing. After much testing and practice the first public presentation of the Yak-36 was made on 9 July 1967 at an air show at Moscow-Domodedovo airport, marking the 50th Anniversary of the October Revolution. After the promising results obtained from the flight test programme of the Yak-36, the next development step was the Yakovlev Yak-36M which flew for the first time on 27 September 1970.[1]
Aircraft on display
The second Yak-36 prototype, b/n 35, is now on display at the Central Air Force Museum at Monino, outside Moscow, Russia.[3]
Specifications (Yak-36)
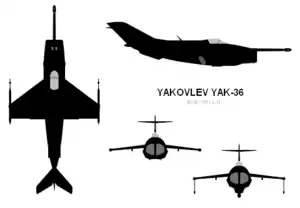
Data from Yakovlev Yak-36, Yak-38 & Yak-41[1]
General characteristics
- Crew: one
- Length: 17 m (55 ft 9 in)
- Wingspan: 10 m (32 ft 10 in)
- Height: 4.5 m (14 ft 9 in)
- Wing area: 17 m2 (180 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 5,300 kg (11,684 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 8,900 kg (19,621 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 2,600 kg (5,732.02 lb)
- Powerplant: 2 × Tumansky R-27-300 Vectored thrust axial flow turbojets, 51.993 kN (11,688 lbf) thrust each
Performance
- Maximum speed: 900 km/h (560 mph, 490 kn)
- Range: 370 km (230 mi, 200 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 12,000 m (39,000 ft) Hovering ceiling 1,900 m (6,233.60 ft)
- Rate of climb: 140 m/s (28,000 ft/min)
Armament
- Guns: 2 x 23 mm (0.91 in) GSh-23L cannon (UPK-23-250 gunpods)
- Hardpoints: 2 with a capacity of 100kg, with provisions to carry combinations of:
- Rockets: S-5K
- Missiles: R-3S air-to-air missiles
- Bombs: FAB-100 and FAB-250
- Rockets: 2 x UB-16-57UM FFAR rocketpods (16 rockets each)
See also
Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
References
- Gordon, Yefim (2008). Yakovlev Yak-36, Yak-38 & Yak-41. Red Star. Vol. 36. Midland publishing. pp. 9–30. ISBN 978-1-85780-287-0.
- Gordon, Yefim; Dmitry Komissarov; Sergey Komissarov (2005). OKB Yakovlev (1st ed.). Hinkley: Midland publishing. ISBN 1-85780-203-9.
- "Yakovlev Yak-36 "Freehand"". Moscow: www.moninoaviation.com. Retrieved 7 January 2012.