Bluetongue disease
Bluetongue disease is a noncontagious, insect-borne, viral disease of ruminants, mainly sheep and less frequently cattle,[1] yaks,[2] goats, buffalo, deer, dromedaries, and antelope. It is caused by Bluetongue virus (BTV). The virus is transmitted by the midges Culicoides imicola, Culicoides variipennis, and other culicoids.
| Bluetongue virus | |
|---|---|
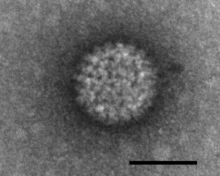 | |
| Electron micrograph of Bluetongue virus, cale bar = 50 nm | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Duplornaviricota |
| Class: | Resentoviricetes |
| Order: | Reovirales |
| Family: | Reoviridae |
| Genus: | Orbivirus |
| Species: | Bluetongue virus |
Signs


In sheep, BTV causes an acute disease with high morbidity and mortality. BTV also infects goats, cattle, and other domestic animals, as well as wild ruminants (for example, blesbuck, white-tailed deer, elk, and pronghorn antelope).[3]
Major signs are high fever, excessive salivation, swelling of the face and tongue, and cyanosis of the tongue. Swelling of the lips and tongue gives the tongue its typical blue appearance, though this sign is confined to a minority of the animals. Nasal signs may be prominent, with nasal discharge and stertorous respiration.
Some animals also develop foot lesions, beginning with coronitis, with consequent lameness. In sheep, this can lead to knee-walking. In cattle, constant changing of position of the feet gives bluetongue the nickname the dancing disease.[4] Torsion of the neck (opisthotonos or torticollis) is observed in severely affected animals.
Not all animals develop signs, but all those that do lose condition rapidly, and the sickest die within a week. For affected animals that do not die, recovery is very slow, lasting several months.
The incubation period is 5–20 days, and all signs usually develop within a month. The mortality rate is normally low, but it is high in susceptible breeds of sheep. In Africa, local breeds of sheep may have no mortality, but in imported breeds, it may be up to 90%.[5]
In cattle, goats, and wild ruminants, infection is usually asymptomatic despite high virus levels in blood. Red deer are an exception, and in them the disease may be as acute as in sheep.[6]
Microbiology
Bluetongue is caused by the pathogenic virus, Bluetongue virus (BTV),[3] of the genus Orbivirus, of the Reoviridae family. Twenty-six serotypes are now recognised for this virus.[7]
The virus particle consists of 10 strands of double-stranded RNA surrounded by two protein shells. Unlike other arboviruses, BTV lacks a lipid envelope. The particle has a diameter of 86 nm.[8] The structure of the 70 nm core was determined in 1998 and was at the time the largest atomic structure to be solved.[9]
The two outer capsid proteins, VP2 and VP5, mediate attachment and penetration of BTV into the target cell. The virus makes initial contact with the cell with VP2, triggering receptor-mediated endocytosis of the virus. The low pH within the endosome then triggers BTV's membrane penetration protein VP5 to undergo a conformational change that disrupts the endosomal membrane.[8] Uncoating yields a transcriptionally active 470S core particle which is composed of two major proteins VP7 and VP3, and the three minor proteins VP1, VP4 and VP6 in addition to the dsRNA genome. There is no evidence that any trace of the outer capsid remains associated with these cores, as has been described for reovirus. The cores may be further uncoated to form 390S subcore particles that lack VP7, also in contrast to reovirus. Subviral particles are probably akin to cores derived in vitro from virions by physical or proteolytic treatments that remove the outer capsid and causes activation of the BTV transcriptase. In addition to the seven structural proteins, three non-structural (NS) proteins, NS1, NS2, NS3 (and a related NS3A) are synthesised in BTV-infected cells. Of these, NS3/NS3A is involved in the egress of the progeny virus. The two remaining non-structural proteins, NS1 and NS2, are produced at high levels in the cytoplasm and are believed to be involved in virus replication, assembly and morphogenesis.[3]
Epidemiology

Bluetongue has been observed in Australia, the US, Africa, the Middle East, Asia, and Europe. An outline of the transmission cycle of BTV is illustrated in article Parasitic flies of domestic animals.
Its occurrence is seasonal in the affected Mediterranean countries, subsiding when temperatures drop and hard frosts kill the adult midge vectors.[10] Viral survival and vector longevity is seen during milder winters.[11] A significant contribution to the northward spread of bluetongue disease has been the ability of C. obsoletus and C.pulicaris to acquire and transmit the pathogen, both of which are spread widely throughout Europe. This is in contrast to the original C.imicola vector, which is limited to North Africa and the Mediterranean. The relatively recent novel vector has facilitated a far more rapid spread than the simple expansion of habitats north through global warming.[12]
In August 2006, cases of bluetongue were found in the Netherlands, then Belgium, Germany, and Luxembourg.[13][14] In 2007, the first case of bluetongue in the Czech Republic was detected in one bull near Cheb at the Czech-German border.[15] In September 2007, the UK reported its first ever suspected case of the disease, in a Highland cow on a rare-breeds farm near Ipswich, Suffolk.[16] Since then, the virus has spread from cattle to sheep in Britain.[17] By October 2007, bluetongue had become a serious threat in Scandinavia and Switzerland[18] and the first outbreak in Denmark was reported.[19] In autumn 2008, several cases were reported in the southern Swedish provinces of Småland, Halland, and Skåne,[20] as well as in areas of the Netherlands bordering Germany, prompting veterinary authorities in Germany to intensify controls.[21] Norway had its first finding in February 2009, when cows at two farms in Vest-Agder in the south of Norway showed an immune response to bluetongue.[22] Norway have since been declared free of the disease in 2011.
Although the disease is not a threat to humans, the most vulnerable common domestic ruminants in the UK are cattle, goats, and especially, sheep.
Overwintering
A puzzling aspect of BTV is its survival between midge seasons in temperate regions. Adults of Culicoides are killed by cold winter temperatures, and BTV infections typically do not last for more than 60 days, which is not long enough for BTV to last until the next spring. It is believed that the virus somehow survives in overwintering midges or animals. Multiple mechanisms have been proposed. A few adult Culicoides midges infected with BTV may survive the mild winters of the temperate zone. Some midges may even move indoors to avoid the cold temperature of the winter. Additionally, BTV could cause a chronic or latent infection in some animals, providing another means for BTV to survive the winter. BTV can also be transmitted from mother to fetus. The outcome is abortion or stillbirth if fetal infection occurs early in gestation and survival if infection occurs late. However infection at an intermediate stage, before the fetal immune system is fully developed, may result in a chronic infection that lingers until the first months after birth of the lamb. Midges then spread the pathogen from the calves to other animals, starting a new season of infection.[23]
Treatment and prevention
Prevention is effected via quarantine, inoculation with live modified virus vaccine, and control of the midge vector, including inspection of aircraft.
Vaccines
Protection by live attenuated vaccines (LAVs) are serotype specific. Multiserotype LAV cocktails can induce neutralizing antibodies against unincluded serotypes, and subsequent vaccinations with three different pentavalent LAV cocktails induce broad protection. These pentavalent cocktails contain 15 different serotypes in total: serotypes 1 through 14, as well as 19.[24]
Immunization with any of the available vaccines, though, precludes later serological monitoring of affected cattle populations, a problem that could be resolved using next-generation subunit vaccines.[25]
In January 2015, Indian researchers launched a vaccine named Raksha Blu that is designed to protect livestock against five strains of the bluetongue virus prevalent in the country.[26]
History
Although bluetongue disease was already recognized in South Africa in the early 19th century, a comprehensive description of the disease was not published until the first decade of the 20th century.[27] In 1906, Arnold Theiler showed that bluetongue was caused by a filterable agent. He also created the first bluetongue vaccine, which was developed from an attenuated BT[28] V strain.[29] For many decades, bluetongue was thought to be confined to Africa. The first confirmed outbreak outside of Africa occurred in Cyprus in 1943.[27] Recently, a vessel owned by Khalifeh Livestock Trading and managed by Talia Shipping Line, both based in Lebanon, has been denied right to dock in Spain, as it has about 895 male calves suspected to be infected by bluetongue disease.[28][30]
Related diseases
African horse sickness is related to bluetongue and is spread by the same midges (Culicoides species). It can kill the horses it infects and mortality may go as high as 90% of the infected horses during an epidemic.[31]
Epizootic hemorrhagic disease virus is closely related and crossreacts with Bluetongue virus on many blood tests.
References
- "Q&A: Bluetongue disease". BBC. 2008-09-17. Retrieved 2010-01-01.
- Mauroy; et al. (2008). "Bluetongue in Captive Yaks". Emerging Infectious Diseases. 14 (4): 675–76. doi:10.3201/eid1404.071416. PMC 2570917. PMID 18394296.
- Roy P (2008). "Molecular Dissection of Bluetongue Virus". Animal Viruses: Molecular Biology. Caister Academic Press. pp. 305–54. ISBN 978-1-904455-22-6.
- McGrath, Matt (29 September 2007). "'Dancing' disease set for long run". BBC News. Retrieved 2008-10-24.
- Handbook of Animal Diseases in the Tropics, 1976. ISBN 0-901028-10-X
- Jensen, R. and Swift, B.L. Diseases of Sheep, Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, 1982. ISBN 0-8121-0836-1
- Maan S, Maan NS, Nomikou K, Veronesi E, Bachanek-Bankowska K, Belaganahalli MN, Attoui H, Mertens PP (2011). "Complete genome characterisation of a novel 26th bluetongue virus serotype from Kuwait". PLOS ONE. 6 (10): e26147. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...626147M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0026147. PMC 3198726. PMID 22031822.
- Roy P (2008). "Functional mapping of bluetongue virus proteins and their interactions with host proteins during virus replication". Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics. 50 (3): 143–57. doi:10.1007/s12013-008-9009-4. PMID 18299997. S2CID 984334.
- Rossmann MG, Tao Y (March 1999). "Courageous science: structural studies of bluetongue virus core". Structure. 7 (3): R43–R46. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(99)80031-8. PMID 10368304.
- Purse, Bethan V.; Mellor, Philip S.; Rogers, David J.; Samuel, Alan R.; Mertens, Peter P. C.; Baylis, Matthew (February 2005). "Climate change and the recent emergence of bluetongue in Europe". Nature Reviews Microbiology. 3 (2): 171–81. doi:10.1038/nrmicro1090. PMID 15685226. S2CID 62802662.
- "Bluetongue – Europe (51)". International Society for Infectious Diseases. 2007-10-30. Archived from the original on December 26, 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-31.
- Baylis, M.; Caminade, C.; Turner, J.; Jones, A.E. (2017-08-01). "The role of climate change in a developing threat: the case of bluetongue in Europe: -EN- -FR- L'influence du changement climatique dans les menaces sanitaires évolutives : l'exemple de la fièvre catarrhale ovine en Europe -ES- La influencia del cambio climático en una amenaza creciente: el caso de la lengua azul en Europa". Revue Scientifique et Technique (International Office of Epizootics). 36 (2): 467–78. doi:10.20506/rst.36.2.2667. ISSN 0253-1933. PMID 30152470.
- "Blue Tongue confirmed in Belgium and Germany" (Press release). European Commission. 2006-08-21. Retrieved 2006-08-21.
- "Lethal horse disease knocking on Europe's door" (Press release). Horsetalk.co.nz. 2007-03-28. Retrieved 2007-03-27.
- "Bluetongue dobývá Evropskou unii". Agroweb. 2008-02-19. Archived from the original on 2009-03-06. Retrieved 2008-05-29.
- "Bluetongue disease detected in UK". BBC News Online. 2007-09-22. Retrieved 2007-09-22.
- Gray, Richard (2007-10-14). "Bluetongue spreads from cattle to sheep". London: Telegraph.co.uk. Retrieved 2007-10-15.
- "Bluetongue – Europe (50)". International Society for Infectious Diseases. 2007-10-30. Archived from the original on December 26, 2007. Retrieved 2007-10-31.
- "Bluetongue outbreak detected in Denmark – EU", Reuters, 13 October 2007.
- "Blue tongue outbreak spreads south". Thelocal.se. 2008-09-24. Retrieved 2008-09-24.
- Mehlhorn, Heinz; Walldorf, Volker; Klimpel, Sven; Schaub, Günter; Kiel, Ellen; Focke, René; Liebisch, Gabriele; Liebisch, Arndt; Werner, Doreen; Bauer, Christian; Clausen, Henning (2009). "Bluetongue disease in Germany (2007–2008): monitoring of entomological aspects". Parasitology Research. 105 (2): 313–19. doi:10.1007/s00436-009-1416-y. ISSN 1432-1955. PMID 19322587. S2CID 35616241.
- Veterinærinstituttet informs about the outbreak in Vest-Agder Archived 2009-03-06 at the Wayback Machine, Norway National Veterinary Institute, 20 February 2009.
- Wilson A, Darpel K, Mellor PS (August 2008). "Where does bluetongue virus sleep in the winter?". PLOS Biology. 6 (8): e210. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060210. PMC 2525685. PMID 18752350.
- van Rijn, Piet A. (2019-11-21). "Prospects of Next-Generation Vaccines for Bluetongue". Frontiers in Veterinary Science. 6: 407. doi:10.3389/fvets.2019.00407. ISSN 2297-1769. PMC 6881303. PMID 31824966.
- Anderson J, Hägglund S, Bréard E, Comtet L, Lövgren Bengtsson K, Pringle J, Zientara S, Valarcher JF (2013). "Evaluation of the immunogenicity of an experimental DIVA subunit vaccine against Bluetongue virus serotype 8 in cattle". Clinical and Vaccine Immunology. 20 (8): 1115–22. doi:10.1128/CVI.00229-13. PMC 3754508. PMID 23720365.
- Staff Reporter (2015-01-08). "Vaccine for bluetongue disease launched". The Hindu.
- Mertens, Peter (2009). Bluetongue (Biology of Animal Infections) (1 ed.). Academic Press. pp. 7–21. ISBN 978-0123693686.
- Kevany, Sophie (2021-02-25). "Cattle stranded at sea 'face immediate slaughter' if ship docks in Spain, says manager". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 2021-02-28.
- Maclachlan NJ (November 2011). "Bluetongue: history, global epidemiology, and pathogenesis". Preventive Veterinary Medicine. 102 (2): 107–11. doi:10.1016/j.prevetmed.2011.04.005. PMID 21570141.
- Cattle stranded on ship in Spain must be destroyed, say vets amp.theguardian.com, accessed 26 July 2022
- African Horse Sickness – Clinical Findings and Lesions, The Merck Veterinary Manual.
External links
- Introduction to disease in The Merck Veterinary Manual
- Current status of Bluetongue worldwide at World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE). WAHID Interface – OIE World Animal Health Information Database
- Disease card
- UK government page from Defra
- Bluetongue page on warmwell.com
- Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA) Animal Disease Information
- Takamatsu, H; Mellor, PS; Mertens, PP; Kirkham, PA; Burroughs, JN; Parkhouse, RM (January 2003). "A possible overwintering mechanism for bluetongue virus in the absence of the insect vector". The Journal of General Virology. 84 (Pt 1): 227–35. doi:10.1099/vir.0.18705-0. PMID 12533719.

- News and announcements on the Bluetongue outbreak in the UK, Farmers Guardian