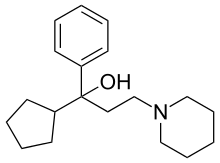
Cycrimine
Cycrimine (trade name Pagitane) is a central anticholinergic drug designed to reduce the levels of acetylcholine in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Its mechanism of action is to bind to the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M1.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| License data | |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.932 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H29NO |
| Molar mass | 287.447 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Synthesis
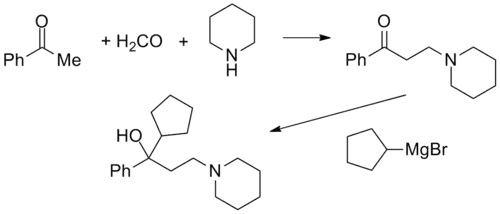
Cycrimine synthesis:[2]
See also
References
- Usdin E, Efron DH, eds. (1979). Psychotropic Drugs and Related Compounds (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: Pergamon Press. p. 218. ISBN 978-0-08-025510-1. OCLC 715151908.
- Denton JJ, Schedl HP, Lawson VA, Neier WB (1950). "Antispasmodics. VII.1 Additional Morpholinyl and Piperidyl Tertiary Alcohols". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 72 (8): 3795–3796. doi:10.1021/ja01164a127.
External links
- Cycrimine at DrugLib.com
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.