Hitchhiker's thumb
Hitchhiker's thumb, also known as distal hyperextensibility of the thumb is the condition of having a thumb that has a distal phalange that bends backwards in an angle of 90°, it is thought to be inherited in an autosomal recessive manner, however, it presents on genetic disorders that are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner[1] This condition is benign (when isolated) and does not cause pain or affect the thumb with the trait negatively.
| Hitchhiker's thumb | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Distal hyperextensibility of the thumb, thumb hypermobility, Z-shaped deformity,[2] duck-bill thumb [3] |
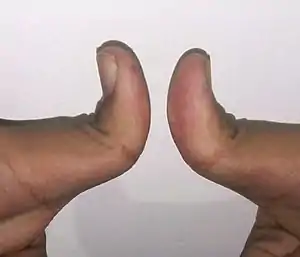 | |
| Example of bilateral hitchhiker's thumb | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics |
| Symptoms | A thumb that can bend backwards at more than a 90° degree angle |
| Complications | If it presents as an isolated trait, none |
| Duration | Life-long |
| Causes | May either present as an isolated trait, or be a symptom of a condition such as a hypermobility spectrum disorder[1] |
| Risk factors | Family history |
| Frequency | 24-36% of the U.S. population [4] |
If a person has the genes for this condition, it might present bilaterally, unilaterally, or on none of the thumbs.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms vary among people with hitchhiker's thumbs, those who have it as an isolated trait aren't affected by any symptoms, however, this trait is sometimes a symptom of other conditions, such as a hypermobility spectrum disorder.
The signs of this trait are having a thumb with a distal phalange that is able to bend backwards beyond the normal range of motion. Some people with hitchhiker's thumb also have a Z-shaped deformity, named after the appearance of this deformity, which is that of the letter Z.

Causes
The exact cause of isolated hitchhiker's thumb is not known, it is thought to be inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. [5][1]
However, this trait is often a symptom of an underlying condition, such as
- Diastrophic dysplasia
- Hypermobility spectrum disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Diagnosis
The trait does not generally need a medical diagnosis, however, it can help with the diagnosis of an individual who is suspected of having a certain condition.
Treatment
If it is not associated with any condition, and does not need treatment.
Incidence
Hitchhiker's thumbs affect 24-36% of the U.S. population.[4]
See also
- Hypermobility (joints)
- Ligamentous laxity
- Hypermobility spectrum disorder
- Ehlers-Danlos syndromes
- Diastrophic dysplasia
- Thumb
References
- "Hitchhiker's Thumb". Healthline. November 27, 2017.
- "What Is Hitchhiker's Thumb?". WebMD.
- Shetty, Aditya. "Hitchhiker thumb deformity | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia.
- "Do you have the genetics for the Hitchhiker's Thumb?". Transformational Bioinformatics. May 9, 2019.
- "What is Hitchhiker's Thumb? Inherited Traits and Body Quirks". www.brighthub.com. June 30, 2009.