Male chest reconstruction
Male chest reconstruction refers to any of various surgical procedures to masculinise the chest by removing breast tissue or altering the nipples and areolae. Male chest reconstruction may be performed in cases of gynecomastia and gender dysphoria. Transmasculine people may pursue chest reconstruction, also known as top surgery, as part of transitioning.
| Male chest reconstruction | |
|---|---|
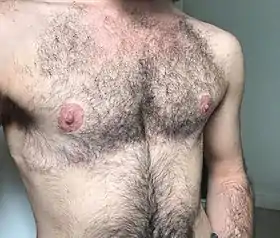 Transmasculine individual with healed double incision chest reconstruction | |
| ICD-9-CM | 85 |
The removal of breast tissue in male chest reconstruction is a type of mastectomy called a subcutaneous mastectomy. Subcutaneous means "under the skin". This type of mastectomy removes tissue from inside the breast (subcutaneous tissue), as well as excess skin. The surgeon then contours the chest into a masculine shape, altering the size and position of the areolae and nipples as needed.
Patients
Male chest reconstruction surgery candidates desire a flat chest that appears masculine. These candidates may include cisgender men with gynecomastia; transgender men who are medically transitioning and have chest dysphoria; and non-binary people with breasts,[1] who, like transgender men, can experience chest dysphoria.[2][3]
Gynecomastia is a common breast deformity that can occur in men, which may require surgical intervention. Causes of gynecomastia may vary but may include drug side effects or genetics.[2]
People assigned female at birth who are transitioning to male, masculine, or non-binary genders may experience gender dysphoria caused by their chest and/or gender euphoria after the surgical recovery.[3]
Canadian actor Elliot Page underwent the surgery circa March 2021; he has stated, "It has completely transformed my life… [It’s] not only life-changing but lifesaving.”[4]
Procedures
Inverted "T"
A transverse inframammary incision with free nipple areolar grafts may be one approach. If there is too much blousing of the skin, the alternatives are to extend the incision laterally (chasing a dog ear) or to make a vertical midline incision (inverted T).
The areola is trimmed to a pre-agreed-upon diameter and the nipple sectioned with a pie-shaped excision and reconstituted. There may be varying sensory loss because of nerve disruption.
Double incision
One of the most common male chest reconstructive procedures, double incision involves an incision above and below the breast mass, the removal of the fatty and glandular tissue, and the closure of the skin. This method leaves scars under the pectoral muscles, stretching from the underarms to the medial pectoral.
Double incision is usually accompanied by free nipple grafts to make male-looking nipples. The areola and nipple is removed from the breast tissue, cutting away along the circumference and removing the top layer of flesh from the rest of the tissue. After the chest has been reconstructed, the nipples are grafted on in the appropriate male position. The areolae are often sized down as well as the nipples themselves, as female areolae are often larger in circumference and the nipples protrude farther.
Nipple grafts are generally associated with double incision style chest reconstruction, but may be used in any reconstruction procedure if necessary. With nipple grafts comes the possibility of rejection. In such cases, the nipple is often tattooed back on cosmetically or further surgical procedures may be applied.
Some sensation will usually return to the grafted nipples over time. However, the procedure severs the nerves that go into the nipple-areola and there is a substantial likelihood for loss of sensation. [5]
Keyhole
To remove the glandular and fatty tissue which comprise the breast mass and the added skin that drapes the mass, there are three basic approaches.
For petite breasts, such as an A or a small B, a peri-areolar incision can be done. That is a circular incision around the areola, combined with an inner circular incision to remove some of the excess areola. Drawing the skin into the center will result in some puckering, but this often smooths out with time. There will be significant tension on the scar line, and to prevent spreading of the scar, a permanent fixation suture is needed. Leaving outer dermis (raw skin) underneath the marginalized areola helps in its survival.
The keyhole incision (think skeleton key) augments the periareolar incision further by making a vertical closure underneath (lollipop), which results after the unwanted skin is pulled in from side to side and the excess is removed.[6]
An anchor incision adds to that a transverse incision usually in the infra mammary fold to further remove excessive skin. Draping or blousing is not desirable. This is reserved for much larger breasts or topographically a larger surface area as seen in women with postpartum breast atrophy.
The nipple areolar complex may be supported by a pedicle which has the advantage of leaving some sensation and blood supply intact, but can have the disadvantage when the pedicle has sufficient bulk not to provide the flat look most FTM patients desire.
"Dog ear"
Occasionally the side limbs may be quite long, and the expression doctors use is "chasing a dog ear" into the axilla (or underarm). A dog ear is an unpleasant ruffle of skin in the corner of an incision when there is too much gathering usually at an angle greater than 30 degrees.[7] Using a curved incision can reduce the chances of dog ears developing because it requires less gathering of skin to be done, but some patients dislike the appearance of the curved scar as it can mimic the appearance of breasts.
Not uncommonly the surgeon will revise the incision lines after 3 or more months of settling shows some residual problem areas.
See also
- Subcutaneous tissue
- List of transgender-related topics
- Sex reassignment therapy
- Trans man
References
- Sangree, Colby (23 March 2017). "A Non-Binary Perspective On Top Surgery". HuffPost news. Retrieved 7 August 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - Waltho, Daniel; Hatchell, Alexandra; Thoma, Achilleas (2017). "Gynecomastia Classification for Surgical Management: A Systematic Review and Novel Classification System". Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 139 (3): 638e–648e. doi:10.1097/PRS.0000000000003059. ISSN 0032-1052. PMID 28234829. S2CID 8519689.
- Olson-Kennedy, Johanna; Warus, Jonathon (February 2017). "The Impact of Male Chest Reconstruction on Chest Dysphoria in Transmasculine Adolescents and Young Men; A Preliminary Study". Journal of Adolescent Health. 60 (2): S88. doi:10.1016/j.jadohealth.2016.10.354. ISSN 1054-139X.
- Head, Ally (2021-05-26). "Elliot Page just shared his first shirtless photo since top surgery and we're very here for it". Marie Claire. Retrieved 2022-06-02.
- "FTM Top Surgery and Sensation". TopSurgery.net. Retrieved 17 June 2016.
- "Gender Affirmation Washington DC | Male to Female Surgery". West End Plastic Surgery. Retrieved 2019-09-20.
- "What Are Dog Ears and How Can I Avoid Them?". TopSurgery.net. Retrieved 2019-09-20.