Saridegib
Saridegib, also known as IPI-926, is an experimental drug candidate undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of various types of cancer, including hard-to-treat hematologic malignancies such as myelofibrosis and ligand-dependent tumors such as chondrosarcoma.[1] IPI-926 exhibits its pharmacological effect by inhibition of the G protein-coupled receptor smoothened, a component of the hedgehog signaling pathway.[2] Chemically, it is a semi-synthetic derivative of the alkaloid cyclopamine. The process begins with cyclopamine extracted from harvested Veratrum californicum which is taken through a series of alterations resulting in an analogue of the natural product cyclopamine, making IPI-926 the only compound in development/testing that is not fully synthetic.[2]
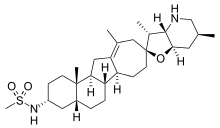 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
N-[(5βH)-5,6-Dihydro-17,23β-epoxy-16a-homoveratraman-3α-yl]methanesulfonamide | |
| Preferred IUPAC name
N-[(2S,3R,3′R,3aS,4′aR,6S,6′aR,6′bS,7aR,12′aS,12′bS)-3,6,11′,12′b-Tetramethyl-2′,3′,3a,4,4′,4′a,5,5′,6,6′,6′a,6′b,7,7′,7a,8′,10′,12′,12′a,12′b-icosahydro-1′H,3H-spiro[furo[3,2-b]pyridine-2,9′-naphtho[2,1-a]azulen]-3′-yl]methanesulfonamide | |
| Other names
saridegib | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C29H48N2O3S |
| Molar mass | 504.77 g·mol−1 |
| Pharmacology | |
| Oral | |
| Legal status |
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Saridegib is a member of a class of anti-cancer compounds known as hedgehog pathway inhibitors.
References
- "Pipeline: IPI-926". Infinity Pharmaceuticals. Archived from the original on 2012-01-19.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - Tremblay, MR; Lescarbeau, A; Grogan, MJ; Tan, E; Lin, G; Austad, BC; Yu, LC; Behnke, ML; et al. (2009). "Discovery of a potent and orally active hedgehog pathway antagonist (IPI-926)". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 52 (14): 4400–18. doi:10.1021/jm900305z. PMID 19522463.