Triazolopyridine
Triazolopyridines are a class of heterocyclic chemical compounds with a triazole ring fused to a pyridine ring. There are multiple isomers which differ by the location of the nitrogen atoms and the nature of the ring fusion.
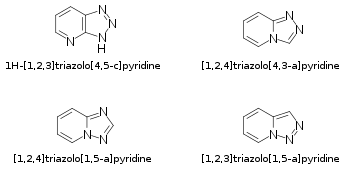
Chemical structures of selected examples of triazolopyridine isomers and their IUPAC names
The term triazolopyridine can also refer to a class of antidepressant drugs whose chemical structure includes a trazolopyridine-derived ring system.[1] One example is trazodone.[2]
Other pharmaceutical drugs that contain a triazolopyridine ring system include filgotinib, tucatinib, and enarodustat. In addition, the reagents used in organic chemistry HATU, HOAt, and PyAOP[3] are triazolopyridine derivatives.
References
- "Triazolopyridine antidepressant". dictionary.com.
- J P Feighner (1980). "Trazodone, a triazolopyridine derivative, in primary depressive disorder". J Clin Psychiatry. 41 (7): 250–255. PMID 6993447.
- Jacques Coste, Patrick Jouin (April 15, 2003). "(7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yloxy)tris(pyrrolidino)phosphonium Hexafluorophosphate". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00199.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.