Laminectomy
A laminectomy is a surgical procedure that removes a portion of a vertebra called the lamina, which is the roof of the spinal canal. It is a major spine operation with residual scar tissue and may result in postlaminectomy syndrome. Depending on the problem, more conservative treatments (e.g., small endoscopic procedures, without bone removal) may be viable.[1]
| Laminectomy | |
|---|---|
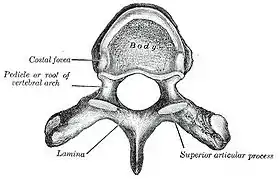 Upper view of a human vertebra, with the laminae visible | |
| ICD-9-CM | 03.09 |
| MeSH | D007796 |
| MedlinePlus | 007389 |
Method
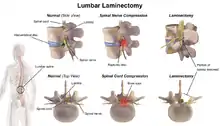
The lamina is a posterior arch of the vertebral bone lying between the spinous process (which juts out in the middle) and the more lateral pedicles and the transverse processes of each vertebra. The pair of laminae, along with the spinous process, make up the posterior wall of the bony spinal canal. Although the literal meaning of laminectomy is 'excision of the lamina', a conventional laminectomy in neurosurgery and orthopedics involves excision of the supraspinous ligament and some or all of the spinous process. Removal of these structures with an open technique requires disconnecting the many muscles of the back attached to them. A laminectomy performed as a minimal spinal surgery procedure is a tissue-preserving surgery that leaves more of the muscle intact and spares the spinal process. Another procedure, called the laminotomy, is the removal of a mid-portion of one lamina and may be done either with a conventional open technique or in a minimalistic fashion with the use of tubular retractors and endoscopes.
The reason for lamina removal is rarely, if ever, because the lamina itself is diseased; rather, it is done to break the continuity of the rigid ring of the spinal canal to allow the soft tissues within the canal to: 1) expand (decompress); 2) change the contour of the vertebral column; or 3) permit access to deeper tissue inside the spinal canal. A laminectomy is also the name of a spinal operation that conventionally includes the removal of one or both lamina, as well as other posterior supporting structures of the vertebral column, including ligaments and additional bone. The actual bone removal may be carried out with a variety of surgical tools, including drills, rongeurs and lasers.
The success rate of a laminectomy depends on the specific reason for the operation, as well as proper patient selection and the surgeon's technical ability. The first laminectomy was performed in 1887 by Victor Alexander Haden Horsley,[2] a professor of surgery at University College London. A laminectomy can treat severe spinal stenosis by relieving pressure on the spinal cord or nerve roots, provide access to a tumor or other mass lying in or around the spinal cord, or help in tailoring the contour of the vertebral column to correct a spinal deformity such as kyphosis. A common type of laminectomy is performed to permit the removal or reshaping of a spinal disc as part of a lumbar discectomy. This is a treatment for a herniated, bulging, or degenerated disc.
The recovery period after a laminectomy depends on the specific operative technique, with minimally invasive procedures having significantly shorter recovery periods than open surgery. Removal of substantial amounts of bone and tissue may require additional procedures such as spinal fusion to stabilize the spine and generally require a much longer recovery period than a simple laminectomy.
With spinal fusion, the recovery time may be longer. In some cases after laminectomy and spinal fusion, it may take several months to return to normal activities.[1] Potential complications include bleeding, infection, blood clots, nerve injury, and spinal fluid leak.[1]
For spinal stenosis
Most commonly, a laminectomy is performed to treat spinal stenosis. Spinal stenosis is the single most common diagnosis that leads to spinal surgery, of which a laminectomy represents one component. The lamina of the vertebra is removed or trimmed to widen the spinal canal and create more space for the spinal nerves and thecal sac. Surgical treatment that includes a laminectomy is the most effective remedy for severe spinal stenosis; however, most cases of spinal stenosis are not severe enough to require surgery. When the disabling symptoms of spinal stenosis are primarily neurogenic claudication and the laminectomy is done without spinal fusion, there is generally a more rapid recovery with less blood loss.[3] However, if the spinal column is unstable and fusion is required, the recovery period can last from several months to more than a year, and the likelihood of symptom relief is far less probable.[4]
Results
In most known cases of lumbar and thoracic laminectomies,[5] patients tend to recover slowly, with recurring pain or spinal stenosis persisting for up to 18 months after the procedure. According to a World Health Organization census in 2001, most patients who had undergone a lumbar laminectomy recovered normal function within one year of their operation.
Back surgery can relieve pressure on the spine, but it is not a cure-all for spinal stenosis. There may be considerable pain immediately after the operation, and pain may persist on a longer-term basis. For some people, recovery can take weeks or months and may require long-term occupational and physical therapy. Surgery does not stop the degenerative process and symptoms may reappear within several years.[1]
Additional images
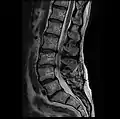 MRI lumbar spine with degeneration, post-hemilaminectomy L4-5 (sagittal T2 FRFSE)
MRI lumbar spine with degeneration, post-hemilaminectomy L4-5 (sagittal T2 FRFSE)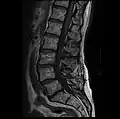 MRI lumbar spine with degeneration, post-hemilaminectomy L4-5 (sagittal T1 FSE)
MRI lumbar spine with degeneration, post-hemilaminectomy L4-5 (sagittal T1 FSE) MRI lumbar spine with degeneration, post-hemilaminectomy L4-5 (sagittal FAST STIR)
MRI lumbar spine with degeneration, post-hemilaminectomy L4-5 (sagittal FAST STIR)- MRI lumbar spine post-hemilaminectomy (sagittal T2 FRFSE)
- MRI lumbar spine post-hemilaminectomy (sagittal T1 FSE)
- Contrast MRI lumbar spine post-hemilaminectomy (sagittal T1 FSE FS)
- MRI lumbar spine pre-hemilaminectomy (sagittal T2 FRFSE)
- MRI lumbar spine pre-hemilaminectomy (sagittal T1 FSE)
- MRI lumbar spine pre-hemilaminectomy (sagittal FAST STIR)
See also
- Artificial facet replacement
- Failed back syndrome
- Spinal stenosis
References
- "Laminectomy". Mayo Clinic. 1 July 2020. Retrieved 25 December 2021.
- Black, Peter McL; Tan, Tze-Ching (2002-03-01). "Sir Victor Horsley (1857–1916): Pioneer of Neurological Surgery". Neurosurgery. 50 (3): 607–612. doi:10.1097/00006123-200203000-00032. ISSN 0148-396X. PMID 11841730.
- Phan, Kevin; Mobbs, Ralph J. (2016). "Minimally Invasive Versus Open Laminectomy for Lumbar Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis". Spine. 41 (2): E91–E100. doi:10.1097/BRS.0000000000001161. ISSN 0362-2436. PMID 26555839. S2CID 25947270.
- "Laminectomy". Nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 19 December 2012.
- "Patient agreement to investigation or treatment - Thoracic Laminectomy" (PDF). Cuh.org.uk. August 2010. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-08-31.