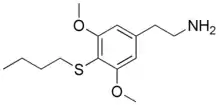
Thiobuscaline
Thiobuscaline, or 3,5-dimethoxy-4-butylthiophenethylamine, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug.[1]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-[4-(Butylsulfanyl)-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl]ethan-1-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C14H23NO2S |
| Molar mass | 269.403 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
History
It is an analog of buscaline.[1] Thiobuscaline was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin.[2] In his book PiHKAL (Phenethylamines i Have Known And Loved), the dosage range is listed as 60–120 mg, and the duration is listed as 8 hours.[3] Thiobuscaline is an entheogen, and it causes a threshold. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of thiobuscaline.
References
- The Neuropsychiatric Complications of Stimulant Abuse. Academic Press. 2015-06-05. ISBN 978-0-12-803003-5.
- Baumann, Michael H; Ayestas, Mario A; Partilla, John S; Sink, Jacqueline R; Shulgin, Alexander T; Daley, Paul F; Brandt, Simon D; Rothman, Richard B; Ruoho, Arnold E; Cozzi, Nicholas V (2011-04-12). "The Designer Methcathinone Analogs, Mephedrone and Methylone, are Substrates for Monoamine Transporters in Brain Tissue". Neuropsychopharmacology. 37 (5): 1192–1203. doi:10.1038/npp.2011.304. ISSN 0893-133X. PMC 3306880. PMID 22169943.
- Shulgin, Alexander T.; Shulgin, Ann (1991). PiHKAL: A Chemical Love Story (1st ed.). Berkeley, CA: Transform Press. ISBN 978-0-9630096-0-9. OL 22859055M.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.