Fosbretabulin
Fosbretabulin (also known as combretastatin A-4 phosphate or CA4P) is a microtubule destabilizing experimental drug, a type of vascular-targeting agent, a drug designed to damage the vasculature (blood vessels) of cancer tumours causing central necrosis. It is a derivative of combretastatin. It is formulated as the salts fosbretabulin disodium and fosbretabulin tromethamine.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Combretastatin A-4 phosphate; CA4P; CA4PD; fosbretabulin disodium; fosbretabulin tromethamine |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
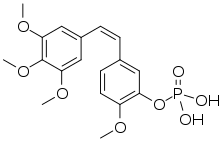
| Formula | C18H21O8P |
| Molar mass | 396.332 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Fosbretabulin is a prodrug. In vivo, it is dephosphorylated to its active metabolite, combretastatin A-4.[2]
In July 2007, the pharmaceutical company OXiGENE initiated a 180-patient phase III clinical trial of fosbretabulin in combination with carboplatin for the treatment of anaplastic thyroid cancer.[3] There is currently no fully FDA approved treatment for this form of cancer. By 2017, it had completed multiple clinical trials (e.g. for solid tumours,[4] non-small cell lung cancer[5]) with more in progress.[6]
See also
- Combretastatin, e.g. for the chemical synthesis
References
- "A Ph 2 Study to Investigate the Safety and Activity of Fosbretabulin Tromethamine (CA4P) in the Treatment of Well-Differentiated, Low-to-Intermediate-Grade Unresectable, Recurrent or Metastatic PNET or GI-NET Neuroendocrine Tumors/Carcinoid With Elevated Biomarkers". October 31, 2017 – via clinicaltrials.gov.
- "Fosbretabulin disodium". www.cancer.gov.
- "A Phase II/III Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Combretastatin A-4 Phosphate in Combination With Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in Comparison With Paclitaxel and Carboplatin Against Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma [FACT]". May 12, 2014 – via clinicaltrials.gov.
- "A Randomized Open-Labeled Phase II Study of Combretastatin A-4 Phosphate in Combination With Paclitaxel and Carboplatin to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy in Subjects With Advanced Imageable Malignancies". October 28, 2011 – via clinicaltrials.gov.
- "A Phase II Study to Assess the Safety and Efficacy of the Combination of Carboplatin, Paclitaxel, and Bevacizumab ± Combretastatin A4 Phosphate (CA4P) Followed by Bevacizumab ± CA4P in Subjects With Chemotherapy Naïve Stage IIIB/IV Non-Squamous Cell Histology Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC)". January 22, 2015 – via clinicaltrials.gov.
- "Search of: CA4P - List Results - ClinicalTrials.gov". clinicaltrials.gov.