Meningeal lymphatic vessels
The meningeal lymphatic vessels (or meningeal lymphatics) are a network of conventional lymphatic vessels located parallel to the dural venous sinuses and middle meningeal arteries of the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). As a part of the lymphatic system, the meningeal lymphatics are responsible for draining immune cells, small molecules, and excess fluid from the CNS into the deep cervical lymph nodes.[1][2] Cerebrospinal fluid, and interstitial fluid are exchanged, and drained by the meningeal lymphatic vessels.[3]
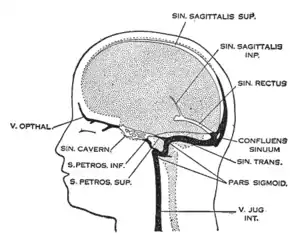
While it was historically believed that both the brain and meninges were devoid of lymphatic vasculature, recent studies by Antoine Louveau and Jonathan Kipnis at the University of Virginia, submitted in October 2014, and by Aleksanteri Aspelund, Salli Antila and Kari Alitalo at the University of Helsinki submitted in December 2014, identified and described the basic biology of the meningeal lymphatics using a combination of histological, live-imaging, and genetic tools.[1][2] In general, their work is thought to extend that of the Danish neuroscientist Maiken Nedergaard in identifying the pathway connecting the glymphatic system to the meningeal compartment.
The role that the meningeal lymphatics plays in neurological disease is yet to be explored. It is hypothesized that they may contribute to autoimmune and inflammatory diseases of the CNS due to their role in connecting the immune and nervous systems.
Background
In peripheral organs, lymphatic vessels are responsible for conducting lymph between different parts of the body. In general, lymphatic drainage is important for maintaining fluid homeostasis as well as providing a means for immune cells to traffic into draining lymph nodes from other parts of the body, allowing for immune surveillance of bodily tissues.
The first mention of meningeal lymphatic vessels can be attributed to Paolo Mascagni, whose anatomical work towards the end of the eighteenth century suggested their presence; however, this work received little attention or acceptance.[4][5] In 1953, Italian scientist Lecco identified putative lymphatic vessels in post-mortem human dura. Further research in the 1960s described the existence of meningeal lymphatics,[6] but these findings were not accepted by the field due to their limited methodology.[7]
Prior to the discovery of true meningeal lymphatic vessels, it was generally believed that the mammalian CNS did not contain a lymphatic system and thus relied upon alternative routes of waste clearance such as the glymphatic system,[8] a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) drainage pathway under the cribriform plate and into the lymphatics of the nasal mucosa,[9] and arachnoid granulations to clear itself of excess protein, fluid, and metabolic waste products. Furthermore, the presumed absence of CNS lymphatics was an important pillar in the long-held dogma that the CNS is an immune-privileged tissue to which immune cells have highly restricted access under normal physiological conditions.
Discovery
Although, several studies proposed the existence of lymphatic vessels in the dura mater, the presence of the meningeal lymphatic system was accepted in 2015, when two independent studies published by Louveau et al.[1] and Aspelund et al.[2] provided convincing data using novel methods. Louveau et al. noticed an unusual alignment of immune cells along the dural sinus using a meningeal whole-mount technique. Using lymphatic endothelial cell-specific markers and electron microscopy, the authors found that the immune cells were not inside blood vessels, but rather were organized inside lymphatic vessels within the meninges, a system of membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord.[1]
Aspelund et al. had discovered that in the eye, another immune-privileged organ, the Schlemm's canal is a lymphatic-like vessel.[10] As Schlemm's canal was previously considered to be a venous sinus, the authors subsequently hypothesized that similar vessels may also be found in the brain due to its similarly immune-privileged status.[2] However, a recent study reported the absence of lymphatic vessels in the spinal cord dura of rat despite harboring numerous LYVE1+ cells.[11]
In an interview with Ira Flatow on NPR's Science Friday, Kipnis described the meningeal lymphatics as "well-hidden" when asked how, unlike the rest of the lymphatic system, they had remained unmapped into the 21st century.[12] While many scientists study the brain parenchyma proper, Kipnis explained, his lab is relatively unique in studying the meninges:
We are among the few labs who are interested in this very unique area of the brain: the coverings of the brain - the so-called 'meninges.' We've been looking into this area for a few years now," Kipnis said. "I was lucky to have a phenomenal post-doctoral fellow in my lab, Dr. Antoine Louveau, who developed a very unique technique of mounting this entire covering as a whole-mount. I think this is what allowed us to find those vessels.[12]
Visualization
To visualize the dura mater using immunohistochemistry, the dura must first be fixed within the skullcap. It is prepared by cutting around the base of the skull (inferior to the post-tympanic hook) and removing the lower portion of the skull and brain. Following fixation, the dura can be dissected out of the skullcap as a single piece of tissue that can be utilized for histological analysis.[13]
In transgenic mice containing Prox1-GFP or Vegfr3-LacZ reporter genes, the lymphatic vessels may be visualized by fluorescent microscopy or after X-gal staining, respectively.[2]
The meningeal lymphatics may also be visualized non-invasively by MRI, using MRI contrast agents such as gadobutrol and gadofosveset to reveal the presence of the vessels near the dura mater.[14]
Biology
Anatomy and route of drainage
The meningeal lymphatic system is composed of a network of vessels along the dural sinus in the dura which express lymphatic endothelial cell marker proteins, including PROX1, LYVE1, and PDPN. The vessels extend along the length of both the superior sagittal and transverse sinuses and directly connects to the deep cervical lymph nodes.[1] These meningeal lymphatic vessels drain down and exit the skull along the dural venous sinuses and meningeal arteries. Meningeal lymphatic vessels also drain out of the skull alongside cranial nerves and through the cribriform plate. Molecular profiling indicates that the vessels are conventional lymphatic vessels: they express high levels of PROX1, LYVE1, PDPN and VEGFR3, but low levels of PECAM1. Meningeal lymphatic vessels absorb cerebrospinal fluid and drain into the deep cervical lymph nodes.[2]
Several unique attributes differentiate meningeal lymphatic vessels from lymphatic vessels in peripheral organs. Compared to peripheral lymphatic vessels, the meningeal lymphatic network is markedly less complex, with far less tissue coverage and lymphatic branching. Furthermore, meningeal lymphatic vessels are generally smaller than those in the periphery and display a structural homogeneity along the dural sinuses, remaining thinner and mostly unbranched along the superior sagittal sinus while growing larger and more branched along the transverse sinuses.[1] The meningeal lymphatic vessels are also unique for their scarcity of valves, which prevent back-flow of lymph. While the vessels in the superior parts of the skull were mostly devoid of valves, the larger lymphatic vessels of the basal parts only contain scattered valves.[2]
Development
Development of the dural lymphatic system requires expression of vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) and its receptor, VEGFR3 (which is the major signaling pathway for lymphatic growth).[15] Meningeal lymphatic vessels increase in diameter when exposed to recombinant VEGFC[1] and completely fail to develop when VEGFC and VEGFD signaling is inhibited during embryogenesis,[2] indicating that meningeal lymphatics share developmental characteristics with peripheral lymphatics. In addition to its role in the development of the dural lymphatics, VEGFR3 signaling is required for lymphatic vessel maintenance in the adult meninges.[15] Mechanical forces and shear stress generated by lymph flow are also required for later stages of meningeal lymphatic vessel formation and maturation.[16]
Physiological functions
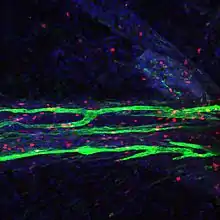
Like peripheral lymphatic vessels, the meningeal lymphatics serve both the tissue drainage and immune cell trafficking functions of the lymphatic system. Multiphoton live imaging experiments performed on anesthetized mice have demonstrated that the meningeal lymphatics are capable of draining fluorescent dyes injected intracisternally into the CSF, indicating that the meningeal lymphatics are capable of draining fluid from their surrounding environment. Histological analysis revealed that the meningeal lymphatics constitutively contain T cells, B cells, and MHC class II-expressing myeloid cells, demonstrating that meningeal lymphatic vessels are capable of carrying immune cells.[1]
Furthermore, tracing the outflow of compounds injected into the brain parenchyma have indicated that meningeal lymphatics function downstream of the glymphatic system. Genetically engineered mice which lack the meningeal lymphatic vessels demonstrated attenuated clearance of macromolecules from the brain. The uptake of tracers from the brain into deep cervical lymph nodes was completely abrogated. However, brain interstitial fluid pressure and water content were unaffected. These data suggested that meningeal lymphatic vessels are important for the clearance of macromolecules from the brain parenchyma, but in physiological settings the brain can compensate in solute clearance.[2]
Role in disease
The role that the meningeal lymphatics play in diseases of the nervous system is an area of active research, particularly for neurological disorders in which immunity is a fundamental player, such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Hennekam syndrome, and Prader-Willi syndrome. Impaired clearance of ISF waste has been associated with accelerated accumulation of toxic amyloid beta, the main component of amyloid plaques in AD.[7]
Significance
The paper by Jonathan Kipnis and his postdoctoral fellow Antoine Louveau was published in 2015 and by 2017, this paper had been cited more than 1200 times.[1]
The discovery of meningeal lymphatic vessels has attracted attention from many sources, and was touted as a scientific breakthrough in lists such as Scientific American's "Top 10 Science Stories of 2015", Science Magazine's "Breakthrough of the Year", Huffington Post's "Eight Fascinating Things We Learned About the Mind in 2015" and the National Institutes of Health's director Francis Collins's year end review.[17][18] In 2017, Business Insider highlighted this as the biggest discovery ever made in Virginia.[19] In 2019, the history of the brain lymphatic system was narrated by Stefano Sandrone et al in Nature Medicine.[5]
References
- Antoine Louveau, Igor Smirnov, Timothy J. Keyes, Jacob D. Eccles, Sherin J. Rouhani, J. David Peske, Noel C. Derecki, David Castle, James W. Mandell, Kevin S. Lee, Tajie H. Harris, Jonathan Kipnis. (2015). "Structural and functional features of central nervous system lymphatic vessels". Nature. 523 (7560): 337–41. Bibcode:2015Natur.523..337L. doi:10.1038/nature14432. PMC 4506234. PMID 26030524.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - Aleksanteri Aspelund, Salli Antila, Steven T. Proulx, Tine Veronica Karlsen, Sinem Karaman, Michael Detmar, Helge Wiig, Kari Alitalo. (2015). "A dural lymphatic vascular system that drains brain interstitial fluid and macromolecules". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 212 (7): 991–9. doi:10.1084/jem.20142290. PMC 4493418. PMID 26077718.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - Dupont, G; et al. (January 2019). "Our current understanding of the lymphatics of the brain and spinal cord". Clinical Anatomy. 32 (1): 117–121. doi:10.1002/ca.23308. PMID 30362622.
- Moreno-Zambrano, D; Santana, D; Avila, D; Santibáñez, Rocío (Apr 9, 2018). "Lymphatics of the Central Nervous System: Forgotten first descriptions. (S39.003)". Neurology. 90 (15).
- Sandrone, S; Moreno-Zambrano, D; Kipnis, J; van Gijn, J (April 2019). "A (delayed) history of the brain lymphatic system". Nature Medicine. 25 (4): 538–540. doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0417-3. PMID 30948855. S2CID 96434900.
- Földi, M.; Gellért, A.; Kozma, M.; Poberai, M.; Zoltán, O. T.; Csanda, E. (1966). "New contributions to the anatomical connections of the brain and the lymphatic system". Acta Anatomica. 64 (4): 498–505. doi:10.1159/000142849. ISSN 0001-5180. PMID 5957959.
- Da Mesquita S, Fu Z, Kipnis J (2018). "The Meningeal Lymphatic System: A New Player in Neurophysiology". Neuron. 100 (2): 375–388. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2018.09.022. PMC 6268162. PMID 30359603.
- Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, Benveniste H, Vates GE, Deane R, Goldman SA, Nagelhus EA, Nedergaard M (2012). "A Paravascular Pathway Facilitates CSF Flow Through the Brain Parenchyma and the Clearance of Interstitial Solutes, Including Amyloid β". Sci Trans Med. 4 (147): 147ra111. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.3003748. PMC 3551275. PMID 22896675.
- Cserr HF, Harling-Berg CJ, Knopf PM (1992). "Drainage of brain extracellular fluid into blood and deep cervical lymph and its immunological significance". Brain Pathol. 2 (4): 269–76. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.1992.tb00703.x. PMID 1341962. S2CID 45444024.
- Aleksanteri Aspelund, Tuomas Tammela, Salli Antila, Harri Nurmi, Veli-Matti Leppänen, Georgia Zarkada, Lukas Stanczuk, Mathias Francois, Taija Mäkinen, Pipsa Saharinen, Ilkka Immonen, Kari Alitalo. (2014). "The Schlemm's canal is a VEGF-C/VEGFR-3-responsive lymphatic-like vessel". The Journal of Clinical Investigation. 124 (9): 3975–86. doi:10.1172/JCI75395. PMC 4153703. PMID 25061878.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - Brezovakova, Veronika; Jadhav, Santosh (10 February 2020). "Identification of Lyve‐1 positive macrophages as resident cells in meninges of rats". Journal of Comparative Neurology. 528 (12): 2021–2032. doi:10.1002/cne.24870. PMID 32003471. S2CID 210984721.
- Lim, Alexa (5 June 2015). "A potential "missing link" between the brain and immune system". National Public Radio. Retrieved 24 June 2015.
- Antoine Louveau, Jonathan Kipnis. (2015). "Dissection and immunostaining of mouse whole-mount meninges". Protocol Exchange. doi:10.1038/protex.2015.047.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link) - Absinta M, Ha SK, Nair G, Sati P, Luciano NJ, Palisoc M, et al. (2017). "Human and nonhuman primate meninges harbor lymphatic vessels that can be visualized noninvasively by MRI". eLife. 6. doi:10.7554/eLife.29738. PMC 5626482. PMID 28971799.
- Antila, Salli; Karaman, Sinem; Nurmi, Harri; Airavaara, Mikko; Voutilainen, Merja H; Mathivet, Thomas; Chilov, Dmitri; Li, Zhilin; Koppinen, Tapani; Park, Jun-Hee; Fang, Shentong (2017-12-04). "Development and plasticity of meningeal lymphatic vessels". The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 214 (12): 3645–3667. doi:10.1084/jem.20170391. ISSN 1540-9538. PMC 5716035. PMID 29141865.
- Bálint, László; Ocskay, Zsombor; Deák, Bálint András; Aradi, Petra; Jakus, Zoltán (14 January 2020). "Lymph Flow Induces the Postnatal Formation of Mature and Functional Meningeal Lymphatic Vessels". Frontiers in Immunology. 10: 3043. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.03043. ISSN 1664-3224. PMC 6970982. PMID 31993056.
- "NIH, Scientific American, Science salute UVA brain discovery". Retrieved 22 December 2016.
- "Media coverage of our discoveries". Retrieved 22 December 2016.
- "The biggest scientific discoveries in every state". Business Insider. 2017-06-28.