Alveolar septum
The alveolar septum separates adjacent alveoli in lung tissue. The minimal components of an alveolar septum consist of the basement membranes of alveolar-lining epithelium (mostly type I pneumocytes) and capillary endothelium. Thicker alveolar septa may also contain elastic fibers, type I collagen, interstitial cells, smooth muscle cells, mast cells, lymphocytes and also monocytes.
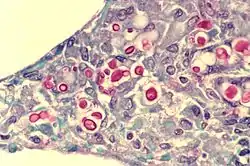
Cryptococcosis of lung in patient with AIDS. Mucicarmine stain. Histopathology of lung shows widened alveolar septum containing a few inflammatory cells and numerous yeasts of Cryptococcus neoformans. The inner layer of the yeast capsule stain red .
References
- Robbins and Cotran, Pathologic Basis of Disease, 7th Ed. pp 712–713.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.