Cocaine reverse ester
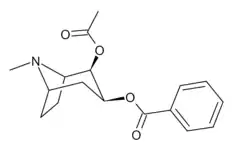
Cocaine reverse ester, (also known as Reverse ester cocaine or REC) is a tropane derivative drug which is a reverse ester of cocaine, with the 2-COOCH3 methoxycarbonyl group swapped to an isomeric OCOCH3 acetoxy group. It was synthesised because of the observation that the reverse ester pairs of several structurally related substances show similar activity to each other (see e.g. methylphenidate vs phacetoperane, pethidine vs desmethylprodine). Cocaine reverse ester however did not produce cocaine-like stimulant effects in animal studies,[1] and is also illegal in many jurisdictions as a structural isomer of cocaine; nevertheless it has attracted attention from vendors of quasi-legal designer drugs as a potential alternative to cocaine.
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H21NO4 |
| Molar mass | 303.358 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
- 3-(p-Fluorobenzoyloxy)tropane
- 4′-Fluorococaine
- Benzoylecgonine
- Methylecgonine cinnamate
- Salicylmethylecgonine
References
- Daum SJ, Martini CM, Kullnig RK, Clarke RL (May 1972). "Compounds affecting the central nervous system. I. Tropane-2 ,3 -diol derivatives. A reverse ester of cocaine". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 37 (10): 1665–9. doi:10.1021/jo00975a045. PMID 5031343.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.