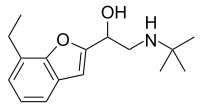
Bufuralol
Bufuralol is a potent beta-adrenoceptor antagonist with partial agonist activity.[1] It is metabolized by CYP2D6.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-(tert-Butylamino)-1-(7-ethyl-1-benzofuran-2-yl)ethan-1-ol | |
| Other names
2-(tert-Butylamino)-1-(7-ethylbenzofuran-2-yl)ethan-1-ol 2-(tert-Butylamino)-1-(7-ethyl-1-benzofuran-2-yl)ethanol | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.053.720 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C16H23NO2 |
| Molar mass | 261.365 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Most beta blockers are aryloxypropanolamine-based. In this rare exception, the benzofuran oxygen is part of a ring instead of derived from the epichlorohydrin precursor.
References
- Pringle, TH; Francis, RJ; East, PB; Shanks, RG (1986). "Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic studies on bufuralol in man". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 22 (5): 527–34. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02931.x. PMC 1401192. PMID 2878678.
- Flockhart DA (2007). "Drug Interactions: Cytochrome P450 Drug Interaction Table". Indiana University School of Medicine. Retrieved on July 2011
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.