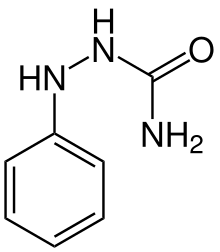
Phenicarbazide
Phenicarbazide is a semicarbazide and an antipyretic substance. It is carcinogenic in mice.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1-Phenylsemicarbazide; Kryogenin |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.794 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H9N3O |
| Molar mass | 151.169 g·mol−1 |
InChI
| |
| | |
Preparation
Phenicarbazide can be obtained by mixing phenylhydrazine with acetic acid in aqueous solution with the addition of potassium cyanide. It is also obtained from the reaction of phenylhydrazine with urea.[2]
Properties
Phenicarbazide is a flammable, hard to ignite, crystalline, beige solid that is practically insoluble in water. It decomposes on heating.[3]
Uses
Phenicarbazide is an intermediate in the syntheses of a series of chemical compounds by cyclocondensation reactions.[4] It was investigated as an analgesic and antipyretic in the 1970s and was used in combination preparations.
References
- "Phenicarbazide". International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) - Summaries & Evaluations. 25 March 1998.
- Bruchhausen F, Ebel S, Hackenthal E, Holzgrabe U, Albinus M, Amschler G, Angerer E (1999). Hagers Handbuch der Pharmazeutischen Praxis : Stoffe L-Z Folgeband 5 (5. vollständig neubearbeitete Auflage ed.). Berlin, Heidelberg. p. 420. ISBN 978-3-642-58388-9. OCLC 913646782.
- "Phenicarbazid". GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank. Retrieved 2022-10-18.
- "1-Phenylsemicarbazide". Sigma-Aldrich.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.