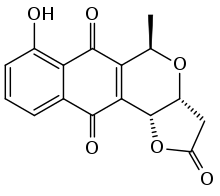
Kalafungin
Kalafungin is a substance discovered in the 1960s and found to act as a broad-spectrum antibiotic in vitro. It was isolated from a strain of the bacterium Streptomyces tanashiensis.[1][2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | U-19718 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H12O6 |
| Molar mass | 300.266 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
It is not known to be marketed anywhere in the world.[3]
References
- Bergy ME (July 1968). "Kalafungin, a new broad spectrum antibiotic. Isolation and characterization". The Journal of Antibiotics. 21 (7): 454–7. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.21.454. PMID 4303501.
- Johnson LE, Dietz A (December 1968). "Kalafungin, a new antibiotic produced by Streptomyces tanashiensis strain Kala". Applied Microbiology. 16 (12): 1815–21. doi:10.1128/AEM.16.12.1815-1821.1968. PMC 547777. PMID 5726156.
- "Kalafungin search results". Drugs.com. Retrieved 2021-03-31.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.