Zonule of Zinn
The zonule of Zinn (/ˈtsɪn/) (Zinn's membrane, ciliary zonule) (after Johann Gottfried Zinn) is a ring of fibrous strands forming a zonule (little band) that connects the ciliary body with the crystalline lens of the eye. These fibers are sometimes collectively referred to as the suspensory ligaments of the lens, as they act like suspensory ligaments.
| Zonule of Zinn | |
|---|---|
 Anatomy of the anterior part of the human eye. "Suspensory ligaments" are labeled at left. | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | zonula ciliaris |
| TA98 | A15.2.05.015 |
| TA2 | 6795 |
| FMA | 58838 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Development
The ciliary epithelial cells of the eye probably synthesize portions of the zonules.[1]
Anatomy
The zonule of Zinn is split into two layers: a thin layer, which lines the hyaloid fossa, and a thicker layer, which is a collection of zonular fibers. Together, the fibers are known as the suspensory ligament of the lens.[2] The zonules are about 1–2 μm in diameter.[3]
The zonules attach to the lens capsule 2 mm anterior and 1 mm posterior to the equator, and arise of the ciliary epithelium from the pars plana region as well as from the valleys between the ciliary processes in the pars plicata.[4][5]
When colour granules are displaced from the zonules of Zinn (by friction against the lens), the irises slowly fade. In some cases those colour granules clog the channels and lead to glaucoma pigmentosa.
The zonules are primarily made of fibrillin, a connective tissue protein.[1] Mutations in the fibrillin gene lead to the condition Marfan syndrome, and consequences include an increased risk of lens dislocation.[1]
Clinical appearance
The zonules of Zinn are difficult to visualize using a slit lamp, but may be seen with exceptional dilation of the pupil, or if a coloboma of the iris or a subluxation of the lens is present.[6] The number of zonules present in a person appears to decrease with age.[3] The zonules insert around the outer margin of the lens (equator), both anteriorly and posteriorly.[7]
Function
Securing the lens to the optical axis and transferring forces from the ciliary muscle in accommodation. When colour granules are displaced from the zonules of Zinn, caused by friction of the lens, the iris can slowly fade. These colour granules can clog the channels and lead to glaucoma pigmentosa.
Additional images
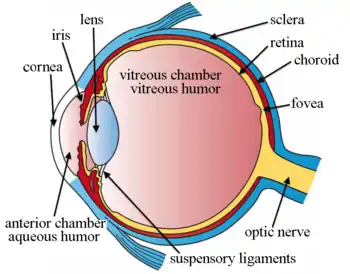 Structures of the eye labeled
Structures of the eye labeled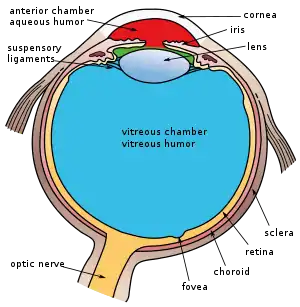 This image shows another labeled view of the structures of the eye
This image shows another labeled view of the structures of the eye
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1018 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1018 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Kaufman, Paul L.; Alm, Albert (2010). Adler's physiology of the eye (11th ed.). St. Louis, Mo: Mosby. pp. 145–146. ISBN 978-0-323-05714-1.
- "Vision - via the optic nerve (CN II)". Archived from the original on September 17, 2008. Retrieved January 12, 2008.
- Bornfeld, Norbert; Spitznas, Manfred; Breipohl, Winrich; Bijvank, Gerhard J. (1974). "Scanning electron microscopy of the zonule of Zinn". Albrecht von Graefes Archiv für Klinische und Experimentelle Ophthalmologie. 192 (2): 117–29. doi:10.1007/BF00410698. PMID 4548321. S2CID 23592537.
- Remington, Lee Ann (2012). Clinical anatomy and physiology of the visual system (3rd ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier/Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 97. ISBN 978-1437719260.
- "2020–2021 BCSC Basic and Clinical Science Course™". www.aao.org.
- McCulloch, C (1954). "The zonule of Zinn: Its origin, course, and insertion, and its relation to neighboring structures". Transactions of the American Ophthalmological Society. 52: 525–85. PMC 1312608. PMID 13274438.
- Farnsworth, P. N.; Mauriello, J. A.; Burke-Gadomski, P; Kulyk, T; Cinotti, A. A. (1976). "Surface ultrastructure of the human lens capsule and zonular attachments". Investigative Ophthalmology. 15 (1): 36–40. PMID 1245377.
External links
- Diagram at unmc.edu
- Diagram at eye-surgery-uk.com
- Diagram and overview at webschoolsolutions.com
- Histology image: 08011loa – Histology Learning System at Boston University
