Bloch's theorem
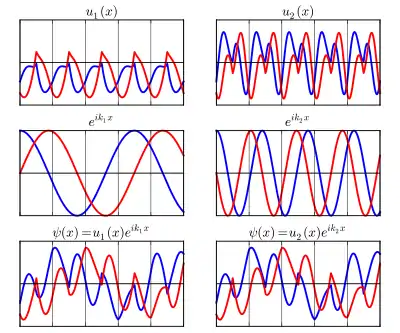
In condensed matter physics, Bloch's theorem states that solutions to the Schrödinger equation in a periodic potential take the form of a plane wave modulated by a periodic function. The theorem is named after the physicist Felix Bloch, who discovered the theorem in 1929.[1] Mathematically, they are written[2]
where is position, is the wave function, is a periodic function with the same periodicity as the crystal, the wave vector is the crystal momentum vector, is Euler's number, and is the imaginary unit.
Functions of this form are known as Bloch functions or Bloch states, and serve as a suitable basis for the wave functions or states of electrons in crystalline solids.
Named after Swiss physicist Felix Bloch, the description of electrons in terms of Bloch functions, termed Bloch electrons (or less often Bloch Waves), underlies the concept of electronic band structures.
These eigenstates are written with subscripts as , where is a discrete index, called the band index, which is present because there are many different wave functions with the same (each has a different periodic component ). Within a band (i.e., for fixed ), varies continuously with , as does its energy. Also, is unique only up to a constant reciprocal lattice vector , or, . Therefore, the wave vector can be restricted to the first Brillouin zone of the reciprocal lattice without loss of generality.
Applications and consequences
Applicability
The most common example of Bloch's theorem is describing electrons in a crystal, especially in characterizing the crystal's electronic properties, such as electronic band structure. However, a Bloch-wave description applies more generally to any wave-like phenomenon in a periodic medium. For example, a periodic dielectric structure in electromagnetism leads to photonic crystals, and a periodic acoustic medium leads to phononic crystals. It is generally treated in the various forms of the dynamical theory of diffraction.
Wave vector
Suppose an electron is in a Bloch state
where u is periodic with the same periodicity as the crystal lattice. The actual quantum state of the electron is entirely determined by , not k or u directly. This is important because k and u are not unique. Specifically, if can be written as above using k, it can also be written using (k + K), where K is any reciprocal lattice vector (see figure at right). Therefore, wave vectors that differ by a reciprocal lattice vector are equivalent, in the sense that they characterize the same set of Bloch states.
The first Brillouin zone is a restricted set of values of k with the property that no two of them are equivalent, yet every possible k is equivalent to one (and only one) vector in the first Brillouin zone. Therefore, if we restrict k to the first Brillouin zone, then every Bloch state has a unique k. Therefore, the first Brillouin zone is often used to depict all of the Bloch states without redundancy, for example in a band structure, and it is used for the same reason in many calculations.
When k is multiplied by the reduced Planck's constant, it equals the electron's crystal momentum. Related to this, the group velocity of an electron can be calculated based on how the energy of a Bloch state varies with k; for more details see crystal momentum.
Detailed example
For a detailed example in which the consequences of Bloch's theorem are worked out in a specific situation, see the article Particle in a one-dimensional lattice (periodic potential).
Bloch's theorem
Bloch's theorem is as follows:
For electrons in a perfect crystal, there is a basis of wave functions with the following two properties:
- Each of these wave functions is an energy eigenstate
- Each of these wave functions is a Bloch state, meaning that this wave function can be written in the form
where u has the same periodicity as the atomic structure of the crystal.
Preliminaries: Crystal symmetries, lattice, and reciprocal lattice
The defining property of a crystal is translational symmetry, which means that if the crystal is shifted an appropriate amount, it winds up with all its atoms in the same places. (A finite-size crystal cannot have perfect translational symmetry, but it is a useful approximation.)
A three-dimensional crystal has three primitive lattice vectors a1, a2, a3. If the crystal is shifted by any of these three vectors, or a combination of them of the form
where ni are three integers, then the atoms end up in the same set of locations as they started.
Another helpful ingredient in the proof is the reciprocal lattice vectors. These are three vectors b1, b2, b3 (with units of inverse length), with the property that ai · bi = 2π, but ai · bj = 0 when i ≠ j. (For the formula for bi, see reciprocal lattice vector.)
Lemma about translation operators
Let denote a translation operator that shifts every wave function by the amount n1a1 + n2a2 + n3a3 (as above, nj are integers). The following fact is helpful for the proof of Bloch's theorem:
Lemma — If a wave function is an eigenstate of all of the translation operators (simultaneously), then is a Bloch state.
Assume that we have a wave function which is an eigenstate of all the translation operators. As a special case of this,
for j = 1, 2, 3, where Cj are three numbers (the eigenvalues) which do not depend on r. It is helpful to write the numbers Cj in a different form, by choosing three numbers θ1, θ2, θ3 with e2πiθj = Cj:
Again, the θj are three numbers which do not depend on r. Define k = θ1b1 + θ2b2 + θ3b3, where bj are the reciprocal lattice vectors (see above). Finally, define
Then
This proves that u has the periodicity of the lattice. Since , that proves that the state is a Bloch state.
Proof
Finally, we are ready for the main proof of Bloch's theorem which is as follows.
As above, let denote a translation operator that shifts every wave function by the amount n1a1 + n2a2 + n3a3, where ni are integers. Because the crystal has translational symmetry, this operator commutes with the Hamiltonian operator. Moreover, every such translation operator commutes with every other. Therefore, there is a simultaneous eigenbasis of the Hamiltonian operator and every possible operator. This basis is what we are looking for. The wave functions in this basis are energy eigenstates (because they are eigenstates of the Hamiltonian), and they are also Bloch states (because they are eigenstates of the translation operators; see Lemma above).
Proof with operators[4]
We define the translation operator
We use the hypothesis of a mean periodic potential
and the independent electron approximation with an hamiltonian
Given the Hamiltonian is invariant for translations it shall commute with the translation operator
and the two operators shall have a common set of eigenfunctions. Therefore we start to look at the eigen-functions of the translation operator:
Given is an additive operator
If we substitute here the eigenvalue equation and dividing both sides for we have
This is true for
where
if we use the normalization condition over a single primitive cell of volume V
and therefore
and
where
Finally
Which is true for a Bloch wave i.e. for with
Group theory proof
All Translations are unitary and Abelian. Translations can be written in terms of unit vectors
We can think of these as commuting operators
The commutativity of the operators gives three commuting cyclic subgroups (given they can be generated by only one element) which are infinite, 1-dimensional and abelian. All irreducible representations of Abelian groups are one dimensional.[6]
Given they are one dimensional the matrix representation and the character are the same. The character is the representation over the complex numbers of the group or also the trace of the representation which in this case is a one dimensional matrix. All these subgroups, given they are cyclic, they have characters which are appropriate roots of unity. In fact they have one generator which shall obey to , and therefore the character . Note that this is straightforward in the finite cyclic group case but in the countable infinite case of the infinite cyclic group (i.e. the translation group here) there is a limit for where the character remains finite.
Given the character is a root of unity, for each subgroup the character can be then written as
If we introduce the Born–von Karman boundary condition on the potential:
where L is a macroscopic periodicity in the direction that can also be seen as a multiple of where
This substituting in the time independent Schrödinger equation with a simple effective Hamiltonian
induces a periodicity with the wave function:
And for each dimension a translation operator with a period L
From here we can see that also the character shall be invariant by a translation of :
and from the last equation we get for each dimension a periodic condition:
where is an integer and
The wave vector identify the irreducible representation in the same manner as , and is a macroscopic periodic length of the crystal in direction . In this context, the wave vector serves as a quantum number for the translation operator.
We can generalize this for 3 dimensions and the generic formula for the wave function becomes:
i.e. specializing it for a translation
and we have proven Bloch’s theorem.
Apart from the group theory technicalities this proof is interesting because it becomes clear how to generalize the Bloch theorem for groups that are not only translations.
This is typically done for Space groups which are a combination of a translation and a point group and it is used for computing the band structure, spectrum and specific heats of crystals given a specific crystal group symmetry like FCC or BCC and eventually an extra basis.[7][8]
In this proof it is also possible to notice how is key that the extra point group is driven by a symmetry in the effective potential but it shall commute with the Hamiltonian.
In the generalized version of the Bloch theorem, the Fourier transform, i.e. the wave function expansion, gets generalized from a discrete Fourier transform which is applicable only for cyclic groups and therefore translations into a character expansion of the wave function where the characters are given from the specific finite point group.
Also here is possible to see how the characters (as the invariants of the irreducible representations) can be treated as the fundamental building blocks instead of the irreducible representations themselves.[9]
Velocity and effective mass of Bloch electrons
If we apply the time-independent Schrödinger equation to the Bloch wave function we obtain
with boundary conditions
Given this is defined in a finite volume we expect an infinite family of eigenvalues; here is a parameter of the Hamiltonian and therefore we arrive at a "continuous family" of eigenvalues dependent on the continuous parameter and thus at the basic concept of an electronic band structure.
This shows how the effective momentum can be seen as composed of two parts,
a standard momentum and a crystal momentum . More precisely the crystal momentum is not a momentum but it stands for the momentum in the same way as the electromagnetic momentum in the minimal coupling, and as part of a canonical transformation of the momentum.
For the effective velocity we can derive
We evaluate the derivatives and given they are the coefficients of the following expansion in q where q is considered small with respect to k
Given are eigenvalues of We can consider the following perturbation problem in q:
Perturbation theory of the second order states that
To compute to linear order in q
where the integrations are over a primitive cell or the entire crystal, given if the integral
is normalized across the cell or the crystal.
We can simplify over q to obtain
and we can reinsert the complete wave functions
For the effective mass
The quantity on the right multiplied by a factor is called effective mass tensor [12] and we can use it to write a semi-classical equation for a charge carrier in a band[13]
where is an acceleration. This equation is analogous to the De Broglie wave type of approximation[14]
As an intuitive interpretation, both of the previous two equations resemble formally and are in a semi-classical analogy with the newton equation in an external Lorentz force.
History and related equations
The concept of the Bloch state was developed by Felix Bloch in 1928[15] to describe the conduction of electrons in crystalline solids. The same underlying mathematics, however, was also discovered independently several times: by George William Hill (1877),[16] Gaston Floquet (1883),[17] and Alexander Lyapunov (1892).[18] As a result, a variety of nomenclatures are common: applied to ordinary differential equations, it is called Floquet theory (or occasionally the Lyapunov–Floquet theorem). The general form of a one-dimensional periodic potential equation is Hill's equation:[19]
where f(t) is a periodic potential. Specific periodic one-dimensional equations include the Kronig–Penney model and Mathieu's equation.
Mathematically Bloch's theorem is interpreted in terms of unitary characters of a lattice group, and is applied to spectral geometry.[20][21][22]
A relevant new theory
Based on Bloch's theorem, the conventional theory of electronic states in crystals could not correctly explain genuine crystals' boundary and size effects. However, about half a century ago, the mathematical theory of periodic differential equations had some significant progress.[23] Based on those new mathematical understandings, a recent new theory of electronic states in low dimensional systems [24] [25] [26] aims to understand such effects. The new theory found that the size and boundary effects of electronic states in each specific dimension in the low-dimensional system are separated in some simple but essential cases. That is, the energies and properties of some electronic states (including but not limited to the surface states) depend only on the system boundary in that dimension. In contrast, the numbers, energies, and properties of other electronic states (they are stationary Bloch states, usually many times more) depend only on the system size in that dimension, see "A more general model: particle in a box with a period potential in Particle in a box."
There is a significant difference between the band structures of Bloch waves in one-dimensional and multi-dimensional space. The Schrödinger differential equation for a one-dimensional periodic potential is an ordinary differential equation that cannot have more than two linearly independent solutions; this leads to each permitted band and each band gap existing alternatively as the energy increases. Correspondingly, a theorem in the theory of ordinary periodic differential equations [23] limits that a boundary-dependent state is either in a band gap or at a band edge. On the other hand, the Schrödinger differential equation for a multi-dimensional periodic potential is a partial differential equation with no limitation to the number of independent solutions. As a result, the permitted bands in a multi-dimensional crystal are often overlapped. The number of band gaps in a multi-dimensional crystal is always finite. Furthermore, there are no band gaps if the potential is minimal. Correspondingly, a theorem in the theory of partial periodic differential equations [23] limits that the energy of a boundary-dependent state in a multi-dimensional crystal must be higher or equal to the upper band edge of the relevant permitted band without giving an upper limit. Therefore, a boundary-dependent state decaying in a specific direction can have energy in the range of a permitted band of the bulk. Theoretically, such cases are rather general in multi-dimensional crystals.
The very existence of the boundary-dependent states or sub-bands leads to the properties of electronic states in a simple low-dimensional system being substantially different from the properties of electronic states based on Bloch's theorem as in conventional solid-state physics. And also significantly different from what is widely believed in the solid-state physics community regarding the properties of electronic states in a low-dimensional system or finite crystal, such as ideas based on effective mass concepts. Since the energy of each boundary-dependent state is always higher than the energies of its relevant Bloch stationary states (see Particle in a box), the energy gap between occupied and vacant states in an ideal low-dimensional system of a cubic semiconductor is smaller than the band gap of the bulk semiconductor. An essential difference between a bulk metal and a bulk semiconductor would not be so clear when the size of the crystal becomes small enough, so the effects of the boundary-dependent electronic states become more significant. A low-dimensional system of a cubic semiconductor crystal could even have the electrical conductivity properties of metal.[25][26]
As a one-electron and non-spin theory, this new theory is more general than the conventional theory of electronic states in crystals based on Bloch's theorem and the well-known "Particle in a box" model in quantum mechanics: The new theory contains the physics cores that the each of the two classical theories has separately: That is, the former's potential periodicity and the latter's boundary and finite size.[25][26]
See also
- Bloch oscillations
- Bloch wave – MoM method
- Electronic band structure
- Nearly free electron model
- Periodic boundary conditions
- Symmetries in quantum mechanics
- Tight-binding model
- Wannier function
References
- Bloch, F. (1929). Über die quantenmechanik der elektronen in kristallgittern. Zeitschrift für physik, 52(7), 555-600.
- Kittel, Charles (1996). Introduction to Solid State Physics. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-14286-7.
- Ashcroft & Mermin 1976, p. 134
- Ashcroft & Mermin 1976, p. 137
- Dresselhaus 2002, pp. 345–348
- Roy 2010
- Dresselhaus 2002, pp. 365–367
- The vibrational spectrum and specific heat of a face centered cubic crystal, Robert B. Leighton
- Group Representations and Harmonic Analysis from Euler to Langlands, Part II
- Ashcroft & Mermin 1976, p. 140
- Ashcroft & Mermin 1976, p. 765 Appendix E
- Ashcroft & Mermin 1976, p. 228
- Ashcroft & Mermin 1976, p. 229
- Ashcroft & Mermin 1976, p. 227
- Felix Bloch (1928). "Über die Quantenmechanik der Elektronen in Kristallgittern". Zeitschrift für Physik (in German). 52 (7–8): 555–600. Bibcode:1929ZPhy...52..555B. doi:10.1007/BF01339455. S2CID 120668259.
- George William Hill (1886). "On the part of the motion of the lunar perigee which is a function of the mean motions of the sun and moon". Acta Math. 8: 1–36. doi:10.1007/BF02417081. This work was initially published and distributed privately in 1877.
- Gaston Floquet (1883). "Sur les équations différentielles linéaires à coefficients périodiques". Annales Scientifiques de l'École Normale Supérieure. 12: 47–88. doi:10.24033/asens.220.
- Alexander Mihailovich Lyapunov (1992). The General Problem of the Stability of Motion. London: Taylor and Francis. Translated by A. T. Fuller from Edouard Davaux's French translation (1907) of the original Russian dissertation (1892).
- Magnus, W; Winkler, S (2004). Hill's Equation. Courier Dover. p. 11. ISBN 0-486-49565-5.
- Kuchment, P.(1982), Floquet theory for partial differential equations, RUSS MATH SURV., 37,1-60
- Katsuda, A.; Sunada, T (1987). "Homology and closed geodesics in a compact Riemann surface". Amer. J. Math. 110 (1): 145–156. doi:10.2307/2374542. JSTOR 2374542.
- Kotani M; Sunada T. (2000). "Albanese maps and an off diagonal long time asymptotic for the heat kernel". Comm. Math. Phys. 209 (3): 633–670. Bibcode:2000CMaPh.209..633K. doi:10.1007/s002200050033. S2CID 121065949.
- Eastham, M.S.P. (1973). The Spectral Theory of Periodic Differential Equations. Edinburgh, Scottish Academic Press.
- Ren, Shang Yuan (2002). "Two Types of Electronic States in One-dimensional Crystals of Finite length". Annals of Physics(N.Y.). 301: 22–30. arXiv:cond-mat/0204211. Bibcode:2002AnPhy.301...22R. doi:10.1006/aphy.2002.6298. S2CID 14490431.
- Ren, Shang Yuan (2006). Electronic States in Crystals of Finite Size: Quantum Confinement of Bloch Waves. New York, Springer. Bibcode:2006escf.book.....R.
- Ren, Shang Yuan (2017). Electronic States in Crystals of Finite Size: Quantum Confinement of Bloch Waves (2 ed.). Singapore, Springer.
Further reading
- Ashcroft, Neil; Mermin, N. David (1976). Solid State Physics. New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston. ISBN 978-0-03-083993-1.
- Dresselhaus, M. S. (2002). "Applications of Group Theory to the Physics of Solids" (PDF). MIT. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 November 2019. Retrieved 12 September 2020.
- Dresselhaus, M. S. (2010). Group theory: application to the physics of condensed matter. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-3-642-06945-1. OCLC 692760083.
- H. Föll. "Periodic Potentials and Bloch's Theorem – lectures in "Semiconductors I"". The University of Kiel.
- M.S.P. Eastham (1973). The Spectral Theory of Periodic Differential Equations. Texts in Mathematics. Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press.
- J. Gazalet; S. Dupont; J.C. Kastelik; Q. Rolland & B. Djafari-Rouhani (2013). "A tutorial survey on waves propagating in periodic media: Electronic, photonic and phononic crystals. Perception of the Bloch theorem in both real and Fourier domains". Wave Motion. 50 (3): 619–654. doi:10.1016/j.wavemoti.2012.12.010.
- Roy, Ricky (May 2, 2010). "Representation Theory" (PDF). University of Puget Sound.