Foley catheter
In urology, a Foley catheter (named for Frederic Foley, who produced the original design in 1929) is a flexible tube that a clinician passes through the urethra and into the bladder to drain urine. It is the most common type of indwelling urinary catheter.
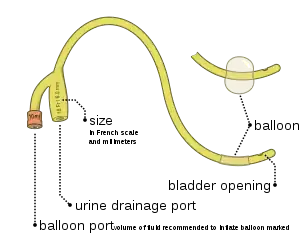
The tube has two separated channels, or lumens, running down its length. One lumen, open at both ends, drains urine into a collection bag. The other has a valve on the outside end and connects to a balloon at the inside tip. The balloon is inflated with sterile water when it lies inside the bladder to stop it from slipping out. Manufacturers usually produce Foley catheters using silicone or coated natural latex. Coatings include polytetrafluoroethylene, hydrogel, or a silicon elastomer – the different properties of these surface coatings determine whether the catheter is suitable for 28-day or 3-month indwelling duration.
Foley catheters should be used only when indicated, as use increases the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infection (UTI) and other adverse effects. While female sex is generally recognised as a risk factor for UTIs, the differences in biological sex are reduced or even diminished while carrying catheters.[1]
History
The name comes from the designer, Frederic Foley, a surgeon who worked in Boston, Massachusetts in the 1930s.[2] His original design was adopted by C. R. Bard, Inc. of Murray Hill, New Jersey, who manufactured the first prototypes and named them in honor of the surgeon.
Types
Foley catheters come in several types:
- Coudé (French for elbowed) catheters have a 45° bend at the tip that facilitates easier passage through an enlarged prostate.
- Councill tip catheters[3] have a small hole at the tip so they can be passed over a wire.
- Three-way, or triple lumen catheters have a third channel used to infuse sterile saline or another irrigating solution. These are used primarily after surgery on the bladder or prostate, to wash away blood and blood clots.
Sizes
The relative size of a Foley catheter is described using French units (F).[4] Alternatively, the size of a 10 F catheter might be expressed as 10 Ch (Charriere units – named after a 19th century French scientific instrument maker, Joseph-Frédéric-Benoît Charrière). The most common sizes are 10 F to 28 F. 1 F is equivalent to 0.33 mm = .013" = 1/77" of diameter. Foley catheters are usually color coded by size with a solid color band at the external end of the balloon inflation tube, allowing for easy identification of the size.[5] Note: Colors for French sizes 5, 6, 8, 10 may vary significantly if intended for pediatric patients. Color for French size 26 may also be pink instead of black.
| Color | French units | mm | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yellow-green | 6 | 2.0 | |
| Cornflower Blue | 8 | 2.7 | |
| Black | 10 | 3.3 | |
| White | 12 | 4.0 | |
| Green | 14 | 4.7 | |
| Orange | 16 | 5.3 | |
| Red | 18 | 6.0 | |
| Yellow | 20 | 6.7 | |
| Purple | 22 | 7.3 | |
| Blue | 24 | 8.0 | |
| Black | 26 | 8.7 | |
Medical uses
Urinary tract
Indwelling urinary catheters are most commonly used to assist people who cannot urinate on their own.[6] Indications for using a catheter include providing relief when there is urinary retention, monitoring urine output for critically ill persons, managing urination during surgery, and providing end-of-life care.[6]
Foley catheters are used during the following situations:
- On patients who are anesthesized or sedated for surgery or other medical care
- On comatose patients
- On some incontinent patients
- On patients whose prostate is enlarged to the point that urine flow from the bladder is cut off
- On patients with acute urinary retention
- On patients who are unable due to paralysis or physical injury to use either standard toilet facilities or urinals
- Following urethral surgeries
- Following ureterectomy
- On patients with kidney disease whose urine output must be constantly and accurately measured
- Before and after cesarean section
- Before and after hysterectomy
- On patients who have had genital injury
- On anorexic patients who are unable to use standard toilets due to physical weakness and whose urine output must be constantly measured
- On patients with fibromyalgia who cannot control their bladder
- On patients who have severe skin impairment and/or breakdown
Cervical
A Foley catheter can also be used to ripen the cervix during induction of labor. When used for this purpose, the procedure is called extra-amniotic saline infusion.[7] In this procedure, the balloon is inserted behind the cervical wall and inflated, for example with 30-80 mL of saline.[7] The remaining length of the catheter is pulled slightly taut and taped to the inside of the woman's leg. The inflated balloon applies pressure to the cervix as the baby's head would prior to labor, causing it to dilate. As the cervix dilates over time, the catheter is readjusted to again be slightly taut and retaped to maintain pressure. When the cervix has dilated sufficiently, the catheter drops out.[8]
Contraindications
Indwelling urinary catheters should not be used to monitor stable people who are able to urinate or for the convenience of the patient or hospital staff. Urethral trauma is the only absolute contraindication to the placement of a urinary catheter. Examination findings such as blood at the urethral meatus, or a high riding prostate necessitate a retrograde urethrogram prior to insertion.[6]
In the United States, catheter-associated urinary tract infection is the most common type of hospital-acquired infection.[6] While UTIs are generally more common among females, the risk factor associated to anatomy is reduced while carrying catheters, some studies even showing no significant differences between the sex.[1] Indwelling catheters should be avoided when there are alternatives, and when patients and caregivers discuss alternatives to indwelling urinary catheters with their physicians and nurses then sometimes an alternative may be found.[6] Physicians can reduce their use of indwelling urinary catheters when they follow evidence-based guidelines for usage, such as those published by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.[6]
Adverse effects
All catheterised bladders become colonised with bacteria within 24 hours. This is not an infection and is very poorly understood by clinicians. Whilst the presence of a catheter does increase the incidence of bloodstream infections secondary to a urinary origin, there is a huge amount of unnecessary, and likely harmful, antimicrobial prescribing on the basis of detection of asymptomatic bacteriuria. The industry is moving to silver-coated catheters in an attempt to reduce the incidence of urinary tract infections, although there is limited evidence of efficacy. An additional problem is that Foley catheters tend to become coated over time with a biofilm that can obstruct the drainage. This increases the amount of stagnant urine left in the bladder, which further contributes to urinary tract infections. When a Foley catheter becomes clogged, it must be flushed or replaced. There is currently not enough adequate evidence to conclude whether washouts are beneficial or harmful.[10]
There are several risks in using a Foley catheter (or catheters generally), including:
- The balloon can break as the healthcare provider inserts the catheter. In this case, all balloon fragments must be removed.
- The balloon might not inflate after it is in place. In some institutions, the healthcare provider checks the balloon inflation before inserting the catheter into the urethra. If the balloon still does not inflate after placement into the bladder, it is discarded and replaced.
- Urine stops flowing into the bag. The healthcare provider checks for correct positioning of the catheter and bag, or for obstruction of urine flow within the catheter tube.
- Urine flow is blocked. The Foley catheter must be discarded and replaced.
- The urethra begins to bleed. The healthcare provider monitors the bleeding.
- Catheterization introduces an infection into the bladder. The risk of bladder or urinary tract infection increases with the number of days the catheter is in place.
- If the balloon is opened before the Foley catheter is completely inserted into the bladder, bleeding, damage and even rupture of the urethra can occur. In some individuals, long-term permanent scarring and strictures of the urethra occur.[11]
- Defective catheters may be supplied, which break in situ. The most common fractures occur near the distal end or at the balloon.
- Catheters can be pulled out by patients while the balloon is still inflated, leading to major complications or even death. This may occur when patients are mentally impaired (e.g. they have Alzheimer's) or are in a mentally altered state (e.g. they are coming out of surgery).
References
- Lee JH, Kim SW, Yoon BI, Ha US, Sohn DW, Cho YH (January 2013). "Factors that affect nosocomial catheter-associated urinary tract infection in intensive care units: 2-year experience at a single center". Korean Journal of Urology. 54 (1): 59–65. doi:10.4111/kju.2013.54.1.59. PMC 3556556. PMID 23362450.
- Foley, FE (1937). "A hemostatic bag catheter: one piece latex rubber structure for control of bleeding and constant drainage following prostatic resection". Journal of Urology. 38: 134–139. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(17)71935-0.
- Siroky, Oates & Babayan 2004, p. 65.
- "Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary". Archived from the original on 2008-02-29. Retrieved 2006-06-18.
- "Indwelling Urinary Catheters: Types". UroToday. Retrieved 22 Jan 2020.
Catheter sizes are colored-coded at the balloon inflation site for easy identification
. - American College of Emergency Physicians, "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question", Choosing Wisely: an initiative of the ABIM Foundation, American College of Emergency Physicians, retrieved January 24, 2014, which cites
- Umscheid CA, Mitchell MD, Doshi JA, Agarwal R, Williams K, Brennan PJ (February 2011). "Estimating the proportion of healthcare-associated infections that are reasonably preventable and the related mortality and costs". Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 32 (2): 101–114. doi:10.1086/657912. PMID 21460463. S2CID 24729897.
- Lo E, Nicolle L, Classen D, Arias KM, Podgorny K, Anderson DJ, et al. (October 2008). "Strategies to prevent catheter-associated urinary tract infections in acute care hospitals". Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 29 Suppl 1 (s1): S41–S50. doi:10.1086/591066. PMID 18840088. S2CID 43797520.
- Munasinghe RL, Yazdani H, Siddique M, Hafeez W (October 2001). "Appropriateness of use of indwelling urinary catheters in patients admitted to the medical service". Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 22 (10): 647–649. doi:10.1086/501837. PMID 11776352. S2CID 43530303.
- Hazelett SE, Tsai M, Gareri M, Allen K (October 2006). "The association between indwelling urinary catheter use in the elderly and urinary tract infection in acute care". BMC Geriatrics. 6 (1): 15. doi:10.1186/1471-2318-6-15. PMC 1618836. PMID 17038177.
- Gardam MA, Amihod B, Orenstein P, Consolacion N, Miller MA (Jul–Sep 1998). "Overutilization of indwelling urinary catheters and the development of nosocomial urinary tract infections". Clinical Performance and Quality Health Care. 6 (3): 99–102. PMID 10182561.
- Gould CV, Umscheid CA, Agarwal RK, Kuntz G, Pegues DA (April 2010). "Guideline for prevention of catheter-associated urinary tract infections 2009". Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology. 31 (4): 319–326. doi:10.1086/651091. PMID 20156062. S2CID 31266013.
- Scott RA, Oman KS, Makic MB, Fink RM, Hulett TM, Braaten JS, et al. (May 2014). "Reducing indwelling urinary catheter use in the emergency department: a successful quality-improvement initiative". Journal of Emergency Nursing. 40 (3): 237–44, quiz 293. doi:10.1016/j.jen.2012.07.022. PMID 23477920.
- Guinn DA, Davies JK, Jones RO, Sullivan L, Wolf D (July 2004). "Labor induction in women with an unfavorable Bishop score: randomized controlled trial of intrauterine Foley catheter with concurrent oxytocin infusion versus Foley catheter with extra-amniotic saline infusion with concurrent oxytocin infusion". American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology. 191 (1): 225–229. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2003.12.039. PMID 15295370.
- WHO article on induction of labour Archived May 19, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- Holland NJ, Sandhu GS, Ghufoor K, Frosh A (Jan–Feb 2001). "The Foley catheter in the management of epistaxis". International Journal of Clinical Practice. 55 (1): 14–15. PMID 11219312.
- Shepherd AJ, Mackay WG, Hagen S (March 2017). "Washout policies in long-term indwelling urinary catheterisation in adults". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2017 (3): CD004012. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004012.pub5. PMC 6464626. PMID 28262925.
- "Foley Catheter Causes, Symptoms, Treatment - Foley Catheter Risks on eMedicineHealth". Emedicinehealth.com. December 18, 2012. Retrieved 2012-12-19.
Sources
- Siroky MB, Oates RD, Babayan RK, eds. (2004). Handbook of Urology: Diagnosis and Therapy (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Handbook Series) (3rd ed.). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 65. ISBN 978-0781742214.