Rosaramicin
Rosaramicin (rosamicin) is an antibacterial substance that is chemically a lipid-soluble basic macrolide similar to erythromycin but with a better activity against Gram-negative bacteria.
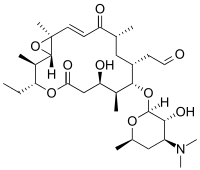 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
{(1S,2R,3R,7R,8S,9S,10R,12R,14E,16S)-3-Ethyl-7-hydroxy-2,8,12,16-tetramethyl-5,13-dioxo-9-[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-(dimethylamino)-β-D-xylo-hexopyranosyloxy]-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadec-14-en-10-yl}acetaldehyde | |
| Preferred IUPAC name
[(1S,2R,3R,7R,8S,9S,10R,12R,14E,16S)-9-{[(2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(Dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy}-3-ethyl-7-hydroxy-2,8,12,16-tetramethyl-5,13-dioxo-4,17-dioxabicyclo[14.1.0]heptadec-14-en-10-yl]acetaldehyde | |
| Other names
Rosamicin; Juvenimicin A3 | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.933 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C31H51NO9 |
| Molar mass | 581.747 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Experiments in dogs have shown that it is more concentrated in the prostate than erythromycin is, and thus may be better for treating infections of that organ.[1]
References
- Baumueller A, Kjaer TB, Madsen PO (September 1977). "Prostatic tissue and secretion concentrations of rosamicin and erythromycin. Experimental studies in the dog". Invest Urol. 15 (2): 158–60. PMID 903212.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.