Ommaya reservoir
An Ommaya reservoir is an intraventricular catheter system that can be used for the aspiration of cerebrospinal fluid or for the delivery of drugs (e.g. chemotherapy) into the cerebrospinal fluid. It consists of a catheter in one lateral ventricle attached to a reservoir implanted under the scalp. It is used to treat brain tumors, leukemia/lymphoma or leptomeningeal disease by intrathecal drug administration. In the palliative care of terminal cancer, an Ommaya reservoir can be inserted for intracerebroventricular injection (ICV) of morphine.[1]
| Ommaya reservoir | |
|---|---|
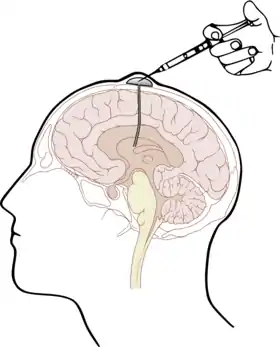 Schematic representation of an implanted Ommaya reservoir. | |
| Specialty | neurology |
It was originally invented in 1963 by Ayub K. Ommaya, a South-Asian-American neurosurgeon.
In January 2017, researchers at University of Texas Southwestern Medical Centre used an Ommaya reservoir to measure the intracranial pressure that is regularly observed in astronauts in zero-gravity conditions.[2][3][4]
References
- Leonidas C. Goudas et al.: Acute Decreases in Cerebrospinal Fluid Glutathione Levels after Intracerebroventricular Morphine for Cancer Pain, International Anesthesia Research Society 1999
- "Intracranial pressure could be key to tackling astronaut vision loss". newatlas.com. 2017-01-20. Retrieved 2017-09-21.
- "Under Pressure: Why Spaceflight Is So Hard on Astronauts' Eyes". Space.com. Retrieved 2017-09-21.
- "Why astronauts suffer from vision problems decoded". deccanchronicle.com/. 2017-01-18. Retrieved 2017-09-21.

