Cellular network
A cellular network or mobile network is a communication network where the link to and from end nodes is wireless. The network is distributed over land areas called "cells", each served by at least one fixed-location transceiver (typically three cell sites or base transceiver stations). These base stations provide the cell with the network coverage which can be used for transmission of voice, data, and other types of content. A cell typically uses a different set of frequencies from neighboring cells, to avoid interference and provide guaranteed service quality within each cell.[1]


| Part of a series on |
| Antennas |
|---|
 |
When joined together, these cells provide radio coverage over a wide geographic area. This enables numerous portable transceivers (e.g., mobile phones, tablets and laptops equipped with mobile broadband modems, pagers, etc.) to communicate with each other and with fixed transceivers and telephones anywhere in the network, via base stations, even if some of the transceivers are moving through more than one cell during transmission.
Cellular networks offer a number of desirable features:[1]
- More capacity than a single large transmitter, since the same frequency can be used for multiple links as long as they are in different cells
- Mobile devices use less power than with a single transmitter or satellite since the cell towers are closer[2]
- Larger coverage area than a single terrestrial transmitter, since additional cell towers can be added indefinitely and are not limited by the horizon
- Capability of utilizing higher frequency signals (and thus more available bandwidth / faster data rates) that are not able to propagate at long distances
- With data compression and multiplexing, several video (including digital video) and audio channels may travel through a higher frequency signal on a single wideband carrier
Major telecommunications providers have deployed voice and data cellular networks over most of the inhabited land area of Earth. This allows mobile phones and mobile computing devices to be connected to the public switched telephone network and public Internet access. Private cellular networks can be used for research[3] or for large organizations and fleets, such as dispatch for local public safety agencies or a taxicab company.[2]
Concept

In a cellular radio system, a land area to be supplied with radio service is divided into cells in a pattern dependent on terrain and reception characteristics. These cell patterns roughly take the form of regular shapes, such as hexagons, squares, or circles although hexagonal cells are conventional. Each of these cells is assigned with multiple frequencies (f1 – f6) which have corresponding radio base stations. The group of frequencies can be reused in other cells, provided that the same frequencies are not reused in adjacent cells, which would cause co-channel interference.
The increased capacity in a cellular network, compared with a network with a single transmitter, comes from the mobile communication switching system developed by Amos Joel of Bell Labs[4] that permitted multiple callers in a given area to use the same frequency by switching calls to the nearest available cellular tower having that frequency available. This strategy is viable because a given radio frequency can be reused in a different area for an unrelated transmission. In contrast, a single transmitter can only handle one transmission for a given frequency. Inevitably, there is some level of interference from the signal from the other cells which use the same frequency. Consequently, there must be at least one cell gap between cells which reuse the same frequency in a standard frequency-division multiple access (FDMA) system.
Consider the case of a taxi company, where each radio has a manually operated channel selector knob to tune to different frequencies. As drivers move around, they change from channel to channel. The drivers are aware of which frequency approximately covers some area. When they do not receive a signal from the transmitter, they try other channels until finding one that works. The taxi drivers only speak one at a time when invited by the base station operator. This is a form of time-division multiple access (TDMA).
History
The first commercial cellular network, the 1G generation, was launched in Japan by Nippon Telegraph and Telephone (NTT) in 1979, initially in the metropolitan area of Tokyo. Within five years, the NTT network had been expanded to cover the whole population of Japan and became the first nationwide 1G network. It was an analog wireless network. The Bell System had developed cellular technology since 1947, and had cellular networks in operation in Chicago and Dallas prior to 1979, but commercial service was delayed by the breakup of the Bell System, with cellular assets transferred to the Regional Bell Operating Companies.
The wireless revolution began in the early 1990s,[5][6][7] leading to the transition from analog to digital networks.[8] This was enabled by advances in MOSFET technology. The MOSFET, originally invented by Mohamed M. Atalla and Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs in 1959,[9][10] was adapted for cellular networks by the early 1990s, with the wide adoption of power MOSFET, LDMOS (RF amplifier), and RF CMOS (RF circuit) devices leading to the development and proliferation of digital wireless mobile networks.[8][11][12]
The first commercial digital cellular network, the 2G generation, was launched in 1991. This sparked competition in the sector as the new operators challenged the incumbent 1G analog network operators.
Cell signal encoding
To distinguish signals from several different transmitters, frequency-division multiple access (FDMA, used by analog and D-AMPS systems), time-division multiple access (TDMA, used by GSM) and code-division multiple access (CDMA, first used for PCS, and the basis of 3G) were developed.[1]
With FDMA, the transmitting and receiving frequencies used by different users in each cell are different from each other. Each cellular call was assigned a pair of frequencies (one for base to mobile, the other for mobile to base) to provide full-duplex operation. The original AMPS systems had 666 channel pairs, 333 each for the CLEC "A" system and ILEC "B" system. The number of channels was expanded to 416 pairs per carrier, but ultimately the number of RF channels limits the number of calls that a cell site could handle. Note that FDMA is a familiar technology to telephone companies, that used frequency-division multiplexing to add channels to their point-to-point wireline plants before time-division multiplexing rendered FDM obsolete.
With TDMA, the transmitting and receiving time slots used by different users in each cell are different from each other. TDMA typically uses digital signaling to store and forward bursts of voice data that are fit into time slices for transmission, and expanded at the receiving end to produce a somewhat normal-sounding voice at the receiver. TDMA must introduce latency (time delay) into the audio signal. As long as the latency time is short enough that the delayed audio is not heard as an echo, it is not problematic. Note that TDMA is a familiar technology for telephone companies, that used time-division multiplexing to add channels to their point-to-point wireline plants before packet switching rendered FDM obsolete.
The principle of CDMA is based on spread spectrum technology developed for military use during World War II and improved during the Cold War into direct-sequence spread spectrum that was used for early CDMA cellular systems and Wi-Fi. DSSS allows multiple simultaneous phone conversations to take place on a single wideband RF channel, without needing to channelize them in time or frequency. Although more sophisticated than older multiple access schemes (and unfamiliar to legacy telephone companies because it was not developed by Bell Labs), CDMA has scaled well to become the basis for 3G cellular radio systems.
Other available methods of multiplexing such as MIMO, a more sophisticated version of antenna diversity, combined with active beamforming provides much greater spatial multiplexing ability compared to original AMPS cells, that typically only addressed one to three unique spaces. Massive MIMO deployment allows much greater channel re-use, thus increasing the number of subscribers per cell site, greater data throughput per user, or some combination thereof. Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) modems offer an increasing number of bits per symbol, allowing more users per megahertz of bandwidth (and decibels of SNR), greater data throughput per user, or some combination thereof.
Frequency reuse
The key characteristic of a cellular network is the ability to re-use frequencies to increase both coverage and capacity. As described above, adjacent cells must use different frequencies, however, there is no problem with two cells sufficiently far apart operating on the same frequency, provided the masts and cellular network users' equipment do not transmit with too much power.[1]
The elements that determine frequency reuse are the reuse distance and the reuse factor. The reuse distance, D is calculated as
- ,
where R is the cell radius and N is the number of cells per cluster. Cells may vary in radius from 1 to 30 kilometres (0.62 to 18.64 mi). The boundaries of the cells can also overlap between adjacent cells and large cells can be divided into smaller cells.[13]
The frequency reuse factor is the rate at which the same frequency can be used in the network. It is 1/K (or K according to some books) where K is the number of cells which cannot use the same frequencies for transmission. Common values for the frequency reuse factor are 1/3, 1/4, 1/7, 1/9 and 1/12 (or 3, 4, 7, 9 and 12 depending on notation).[14]
In case of N sector antennas on the same base station site, each with different direction, the base station site can serve N different sectors. N is typically 3. A reuse pattern of N/K denotes a further division in frequency among N sector antennas per site. Some current and historical reuse patterns are 3/7 (North American AMPS), 6/4 (Motorola NAMPS), and 3/4 (GSM).
If the total available bandwidth is B, each cell can only use a number of frequency channels corresponding to a bandwidth of B/K, and each sector can use a bandwidth of B/NK.
Code-division multiple access-based systems use a wider frequency band to achieve the same rate of transmission as FDMA, but this is compensated for by the ability to use a frequency reuse factor of 1, for example using a reuse pattern of 1/1. In other words, adjacent base station sites use the same frequencies, and the different base stations and users are separated by codes rather than frequencies. While N is shown as 1 in this example, that does not mean the CDMA cell has only one sector, but rather that the entire cell bandwidth is also available to each sector individually.
Recently also orthogonal frequency-division multiple access based systems such as LTE are being deployed with a frequency reuse of 1. Since such systems do not spread the signal across the frequency band, inter-cell radio resource management is important to coordinate resource allocation between different cell sites and to limit the inter-cell interference. There are various means of inter-cell interference coordination (ICIC) already defined in the standard.[15] Coordinated scheduling, multi-site MIMO or multi-site beamforming are other examples for inter-cell radio resource management that might be standardized in the future.
Directional antennas
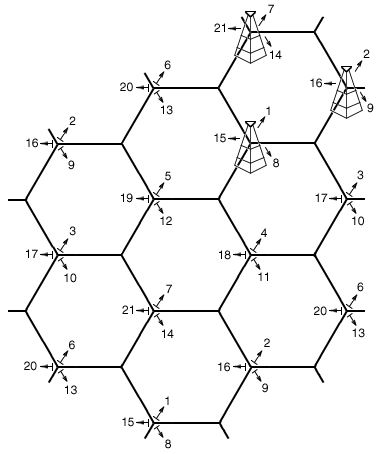
Cell towers frequently use a directional signal to improve reception in higher-traffic areas. In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) limits omnidirectional cell tower signals to 100 watts of power. If the tower has directional antennas, the FCC allows the cell operator to emit up to 500 watts of effective radiated power (ERP).[16]
Although the original cell towers created an even, omnidirectional signal, were at the centers of the cells and were omnidirectional, a cellular map can be redrawn with the cellular telephone towers located at the corners of the hexagons where three cells converge.[17] Each tower has three sets of directional antennas aimed in three different directions with 120 degrees for each cell (totaling 360 degrees) and receiving/transmitting into three different cells at different frequencies. This provides a minimum of three channels, and three towers for each cell and greatly increases the chances of receiving a usable signal from at least one direction.
The numbers in the illustration are channel numbers, which repeat every 3 cells. Large cells can be subdivided into smaller cells for high volume areas.[18]
Cell phone companies also use this directional signal to improve reception along highways and inside buildings like stadiums and arenas.[16]
Broadcast messages and paging
Practically every cellular system has some kind of broadcast mechanism. This can be used directly for distributing information to multiple mobiles. Commonly, for example in mobile telephony systems, the most important use of broadcast information is to set up channels for one-to-one communication between the mobile transceiver and the base station. This is called paging. The three different paging procedures generally adopted are sequential, parallel and selective paging.
The details of the process of paging vary somewhat from network to network, but normally we know a limited number of cells where the phone is located (this group of cells is called a Location Area in the GSM or UMTS system, or Routing Area if a data packet session is involved; in LTE, cells are grouped into Tracking Areas). Paging takes place by sending the broadcast message to all of those cells. Paging messages can be used for information transfer. This happens in pagers, in CDMA systems for sending SMS messages, and in the UMTS system where it allows for low downlink latency in packet-based connections.
Movement from cell to cell and handing over
In a primitive taxi system, when the taxi moved away from a first tower and closer to a second tower, the taxi driver manually switched from one frequency to another as needed. If communication was interrupted due to a loss of a signal, the taxi driver asked the base station operator to repeat the message on a different frequency.
In a cellular system, as the distributed mobile transceivers move from cell to cell during an ongoing continuous communication, switching from one cell frequency to a different cell frequency is done electronically without interruption and without a base station operator or manual switching. This is called the handover or handoff. Typically, a new channel is automatically selected for the mobile unit on the new base station which will serve it. The mobile unit then automatically switches from the current channel to the new channel and communication continues.
The exact details of the mobile system's move from one base station to the other vary considerably from system to system (see the example below for how a mobile phone network manages handover).
Mobile phone network

The most common example of a cellular network is a mobile phone (cell phone) network. A mobile phone is a portable telephone which receives or makes calls through a cell site (base station) or transmitting tower. Radio waves are used to transfer signals to and from the cell phone.
Modern mobile phone networks use cells because radio frequencies are a limited, shared resource. Cell-sites and handsets change frequency under computer control and use low power transmitters so that the usually limited number of radio frequencies can be simultaneously used by many callers with less interference.
A cellular network is used by the mobile phone operator to achieve both coverage and capacity for their subscribers. Large geographic areas are split into smaller cells to avoid line-of-sight signal loss and to support a large number of active phones in that area. All of the cell sites are connected to telephone exchanges (or switches), which in turn connect to the public telephone network.
In cities, each cell site may have a range of up to approximately 1⁄2 mile (0.80 km), while in rural areas, the range could be as much as 5 miles (8.0 km). It is possible that in clear open areas, a user may receive signals from a cell site 25 miles (40 km) away. In rural areas with low-band coverage and tall towers, basic voice and messaging service may reach 50 miles (80 km), with limitations on bandwidth and number of simultaneous calls.
Since almost all mobile phones use cellular technology, including GSM, CDMA, and AMPS (analog), the term "cell phone" is in some regions, notably the US, used interchangeably with "mobile phone". However, satellite phones are mobile phones that do not communicate directly with a ground-based cellular tower but may do so indirectly by way of a satellite.
There are a number of different digital cellular technologies, including: Global System for Mobile Communications (GSM), General Packet Radio Service (GPRS), cdmaOne, CDMA2000, Evolution-Data Optimized (EV-DO), Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution (EDGE), Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS), Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT), Digital AMPS (IS-136/TDMA), and Integrated Digital Enhanced Network (iDEN). The transition from existing analog to the digital standard followed a very different path in Europe and the US.[19] As a consequence, multiple digital standards surfaced in the US, while Europe and many countries converged towards the GSM standard.
Structure of the mobile phone cellular network
A simple view of the cellular mobile-radio network consists of the following:
- A network of radio base stations forming the base station subsystem.
- The core circuit switched network for handling voice calls and text
- A packet switched network for handling mobile data
- The public switched telephone network to connect subscribers to the wider telephony network
This network is the foundation of the GSM system network. There are many functions that are performed by this network in order to make sure customers get the desired service including mobility management, registration, call set-up, and handover.
Any phone connects to the network via an RBS (Radio Base Station) at a corner of the corresponding cell which in turn connects to the Mobile switching center (MSC). The MSC provides a connection to the public switched telephone network (PSTN). The link from a phone to the RBS is called an uplink while the other way is termed downlink.
Radio channels effectively use the transmission medium through the use of the following multiplexing and access schemes: frequency-division multiple access (FDMA), time-division multiple access (TDMA), code-division multiple access (CDMA), and space-division multiple access (SDMA).
Small cells
Small cells, which have a smaller coverage area than base stations, are categorised as follows:
- Microcell -> less than 2 kilometres,
- Picocell -> less than 200 metres,
- Femtocell -> around 10 metres,
- Attocell -> 1–4 metres
Cellular handover in mobile phone networks
As the phone user moves from one cell area to another cell while a call is in progress, the mobile station will search for a new channel to attach to in order not to drop the call. Once a new channel is found, the network will command the mobile unit to switch to the new channel and at the same time switch the call onto the new channel.
With CDMA, multiple CDMA handsets share a specific radio channel. The signals are separated by using a pseudonoise code (PN code) that is specific to each phone. As the user moves from one cell to another, the handset sets up radio links with multiple cell sites (or sectors of the same site) simultaneously. This is known as "soft handoff" because, unlike with traditional cellular technology, there is no one defined point where the phone switches to the new cell.
In IS-95 inter-frequency handovers and older analog systems such as NMT it will typically be impossible to test the target channel directly while communicating. In this case, other techniques have to be used such as pilot beacons in IS-95. This means that there is almost always a brief break in the communication while searching for the new channel followed by the risk of an unexpected return to the old channel.
If there is no ongoing communication or the communication can be interrupted, it is possible for the mobile unit to spontaneously move from one cell to another and then notify the base station with the strongest signal.
Cellular frequency choice in mobile phone networks
The effect of frequency on cell coverage means that different frequencies serve better for different uses. Low frequencies, such as 450 MHz NMT, serve very well for countryside coverage. GSM 900 (900 MHz) is suitable for light urban coverage. GSM 1800 (1.8 GHz) starts to be limited by structural walls. UMTS, at 2.1 GHz is quite similar in coverage to GSM 1800.
Higher frequencies are a disadvantage when it comes to coverage, but it is a decided advantage when it comes to capacity. Picocells, covering e.g. one floor of a building, become possible, and the same frequency can be used for cells which are practically neighbors.
Cell service area may also vary due to interference from transmitting systems, both within and around that cell. This is true especially in CDMA based systems. The receiver requires a certain signal-to-noise ratio, and the transmitter should not send with too high transmission power in view to not cause interference with other transmitters. As the receiver moves away from the transmitter, the power received decreases, so the power control algorithm of the transmitter increases the power it transmits to restore the level of received power. As the interference (noise) rises above the received power from the transmitter, and the power of the transmitter cannot be increased anymore, the signal becomes corrupted and eventually unusable. In CDMA-based systems, the effect of interference from other mobile transmitters in the same cell on coverage area is very marked and has a special name, cell breathing.
One can see examples of cell coverage by studying some of the coverage maps provided by real operators on their web sites or by looking at independently crowdsourced maps such as Opensignal or CellMapper. In certain cases they may mark the site of the transmitter; in others, it can be calculated by working out the point of strongest coverage.
A cellular repeater is used to extend cell coverage into larger areas. They range from wideband repeaters for consumer use in homes and offices to smart or digital repeaters for industrial needs.
Cell size
The following table shows the dependency of the coverage area of one cell on the frequency of a CDMA2000 network:[20]
| Frequency (MHz) | Cell radius (km) | Cell area (km2) | Relative cell count |
|---|---|---|---|
| 450 | 48.9 | 7521 | 1 |
| 950 | 26.9 | 2269 | 3.3 |
| 1800 | 14.0 | 618 | 12.2 |
| 2100 | 12.0 | 449 | 16.2 |
See also

Lists and technical information:
- Mobile technologies
- 2G networks (the first digital networks, 1G and 0G were analog):
- 3G networks:
- 4G networks:
- LTE (TD-LTE)
- LTE Advanced
- LTE Advanced Pro
- WiMAX
- WiMAX-Advanced (WirelessMAN-Advanced)
- Ultra Mobile Broadband (never commercialized)
- MBWA (IEEE 802.20, Mobile Broadband Wireless Access, HC-SDMA, iBurst, has been shut down)
- LTE (TD-LTE)
- 5G networks:
- 5G NR
- 5G-Advanced
Starting with EVDO the following techniques can also be used to improve performance:
- MIMO, SDMA and Beamforming
- Cellular frequencies
- CDMA frequency bands
- GSM frequency bands
- UMTS frequency bands
- LTE frequency bands
- 5G NR frequency bands
- Deployed networks by technology
- List of UMTS networks
- List of CDMA2000 networks
- List of LTE networks
- List of deployed WiMAX networks
- List of 5G NR networks
- Deployed networks by country (including technology and frequencies)
- List of mobile network operators of Europe
- List of mobile network operators of the Americas
- List of mobile network operators of the Asia Pacific region
- List of mobile network operators of the Middle East and Africa
- List of mobile network operators (summary)
- Mobile country code - code, frequency, and technology for each operator in each country
- Comparison of mobile phone standards
Equipment:
- Cellular repeater
- Cellular router
- Professional mobile radio (PMR)
- OpenBTS
Other:
- Cellular traffic
- MIMO (multiple-input and multiple-output)
- Mobile edge computing
- Mobile phone radiation and health
- Network simulation
- Radio resource management (RRM)
- Routing in cellular networks
- Signal strength
- Title 47 of the Code of Federal Regulations
References
- Guowang Miao; Jens Zander; Ki Won Sung; Ben Slimane (2016). Fundamentals of Mobile Data Networks. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1107143210.
- "Be Mobile, Stay Connected | PMN". Privatemobilenetworks.com. Retrieved 23 November 2013.
- Tom Simonite (24 January 2013). "Google's Private Cell Phone Network Could Be a Threat to Cellular Carriers | MIT Technology Review". Technologyreview.com. Retrieved 23 November 2013.
- U.S. Patent 3,663,762, issued 16 May 1972.
- Golio, Mike; Golio, Janet (2018). RF and Microwave Passive and Active Technologies. CRC Press. pp. ix, I-1, 18–2. ISBN 9781420006728.
- Rappaport, T. S. (November 1991). "The wireless revolution". IEEE Communications Magazine. 29 (11): 52–71. doi:10.1109/35.109666. S2CID 46573735.
- "The wireless revolution". The Economist. 21 January 1999. Retrieved 12 September 2019.
- Baliga, B. Jayant (2005). Silicon RF Power MOSFETS. World Scientific. ISBN 9789812561213.
- Sahay, Shubham; Kumar, Mamidala Jagadesh (2019). Junctionless Field-Effect Transistors: Design, Modeling, and Simulation. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 9781119523536.
- "Remarks by Director Iancu at the 2019 International Intellectual Property Conference". United States Patent and Trademark Office. 10 June 2019. Archived from the original on 17 December 2019. Retrieved 20 July 2019.
- Asif, Saad (2018). 5G Mobile Communications: Concepts and Technologies. CRC Press. pp. 128–134. ISBN 9780429881343.
- O'Neill, A. (2008). "Asad Abidi Recognized for Work in RF-CMOS". IEEE Solid-State Circuits Society Newsletter. 13 (1): 57–58. doi:10.1109/N-SSC.2008.4785694. ISSN 1098-4232.
- J. E. Flood. Telecommunication Networks. Institution of Electrical Engineers, London, UK, 1997. chapter 12.
- "Phone Networks". The Reverse Phone. 8 June 2011. Archived from the original on 30 April 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2012.
- Pauli, Volker; Naranjo, Juan Diego; Seidel, Eiko (December 2010). "Heterogeneous LTE Networks and Inter-Cell Interference Coordination" (PDF). Nomor Research. Archived from the original (PDF) on 3 September 2013. Retrieved 2 April 2012.
- Drucker, Elliott, The Myth of Cellular Tower Health Hazards, archived from the original on 2 May 2014, retrieved 19 November 2013
- "Cellular Telephone Basics". Privateline.com. 1 January 2006. p. 2. Archived from the original on 17 April 2012. Retrieved 2 April 2012.
- U.S. Patent 4,144,411 – Cellular Radiotelephone System for Different Cell Sizes – Richard H. Frenkiel (Bell Labs), filed 22 September 1976, issued 13 March 1979
- Paetsch, Michael (1993): The evolution of mobile communications in the US and Europe. Regulation, technology, and markets. Boston, London: Artech House (The Artech House mobile communications library).
- Colin Chandler (3 December 2003). "CDMA 2000 and CDMA 450" (PDF). p. 17.
Further reading
- P. Key, D. Smith. Teletraffic Engineering in a competitive world. Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam Netherlands, 1999. ISBN 978-0444502681. Chapter 1 (Plenary) and 3 (mobile).
- William C. Y. Lee, Mobile Cellular Telecommunications Systems (1989), McGraw-Hill.
External links
- Raciti, Robert C. (July 1995). "CELLULAR TECHNOLOGY". Nova Southeastern University. Archived from the original on 15 July 2013. Retrieved 2 April 2012.
- A History of Cellular Networks
- What are cellular networks? 1G to 6G Features & Evolution