Yomogita
Yomogita (蓬田村, Yomogita-mura) is a village located in Aomori Prefecture, Japan and a part of the Aomori metropolitan area.[1] As of 31 January 2023, the village had an estimated population of 2740 in 1129 households,[2] and a population density of 32 persons per km2. The total area of the village is 80.84 square kilometres (31.21 sq mi).
Yomogita
蓬田村 | |
|---|---|
 Yomogita village hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
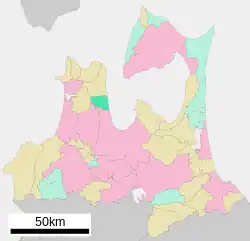
Location of Yomogita in Aomori Prefecture | |
 | |
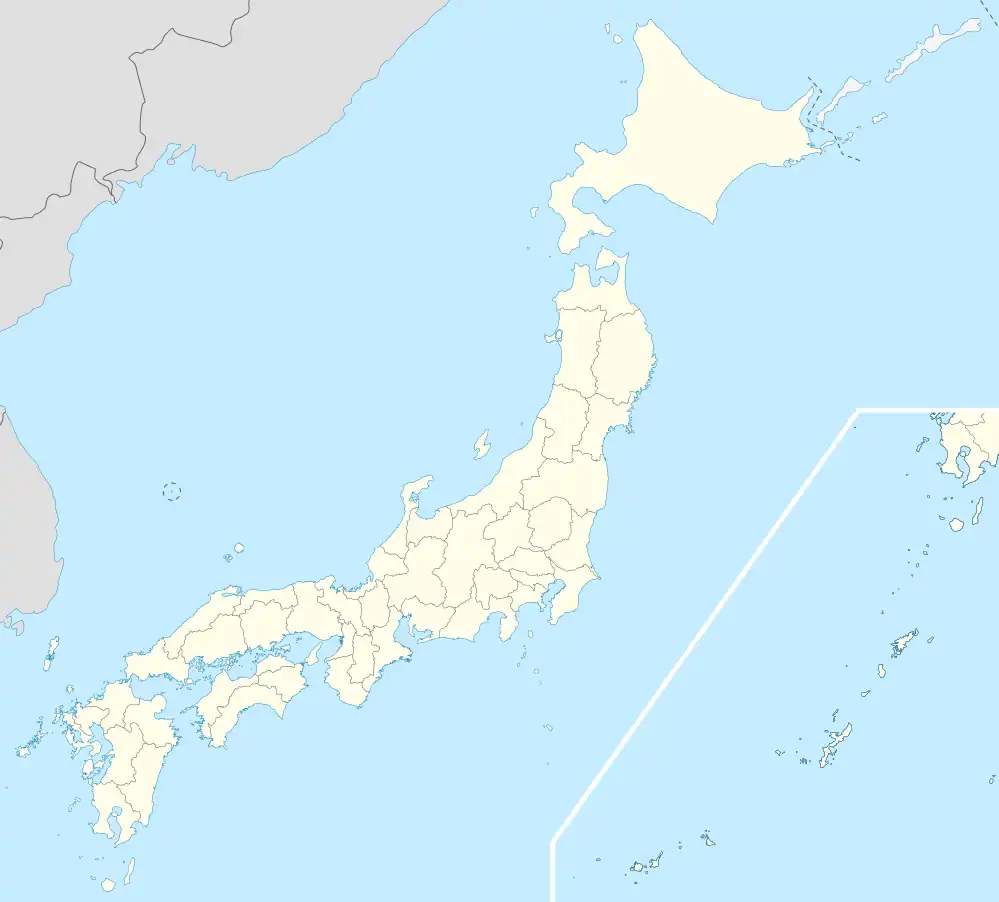 Yomogita | |
| Coordinates: 40°58′18.4″N 140°39′21.7″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Tōhoku |
| Prefecture | Aomori |
| District | Higashitsugaru |
| Area | |
| • Total | 80.84 km2 (31.21 sq mi) |
| Population (January 31, 2023) | |
| • Total | 2,570 |
| • Density | 32/km2 (82/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| Phone number | 0174-27-2111 |
| Address | 1-3 Shiooshi, Yomogita-mura, Higashitsugaru-gun, Aomori-ken 030-1211 |
| Website | Official website |
| Symbols | |
| Bird | Whooper swan |
| Flower | Rosa rugosa |
| Tree | Japanese black pine |

Geography
Yomogita is in Higashitsugaru District of Aomori Prefecture, and occupies a portion of the eastern coastline of Tsugaru Peninsula, facing Mutsu Bay. Mount Okura (677 meters) lies to the west and forms the border with Kitatsugaru. The Yomogita River flow through the village from west to east into Mutsu Bay.
Climate
The village has a cold humid continental climate (Köppen Cfb) characterized by warm short summers and long cold winters with heavy snowfall. The average annual temperature in Yomogita is 10.1 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1266 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 23.1 °C, and lowest in January, at around -1.8 °C.[3]
Demographics
Per Japanese census data,[4] the population of Yomogita peaked in the 1950s and has been in decline since. It is now less than it was a century ago.
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
History
The Kodate site in Yomogita was excavated in 1971, revealing a large quantity of Satsumon pottery, iron tools and traces of pit dwellings, indicating that the Yomogita area was the location of an ancient Satsumon settlement. The area around Yomogita was controlled by the Tsugaru clan of Hirosaki Domain during the Edo period. After the Meiji Restoration, it was formed into a village on April 1, 1889 with the establishment of the modern municipalities system.
Government
Yomogita has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral village council of eight members. Yomogita, collectively with the other municipalities of Higashitsugaru District, contributes one member to the Aomori Prefectural Assembly. In terms of national politics, the town is part of the Aomori 1st district of the lower house of the Diet of Japan.
Economy
The economy of Yomogita is heavily dependent on agriculture (rice and tomatoes) and commercial fishing. Some of the locally caught seafood include sea urchin roe, sea cucumber, scallops, abalone and squid.
Education
Yomogita has one public elementary school and one public junior high school operated by the village government. The village does not have a high school
Transportation
Highway
Noted people from Yomogita
- Hiroyuki Takei, manga artist
References
- "2010 Metropolitan Employment Map". University of Tokyo. Retrieved 6 July 2020.
- official home page (in Japanese)
- Yomogita climate data
- Yomogita population statistics
External links
![]() Media related to Yomogita, Aomori at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Yomogita, Aomori at Wikimedia Commons
- Official website (in Japanese)