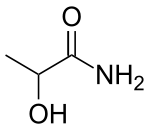
Lactamide
Lactamide is an amide derived from lactic acid. It is a white crystalline solid with a melting point of 73-76 °C.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxypropanamide | |
| Other names
2-Hydroxypropionamide; Lactic acid amide; Lactic amide; α-Hydroxypropionamide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.410 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C3H7NO2 |
| Molar mass | 89.094 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 73 to 76 °C (163 to 169 °F; 346 to 349 K)[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Lactamide can be prepared by the catalytic hydration of lactonitrile.[2]
References
- Chemical Book Lactamide
- US 5756842, Fumio Tanaka, Tsumoru Morimoto, Takako Uchiyama, Takafumi Abe, "Process for preparing lactamide", issued 1998-05-26
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.