Sinus arrhythmia
Sinus arrhythmia is a commonly encountered variation of normal sinus rhythm. Sinus arrhythmia characteristically presents with an irregular rate in which the variation in the R-R interval vary by more than 0.12 seconds (120 milliseconds). Additionally, P waves are typically mono-form and in a pattern consistent with atrial activation originating from the sinus node.[1]
| Sinus arrhythmia | |
|---|---|
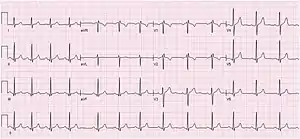 | |
| ECG of a 19-year-old female with sinus arrhythmia | |
| Specialty | Cardiology |
| Diagnostic method | electrocardiogram |
Respiratory sinus arrhythmia
During respiration, the intermittent vagus nerve activation occurs, which results in beat to beat variations in the resting heart rate. During inspiration vagal tone is slowed down and the heart rate goes up (being maximal at the peak of inspiration), while during expiration vagal tone is increased and heart rate decreases, being slowest at end-inspiration.[2][3]
When present, respiratory sinus arrhythmia typically indicates good cardiovascular health and is more commonly seen in young healthy people, especially those with enhanced vagal tone or slower heart rates.[4][3]
See also
References
- "Sinus Arrhythmia - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2022-08-28.
- Soos, Michael P.; McComb, David (2022), "Sinus Arrhythmia", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 30725696, retrieved 2022-08-28
- "Sinus Arrhythmia - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics". www.sciencedirect.com. Retrieved 2022-08-28.
- Soos, Michael P.; McComb, David (2020-08-24). "Sinus Arrhythmia". NCBI Bookshelf. PMID 30725696. Retrieved 17 November 2020.
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.