Mandibular nerve
In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve (ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only afferent fibers, the mandibular nerve contains both afferent and efferent fibers. These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication.[1]
| Mandibular nerve | |
|---|---|
 Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve. | |
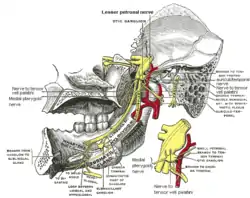 Mandibular division of trigeminal nerve, seen from the middle line. The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. | |
| Details | |
| From | Trigeminal nerve (CN V) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus mandibularis |
| MeSH | D008340 |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.064 |
| TA2 | 6246 |
| FMA | 52996 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
The large sensory root emerges from the lateral part of the trigeminal ganglion and exits the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale. Portio minor, the small motor root of the trigeminal nerve, passes under the trigeminal ganglion and through the foramen ovale to unite with the sensory root just outside the skull.[2]
The mandibular nerve immediately passes between tensor veli palatini, which is medial, and lateral pterygoid, which is lateral, and gives off a meningeal branch (nervus spinosus) and the nerve to medial pterygoid from its medial side. The nerve then divides into a small anterior and large posterior trunk.
The anterior division gives off branches to three major muscles of mastication and a buccal branch which is sensory to the cheek. The posterior division gives off three main sensory branches, the auriculotemporal, lingual and inferior alveolar nerves and motor fibres to supply mylohyoid and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle.
Branches
The mandibular nerve gives off the following branches:
- From the main trunk of the nerve (before the division)
- muscular branches, which are efferent nerves for the medial pterygoid, tensor tympani, and tensor veli palatini muscles (motor)[3]
- meningeal branch (a sensory nerve)
- From the anterior division
- masseteric nerve (motor)
- deep temporal nerves, anterior and posterior (motor)
- buccal nerve (a sensory nerve)
- lateral pterygoid nerve (motor)
- From the posterior division
- auriculotemporal nerve (a sensory nerve)
- lingual nerve (a sensory nerve)
- inferior alveolar nerve (which gives off a motor nerve and a sensory nerve)
- mental nerve (sensory branch) and the nerve to mylohyoid (motor branch)
Supplies
The mandibular nerve innervates:
Anterior Division:
(Motor Innervation - Muscles of mastication)
- Masseteric nerve
- Medial pterygoid nerve
- Tensor Veli Palatini Nerve
- nervous spinosus (sensory) from foramen spinosum
- Lateral pterygoid nerve
- Deep temporal nerve
(Sensory Innervation)
- Buccal nerve
- Inside of the Cheek (buccal mucosa)
Posterior Division
Lingual Split
(Sensory Innervation - NOT Taste)
- Anterior 2/3 of Tongue (mucous membrane)
Inferior Alveolar Split
(Motor Innervation)
(Sensory Innervation)
- Teeth and Mucoperiosteum of mandibular teeth
- Chin and Lower Lip
Auriculotemporal Split
Additional images
 Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve
Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve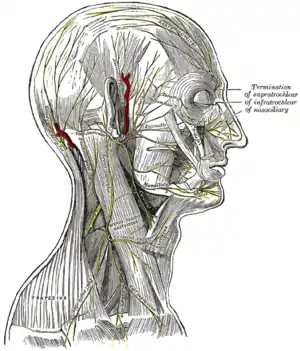 The nerves of the scalp, face, and side of neck.
The nerves of the scalp, face, and side of neck. Mandibular nerve
Mandibular nerve Mandibular nerve
Mandibular nerve
References
- Rodella, L.F.; Buffoli, B.; Labanca, M.; Rezzani, R. (April 2012). "A review of the mandibular and maxillary nerve supplies and their clinical relevance". Archives of Oral Biology. 57 (4): 323–334. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.09.007. ISSN 0003-9969.
- Burchiel, K J (November 1, 2003). "A New Classification for Facial Pain". Neurosurgery. 53 (5): 1164–1167. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000088806.11659.D8. PMID 14580284. S2CID 33538452.
- Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 181
External links
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb3.htm
- Anatomy figure: 27:03-02 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)