Carazolol
Carazolol is a high affinity inverse agonist (also referred to as a beta blocker) of the β-adrenergic receptor.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATCvet code | |
| Identifiers | |
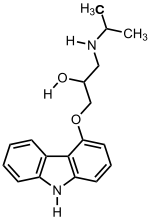
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.055.387 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H22N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 298.38 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
References
- Innis RB, Corrēa FM, Synder SH (1979). "Carazolol, an extremely potent beta-adrenergic blocker: binding to beta-receptors in brain membranes". Life Sci. 24 (24): 2255–64. doi:10.1016/0024-3205(79)90102-4. PMID 41147.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.