Inferior orbital fissure
The inferior orbital fissure is formed by the sphenoid bone and the maxilla. It is located posteriorly along the boundary of the floor and lateral wall of the orbit. It transmits a number of structures, including:
- the zygomatic branch of the maxillary nerve
- the ascending branches from the pterygopalatine ganglion
- the infraorbital vessels, which travel down the infraorbital groove into the infraorbital canal and exit through the infraorbital foramen
- the inferior division of the ophthalmic vein
| Inferior orbital fissure | |
|---|---|
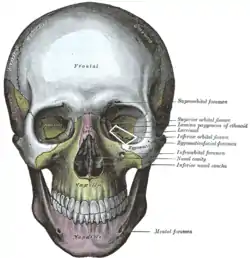 The skull from the front. (Label for inferior orbital fissure is at center right.) | |
 1 Foramen ethmoidale, 2 Canalis opticus, 3 Fissura orbitalis superior, 4 Fossa sacci lacrimalis, 5 Sulcus infraorbitalis, 6 Fissura orbitalis inferior, 7 Foramen infraorbitale | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Fissura orbitalis inferior |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.084 |
| TA2 | 489 |
| FMA | 54802 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Images
 Left infratemporal fossa.
Left infratemporal fossa. Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities.
Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities. Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure.
Dissection showing origins of right ocular muscles, and nerves entering by the superior orbital fissure. Inferior orbital fissure.
Inferior orbital fissure.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 189 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 189 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Inferior orbital fissure.
- lesson3 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (orbitforamina) (#3)
- "Anatomy diagram: 34256.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-12-27.
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2012-07-22.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.