Padimate A
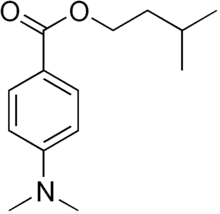
Padimate A is an organic compound that is an ingredient in some sunscreens. It is an ester derivative of PABA. This aromatic chemical absorbs ultraviolet rays thereby preventing sunburn. However, its chemical structure and behaviour is similar to an industrial free radical generator.[1] In Europe this chemical was withdrawn in 1989 for unstated reasons.[1] In the US it was never approved for use in sunscreens.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Methylbutyl 4-(dimethylamino)benzoate | |
| Other names
isoamyl dimethyl PABA Escalol 506, 4-dimethylaminobenzoic acid isopentyl ester | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.040.247 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C14H21NO2 |
| Molar mass | 235.322 |
| Melting point | <25 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Photobiology
The photobiological properties of padimate O and padimate A resemble that of Michler's ketone. These compounds have been shown to increase the lethal effects of UV-radiation on cells.[1] This photochemistry is relevant to the sunscreen controversy.
See also
- Padimate O, a related sunscreen ingredient
References
- Knowland, John; McKenzie, Edward A.; McHugh, Peter J.; Cridland, Nigel A. (1993). "Sunlight-induced mutagenicity of a common sunscreen ingredient". FEBS Letters. 324 (3): 309–313. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(93)80141-G. PMID 8405372. S2CID 23853321.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.