Vaginal ultrasonography
Vaginal ultrasonography is a medical ultrasonography that applies an ultrasound transducer (or "probe") in the vagina to visualize organs within the pelvic cavity. It is also called transvaginal ultrasonography because the ultrasound waves go across the vaginal wall to study tissues beyond it.[1]
Device for both vaginal and abdominal ultrasonography.
Uses
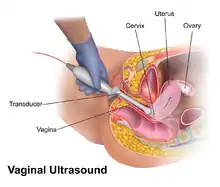
Transvaginal ultrasonography procedure
Vaginal ultrasonography is used both as a means of gynecologic ultrasonography and obstetric ultrasonography.
It is preferred over abdominal ultrasonography in the diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy.[2]
See also
References
- Kumari, Sah Reena; Pritha, Basnet; Tara, Manandhar; Yadav, Prakash Chand; Shah, Sujeet Kumar (2022-05-31). "Comparison of Transvaginal Ultrasonography and Hysteroscopy for Evaluation of Postmenopausal Bleeding: A Cross Sectional Study". doi:10.5281/zenodo.6600349.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - Kirk, E.; Bottomley, C.; Bourne, T. (2013). "Diagnosing ectopic pregnancy and current concepts in the management of pregnancy of unknown location". Human Reproduction Update. 20 (2): 250–61. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmt047. PMID 24101604.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.