Rudiger syndrome
Rudiger syndrome is a congenital disorder characterized by the association of severe growth retardation with abnormalities of the extremities, urogenital abnormalities and facial abnormalities.[1] It has been described in a family where an affected brother and sister died as infants.[2] Both autosomal recessive and autosomal dominant inheritance have been suggested with the disorder.[1][3]
| Rudiger syndrome | |
|---|---|
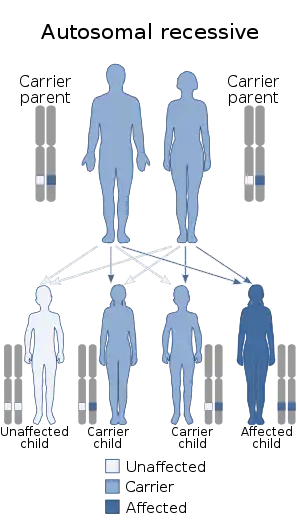 | |
| Rudiger syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner |
The features ectrodactyly, ectodermal dysplasia and cleft palate have been described with Rudiger syndrome, giving it the rarely used designation "EEC syndrome".[3] However, this is not to be confused with the formal EEC syndrome associated with chromosome 7.[4]
It was characterized in 1971.[5]
References
- "Orphanet: Rudiger syndrome". Retrieved August 2, 2010.
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 268650
- Schnitzler, L.; Schubert, B.; Larget-Piet, L.; Berthelot, J.; Cleirens, S.; Taviaux, D. (Feb 1978). "Rudiger (E. E. C.) syndrome: report of a case associated with atopic dermatitis (author's transl)". Annales de Dermatologie et de Vénéréologie. 105 (2): 201–206. PMID 677688.
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 129900
- Rüdiger RA, Schmidt W, Loose DA, Passarge E (December 1971). "Severe developmental failure with coarse facial features, distal limb hypoplasia, thickened palmar creases, bifid uvula, and ureteral stenosis: a previously unidentified familial disorder with lethal outcome". J. Pediatr. 79 (6): 977–81. doi:10.1016/S0022-3476(71)80193-2. PMID 5132310.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.