Palace of Fontainebleau
Palace of Fontainebleau (/ˈfɒntənbloʊ/;[1] French pronunciation: [fɔ̃tɛnblo])[1] or Château de Fontainebleau, located 55 kilometers (34 miles) southeast of the center of Paris, in the commune of Fontainebleau, is one of the largest French royal châteaux. The medieval castle and subsequent palace served as a residence for the French monarchs from Louis VII to Napoleon III. Francis I and Napoleon were the monarchs who had the most influence on the palace as it stands today.[2] It became a national museum in 1927 and was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1981 for its unique architecture and historical importance.[3]
| Palace of Fontainebleau | |
|---|---|
 Château de Fontainebleau | |
 Interactive fullscreen map | |
| Location | Fontainebleau, Seine-et-Marne, France |
| Coordinates | 48°24′8″N 2°42′2″E |
| Official name | Palace and Park of Fontainebleau |
| Type | Cultural |
| Criteria | ii, vi |
| Designated | 1981 (5th session) |
| Reference no. | 160 |
| UNESCO Region | Europe and North America |
History
Medieval palace (12th century)
The earliest record of a fortified castle at Fontainebleau dates to 1137.[4] It became a favorite residence and hunting lodge of the Kings of France because of the abundant game and many springs in the surrounding forest. It took its name from one of the springs, the fountain de Bliaud, located now in the English garden, next to the wing of Louis XV.[5] It was used by King Louis VII, for whom Thomas Becket consecrated the chapel in 1169; by Philip II; by Louis IX (later canonized as Saint Louis), who built a hospital and a convent, the Couvent des Trinitaires, next to the castle; and by Philip IV, who was born and died in the castle.[4]
Renaissance Château of Francis I (1528–1547)
In the 15th century some modifications and embellishments were made to the castle by Isabeau of Bavaria, the wife of King Charles VI, but the medieval structure remained essentially intact until the reign of Francis I (1494–1547). He commissioned the architect Gilles Le Breton to build a palace in the new Renaissance style, recently imported from Italy. Le Breton preserved the old medieval donjon, where the King's apartments were located, but incorporated it into the new Renaissance-style Cour Ovale, or oval courtyard, built on the foundations of the old castle. It included the monumental Porte Dorée, as its southern entrance. as well as a monumental Renaissance stairway, the Portique de Serlio, to give access the royal apartments on the north side.
Beginning in about 1528, Francis constructed the Galerie François I, which allowed him to pass directly from his apartments to the chapel of the Trinitaires. He brought the architect Sebastiano Serlio from Italy, and the Florentine painter Giovanni Battista di Jacopo, known as Rosso Fiorentino, to decorate the new gallery. Between 1533 and 1539 Rosso Fiorentino filled the gallery with murals glorifying the King, framed in stucco ornament in high relief, and lambris sculpted by the furniture maker Francesco Scibec da Carpi. Another Italian painter, Francesco Primaticcio from Bologna, ("Primatice" to the French), joined later in the decoration of the palace. Together their style of decoration became known as the first School of Fontainebleau. This was the first great decorated gallery built in France. Broadly speaking, at Fontainebleau the Renaissance was introduced to France.[6]
 The Porte d'Orée
The Porte d'Orée The Oval Courtyard, with the Medieval donjon, a vestige of the original castle where the King's apartments were located, in the center.
The Oval Courtyard, with the Medieval donjon, a vestige of the original castle where the King's apartments were located, in the center..JPG.webp) The Gallery of Francis I, connecting the King's apartments with the chapel, decorated between 1533 and 1539. It introduced the Italian Renaissance style to France.
The Gallery of Francis I, connecting the King's apartments with the chapel, decorated between 1533 and 1539. It introduced the Italian Renaissance style to France.
In about 1540, Francis began another major addition to the chateau. Using land on the east side of the chateau purchased from the order of the Trinitaires, he began to build a new square of buildings around a large courtyard. It was enclosed on the north by the wing of the Ministers, on the east by the wing of Ferrare, and on the south by a wing containing the new gallery of Ulysses. The chateau was surrounded by a new park in the style of the Italian Renaissance garden, with pavilions and the first grotto in France. Primaticcio created more monumental murals for the gallery of Ulysses.[6]
Château of Henry II and Catherine de' Medici (1547–1570)

Following the death of Francis I, King Henry II decided to continue and expand the chateau. The King and his wife chose the architects Philibert de l'Orme and Jean Bullant to do the work. They extended the east wing of the lower court and decorated it with the first famous horseshoe-shaped staircase. In the oval court, they transformed the loggia planned by Francois into a Salle des Fêtes or grand ballroom with a coffered ceiling. Facing the courtyard of the fountain and the fish pond, they designed a new building, the Pavillon des Poeles (destroyed), to contain the new apartments of the King. The decoration of the new ballroom and the gallery of Ulysses with murals by Francesco Primaticcio and sculptured stucco continued, under the direction of the Mannerists painters Primaticcio and Niccolò dell'Abbate.[7] At Henri's orders the Nymphe de Fontainebleau by Benvenuto Cellini was installed at the gateway entrance of Château d'Anet, the primary domain of Henri's primary mistress Diane de Poitiers (the original bronze lunette is now in the Musée du Louvre, with a replica in place).[8] It was also the birth locale of Francis II of France, King Henry II's firstborn son.
Following the death of Henry II in a jousting accident, his widow, Catherine de' Medici, continued the construction and decoration of the château. She named Primaticcio as the new superintendent of royal public works. He designed the section known today as the wing of the Belle Cheminée, noted for its elaborate chimneys and its two opposing stairways. In 1565, as a security measure due to the Wars of Religion, she also had moat dug around the château to protect it against attack.[7]
_at_Fontainebleau_MET_MM20346.jpg.webp)
 Giorgio Ghisi after Francesco Primaticcio, Three Muses and a Gesturing Putto, 1560s,
Giorgio Ghisi after Francesco Primaticcio, Three Muses and a Gesturing Putto, 1560s,_at_Fontainebleau_MET_DP821338.jpg.webp) Three Muses and a putto above with a lyre, from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau MET
Three Muses and a putto above with a lyre, from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau MET Three Muses and a Putto with a Cymbals
Three Muses and a Putto with a Cymbals
%252C_from_a_series_of_eight_compositions_after_Francesco_Primaticcio's_designs_for_the_ceiling_of_the_Ulysses_Gallery_(destroyed_1738-39)_at_Fontainebleau_MET_DP821346.jpg.webp) Hercules, Bacchus, Pan, and Saturn(?), from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau
Hercules, Bacchus, Pan, and Saturn(?), from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau_at_Fontainebleau_MET_DP821340.jpg.webp) Pluto, Neptune, Minerva, and Apollo, from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau MET DP821340
Pluto, Neptune, Minerva, and Apollo, from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau MET DP821340_at_Fontainebleau_MET_DP821341.jpg.webp) Venus and Cupid, two other goddesses and a putto, from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau MET DP821341.jpg
Venus and Cupid, two other goddesses and a putto, from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau MET DP821341.jpg_at_Fontainebleau_MET_DP821331.jpg.webp) Ceres Seated on Clouds with Two Goddesses and Two Putti, from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau
Ceres Seated on Clouds with Two Goddesses and Two Putti, from a series of eight compositions after Francesco Primaticcio's designs for the ceiling of the Ulysses Gallery (destroyed 1738–39) at Fontainebleau Ulysses and His Companions Fighting the Cicones Before the City of Ismaros, Study for a Destroyed Fresco in the Galerie d'Ulysee, Chateau de Fontainebleau
Ulysses and His Companions Fighting the Cicones Before the City of Ismaros, Study for a Destroyed Fresco in the Galerie d'Ulysee, Chateau de Fontainebleau
Château of Henry IV (1570–1610)

King Henry IV made more additions to the château than any King since Francis I. He extended the oval court toward the west by building two pavilions, called Tiber and Luxembourg. Between 1601 and 1606, he remade all the façades around the courtyard, including that of the chapel of Saint-Saturnin, to give the architecture greater harmony. On the east side, he built a new monumental domed gateway, the Porte du Baptistère. Between 1606 and 1609, he built a new courtyard, the Cour des Offices or Quartier Henry IV, to provide a place for the kitchens and residences for court officials. Two new galleries, the Galerie de Diane de Poitiers and the Galerie des Cerfs, were built to enclose the old garden of Diane. He also added a large jeu de paume, or indoor tennis court, the largest such court existing in the world.[9][10][11]
A "second school of Fontainebleau" of painters and decorators went to work on the interiors. The architect Martin Fréminet created the ornate chapel of the Trinity, while the painters Ambroise Dubois and Toussaint Dubreuil created a series of heroic paintings for the salons. A new wing, named for its central building, La Belle Cheminée, was built next to the large fish pond.
Henry IV also devoted great attention to the park and gardens around the Chateau. The garden of the Queen or garden of Diane, created by Catherine de' Medici, with the fountain of Diane in the center, was located on the north side of the palace. Henry IV's gardener, Claude Mollet, trained at Château d'Anet, created a large parterre of flower beds, decorated with ancient statues and separated by paths into large squares. The fountain of Diana and the grotto were made by Tommaso Francini, who may also have designed the Medici Fountain in the Luxembourg Garden for Marie de Medici. On the south side, Henry created a park, planted with pines, elms and fruit trees, and laid out a grand canal 1200 meters long, sixty years before Louis XIV built his own grand canal at Versailles.[11]
Château from Louis XIII through Louis XIV
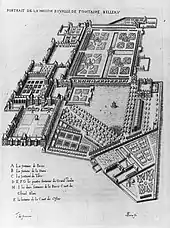
.JPG.webp)
King Louis XIII was born and baptized in the Château, and continued the works begun by his father. He completed the decoration of the chapel of the Trinity, and assigned the court architect Jean Androuet du Cerceau to reconstruct the horseshoe stairway earlier designed by Philibert Delorme on the courtyard that had become known as the Cour de Cheval Blanc. After his death, his widow, Anne of Austria, redecorated the apartments within the Wing of the Queen Mothers (Aile des Reines Mères) next to the Court of the Fountain, designed by Primatrice.[12]
King Louis XIV spent more days at Fontainebleau than any other monarch; he liked to hunt there every year at the end of summer and the beginning of autumn. He made few changes to the exterior of the château, but did build a new apartment for his companion Madame de Maintenon, furnished it with some major works of André-Charles Boulle and demolished the old apartments of the baths under the Gallery of Francis I to create new apartments for the royal princes, and he made some modifications to the apartments of the King. The architect Jules Hardouin-Mansard built a new wing alongside the Galerie des Cerfs and the Galerie de Diane to provide more living space for the Court. He did make major changes in the park and gardens; he commissioned André Le Nôtre and Louis Le Vau to redesign the large parterre into a French formal garden. He removed the hanging garden which Henry IV had built next to the large fish pond, and instead built a pavilion, designed by Le Vau, on a small island in the center of the pond.
Louis XIV signed the Edict of Fontainebleau at the Château on 22 October 1685, revoking the policy of tolerance towards Protestants begun by Henry IV. Louis welcomed many foreign guests there, including the former Queen Christina of Sweden, who had just abdicated her crown. While a guest in the Château on 10 November 1657, Christina suspected her Master of the Horse and reputed lover, the Marchese Gian Rinaldo Monaldeschi, of betraying her secrets to her enemies. Her servants chased him through the halls of the Château and stabbed him to death. Louis XIV came to see her at the Château, did not mention the murder, and allowed her to continue her travels.

On May 19–20, 1717, during the Regency following the death of Louis XIV, the Russian Czar Peter the Great was a guest at Fontainebleau. A hunt for stags was organized for him, and a banquet. Officially the visit was a great success. But in the memoirs published later by members of the delegation, it appears that Peter disliked the French style of hunting, and that he found the Château too small, compared with the other royal French residences. The routine of Fontainebleau also did not suit his tastes; he preferred beer to wine (and brought his own supply with him) and he liked to get up early, unlike the French Court.[13][14]
The renovation projects of Louis XV were more ambitious than those of Louis XIV. To create more lodging for his enormous number of courtiers In 1737–38 the King built a new courtyard, called the Cour de la Conciergerie or the Cour des Princes, to the east of the Galerie des Cerfs. On the Cour du Cheval Blanc, the wing of the Gallery of Ulysses was torn down and gradually replaced by a new brick and stone building, built in stages in 1738–1741 and 1773–74, extending west toward the Pavilion and grotto of the pines.
Between 1750 and 1754, the King commissioned the architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel to build a new wing along the Cour de la Fontaine and the fish pond. The old Pavilion des Poeles was demolished and replaced by the Gros Pavilion, built of cream-colored stone. Lavish new apartments were created inside this building for the King and the Queen. The new meeting room for the Royal Council was decorated by the leading painters of the day, including François Boucher, Carle Vanloo, Jean-Baptiste Marie Pierre and Alexis Peyrotte. A magnificent small theater was created on the first floor of the wing of the Belle Cheminée.
King Louis XVI also made additions to the château to create more space for his courtiers. A new building was constructed alongside the Gallery of Francis I; it created a large new apartment on the first floor, and a number of small apartments on the ground floor, but also blocked the windows on the north side of the Gallery of Francis I. The apartments of Queen Marie-Antoinette were redone, a Turkish-style salon was created for her in 1777, a room for games in 1786–1787, and a boudoir in the arabesque style. Louis XVI and Marie-Antoinette made their last visit to Fontainebleau in 1786, on the eve of the French Revolution.[15]
Château during the Revolution and the First Empire

During the French Revolution the Château did not suffer any significant damage, but all the furniture was sold at auction. The buildings were occupied by the Central School of the Department of Seine-et-Marne, until 1803, when Napoleon I installed a military school there. As he prepared to become Emperor, Napoleon wanted to preserve as much as possible the palaces and protocol of the Old Regime. He chose Fontainebleau as the site of his historic 1804 meeting with Pope Pius VII, who had travelled from Rome to crown Napoleon Emperor. Napoleon had a suite of rooms decorated for the Pope, and had the entire chateau refurnished and decorated. The bedroom of the Kings was transformed into a throne room for Napoleon. Apartments were refurnished and decorated for the Emperor and Empress in the new Empire style. The Cour du Cheval Blanc was renamed the Cour d'Honneur, or Courtyard of Honor. One wing facing the courtyard, the Aile de Ferrare, was torn down and replaced with an ornamental iron fence and gate, making the façade of the Palace visible. The gardens of Diane and the gardens of the Pines were replanted and turned into an English landscape garden by the landscape designer Maximillien Joseph Hurtault.

Napoleon's visits to Fontainebleau were not frequent, because he was occupied so much of the time with military campaigns. Between 1812 and 1814, the château served as a very elegant prison for Pope Pius VII. On 5 November 1810, the chapel of the château was used for the baptism of Napoleon's nephew, the future Napoleon III, with Napoleon serving as his godfather, and the Empress Marie-Louise as his godmother.[16]
Napoleon spent the last days of his reign at Fontainebleau, before abdicating there on 4 April 1814, under pressure from his marechals, Ney, Berthier, and Lefebvre. On 20 April, after failing in an attempt to commit suicide, he gave an emotional farewell to the soldiers of the Old Guard, assembled in the Court of Honor. Later, during the One Hundred Days, he stopped there on 20 March 1815.
In his memoires, written while in exile on Saint Helena, he recalled his time at Fontainebleau; “…the true residence of Kings, the house of the centuries. Perhaps it was not a rigorously architectural palace, but it was certainly a place of residence well thought out and perfectly suitable. It was certainly the most comfortable and happily situated palace in Europe.”
Château during the Restoration and the reign of Louis-Philippe (1815–1848)
Following the restoration of the Monarchy, Kings Louis XVIII and Charles X each stayed at Fontainebleau, but neither made any major changes to the palace. Louis-Philippe was more active, both restoring some rooms and redecorating others in the style of his period. The Hall of the Guards and Gallery of Plates were redecorated in a Neo-Renaissance style, while the Hall of Columns, under the ballroom, was remade in a neoclassical style. He added new stained glass windows, made by the royal manufactory of Sèvres.
Château during the Second Empire

Emperor Napoleon III, who had been baptized at Fontainebleau, resumed the custom of long stays at Fontainebleau, particularly during the summer. Many of the historic rooms, such as the Galerie des Cerfs, were restored to something like their original appearance, while the private apartments were redecorated to suit the tastes of the Emperor and Empress. Numerous guest apartments were squeezed into unused spaces of the buildings. The old theater of the palace, built in the 18th century, was destroyed by a fire in the wing of the Belle Cheminée 1856. Between 1854 and 1857 the architect Hector Lefuel built a new theater in the style of Louis XVI.
On the ground floor of the Gros Pavilion, the Empress Eugénie built a small but rich museum, containing gifts from the King of Siam in 1861, and works of art taken during the pillage of the Summer Palace in Beijing. It also featured paintings by contemporary artists, including Franz Xaver Winterhalter, and the sculptor Charles Henri Joseph Cordier. Close by, in the Lous XV wing, the Emperor established his office, and the Empress made her Salon of Lacquer. These were the last rooms created by the royal residents of Fontainebleau. In 1870, during the Franco-German War, the Empire fell, and the Château was closed.[17]
Château from the Third Republic to the present day
During the Franco-Prussian War, the palace was occupied by the Prussians on 17 September 1870, and briefly used as an army headquarters by Frederic Charles of Prussia from March 1871. Following the war, two of the buildings became the home of the advanced school of artillery and engineering of the French Army, which had been forced to leave Alsace when the province was annexed by Germany. [18] It was occasionally used as a residence by the Presidents of the Third Republic, and to welcome state guests including King Alexander I of Serbia (1891), King George I of Greece (1892) Leopold II of Belgium (1895) and King Alphonse XIII of Spain (1913). It also received a visit by the last survivor of its royal residents, the Empress Eugenie, on 26 June 1920.
The façades the major buildings received their first protection by classification as historic monuments on 20 August 1913. In 1923, following the First World War, it became home of the Écoles d'Art Américaines, schools of art and music, which still exist today. In 1927 it became a national museum. Between the wars the upper floors of the wing of the Belle Cheminée, burned in 1856, were rebuilt by a grant from the Rockefeller Foundation.
During World War II, it was occupied by the Germans on 16 June 1940, and occupied until 10 November, and again from 15 May to the end of October 1941. Following the war, part of the château became a headquarters of the Western Union and later NATO's Allied Forces Central Europe/Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe, until 1966.
The general restoration of the Chateau took place between 1964 and 1968 under President Charles DeGaulle and his Minister of Culture, Andre Malraux. It was classified as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1981. In 2006, the Ministry of Culture purchased the royal stables, and began their restoration.
Beginning in 2007, restoration began of the theater of the château, created by Napoleon III during the Second Empire. The project was funded by the government of Abu-Dhabi, and in exchange the theater was renamed for Sheik Khalifa Bin Zayed al Nahyan. It was inaugurated on 30 April 2014.[19]
On 1 March 2015, the Chinese Museum of the château was robbed by professional thieves. They broke in at about six in the morning, and, despite alarms and video cameras, in seven minutes stole about fifteen of the most valuable objects in the collection, including the replica of the crown of Siam given by the Siamese government to Napoleon III, a Tibetan mandala, and an enamel chimera from the reign of the Qianlong Emperor (1736–1795).[20]
Grand Apartments
Gallery of Francis I

The Gallery of Francis I is one of the first and finest examples of Renaissance decoration in France. It was originally constructed in 1528 as a passageway between the apartments of the King with the oval courtyard and the great chapel of the convent Trinitaires, but in 1531 Francis I made it a part of his royal apartments, and between 1533 and 1539 it was decorated by artists and craftsmen from Italy, under the direction of the painter Rosso Fiorentino, or Primatice, in the new Renaissance style. The lower walls of the passage were the work of the master Italian furniture maker Francesco Scibec da Carpi; they are decorated with the coat of arms of France and the salamander, the emblem of the King. The upper walls are covered by frescoes framed in richly sculpted stucco. The frescoes used mythological scenes to illustrate the virtues of the King.
On the side of gallery with windows, the frescoes represent Ignorance Driven Out; The Unity of the State; Cliobis and Biton; Danae; The Death of Adonis; The Loss of Perpetual Youth; and The Battle of the Centaurs and the Lapithes.
On the side of the gallery facing the windows, the frescoes represent: A Sacrifice; The Royal Elephant; The Burning of Catane; The Nymph of Fontainebleau (painted in 1860–61 by J. Alaux to cover a former entry to the gallery); The Sinking of Ajax;The Education of Achilles and The Frustration of Venus.[21]
Ballroom



The ballroom was originally begun as an open passageway, or loggia, by Francis I. In about 1552 King Henry II closed it with high windows and an ornate coffered ceiling, and transformed it into a room for celebrations and balls. The 'H', the initial of the King, is prominent in the decor, as well as figures of the crescent moon, the symbol of Henry's mistress Diane de Poitiers.
At the western end is a monumental fireplace, decorated with bronze statues originally copied from classical statues in Rome. At the eastern end of the room is a gallery where the musicians played during balls. The decor was restored many times over the years. The floor, which mirrors the design of the ceiling, was built by Louis-Philippe in the first half of the 19th century.
The frescoes on the walls and pillars were painted beginning in 1552 by Nicolo dell'Abate, following drawings by Primatice. On the garden side of the ballroom, they represent: The Harvest; Vulcan forging weapons for Love at the request of Venus; Phaeton begging the sun to let him drive his chariot; and Jupiter and Mercury at the home of Philemon and Baucis.
The frescoes on the side of the Oval Courtyard represent: The feast of Bacchus; Apollo and the Muses on Mount Parnassus; The Three Graces dancing before the gods; and The wedding feast of Thetis and Peleus.
A fresco behind the gallery of musicians shows musicians of the period performing.
St. Saturnin's Chapels
Behind the ballroom, there is St. Saturnin's Chapel. The lower chapel was originally built in the 12th century, but was destroyed and completely rebuilt under Francis I. The windows made in Sèvres were installed during the Louis Philippe's period and were designed by his daughter Marie, an artist herself.[22] The upper chapel was the royal chapel decorated by Philibert de l'Orme.[23] The ceiling, made in the same style as the ballroom, ends with a dome.
Room of the Guards

A room for the guards was always located next to the royal bedchambers. The Salle des Gardes was built during the reign of Charles IX. Some traces of the original decor remain from the 1570s, including the vaulted ceiling and a frieze of military trophies attributed to Ruggiero d'Ruggieri. In the 19th century Louis Philippe turned the room into a salon and redecorated it with a new parquet floor of exotic woods echoing the design of the ceiling, and a monumental fireplace (1836), which incorporates pieces of ornament from demolished rooms from 15th and early 16th century. The bust of Henry IV, attributed to Mathieu Jacquet, is from that period, as are the two figures on either side of the fireplace. The sculpted frame around the bust, by Pierre Bontemps, was originally in the bedchamber of Henry II. The decorations added by Louis Philippe include a large vase decorated with Renaissance themes, made by the Sèvres porcelain manufactory in 1832. During the reign of Napoleon III, the hall was used as a dining room.[24][25]
Stairway of the King

The stairway of the King was installed in 1748 and 1749, in the space occupied during the reign of Francis I by the bedroom of Anne de Pisseleu, the Duchess of Étampes, a favorite of the King. It was designed by the architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel, who used many decorative elements from the earlier room, which had originally been decorated by Primatice. The upper portion of the walls is divided into panels, oval and rectangular, with scenes representing the love life of Alexander the Great. The paintings are framed by large statues of women by Primatice. The eastern wall of the room was destroyed during the reconstruction, and was replaced during the reign of Louis Philippe in the 19th century with paintings by Abel de Pujol.[26]
Queen's bedroom
.jpg.webp)
All of the Queens and Empresses of France from Marie de Medici to the Empress Eugènie, slept in the bedchamber of the Queen. The ornate ceiling over the bed was made in 1644 by the furniture-maker Guillaume Noyers for the Dowager Queen Anne of Austria, the mother of Louis XIV, and bears her initials. The room was redecorated by Marie Leszczynska, the Queen of Louis XV in 1746–1747. The ceiling of the alcove, the decoration around the windows and the wood panelling were made by Jacques Vererckt and Antoine Magnonais in the rocaille style of the day. The decoration of the fireplace dates to the same period.
The doors have an arabesque design, and were made for Marie-Antoinette, as were the sculpted panels over the doors, installed in 1787. The bed was also made specially for Marie Antoinette, but did not arrive until 1797, after the Revolution and her execution,and thus escaped the sales that had already happened earlier in the decade. It was used instead by Napoleon's wives, the Empress Josephine and Marie-Louise of Austria.
The walls received their ornamental textile covering, with a design of flowers and birds, in 1805. It was restored in 1968–1986 using the original fabric as a model. The furniture in the room all dates to the First Empire. The balustrade around the bed was originally made for the throne room of the Tuileries Palace in 1804. The armchairs with a sphinx pattern, the consoles and screen and the two chests of drawers were placed in the room in 1806.[27]
Boudoir of Marie-Antoinette

The boudoir next to the Queen's bedroom was created for Queen Marie-Antoinette in 1786, and permitted the Queen to have a measure of privacy. The room is the best surviving example of the decorative style just before the French Revolution, inspired by ancient Roman models, with delicately painted arabesques, cameos, vases, antique figures and garlands of flowers against a silver background, framed by gilded and sculpted woodwork.[28]
The room was made for the Queen by the same team of artists and craftsmen who also made the game room; the design was by the architect Pierre Rousseau (1751-1829); the wood panelling was sculpted by Laplace, and painted by Michel-Hubert Bourgeois and Louis-François Touzé. Eight figures of the Muses were made in plaster by Roland; the ornate mantle of the fireplace was made by Jacques-François Dropsy, and decorated with glided bronze works by Claude-Jean Pitoin. The mahogany parquet floor, decorated with the emblems of the Queen, was made by Bernard Molitor, and finished in 1787. The painted ceiling, by Jean-Simon Berthélemy, shows Aurora with a group of angels.[29]
The furnishings were designed for the room by Jean-Henri Riesener, using the finest materials available; mother of pearl, gilded bronze, brass, satin and ebony. Some of the original furnishings remain, including the cylindrical desk and the table, which were made between 1784 and 1789. The two armchairs are copies of the originals made by Georges Jacob which are now in the Gulbenkian Museum in Lisbon, while the footstool is the original.[29]
Throne Room of Napoleon (former bedroom of the King)
.jpg.webp)
In 1808 Napoleon decided to install his throne in the former bedroom of the Kings of France from Henry IV to Louis XVI, on the place where the royal bed had been. Under the Old Regime, the King's bed was a symbol of royal authority in France and was saluted by courtiers who passed by it. Napoleon wanted to show the continuity of his Empire with the past monarchies of France.[30] The majority of the carved wood ceiling, the lower part of the wood panelling, and the doors date to the reign of Louis XIII. The ceiling directly over the throne was made at the end of the reign of Louis XIV. Louis XV created the portion of the ceiling directly over the throne, a new chimney, sculpted wooden medallions near the fireplace, the designs over the doors, and the fine carved woodwork facing the throne (1752–54). He also had the ceiling painted white and gilded and decorated with mosaics, to match the ceiling of the bedroom of the Queen.[30]
Napoleon added the standards with his initial and the Imperial eagle. The decoration around the throne was originally designed in 1804 by Jacob-Desmalter for the Palace of Saint-Cloud, and the throne itself came from the Tuileries Palace.
The chimney was originally decorated with a portrait of Louis XIII painted by Philippe de Champaigne, which was burned in 1793 during the French Revolution. Napoleon replaced it with a portrait of himself, by Robert Lefèvre. In 1834, King Louis-Philippe took down Napoleon's picture and replaced with another of Louis XIII, from a painter of the school of Champaigne,[31]
Council Chamber

The Council Chamber, where the Kings and Emperors met their closest advisors, was close to the Throne Room. It was originally the office of Francis I, and was decorated with painted wooden panels showing following designs of Primatice, the virtues and the heroes of antiquity. The room was enlarged under Louis XIV, and the decorator, Claude Audran, followed the same theme. The room was entirely redecorated between 1751 and 1754 by the architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel, with arcades and wooded panels showing the virtues, and allegories of the seasons and the elements, painted by Jean-Baptiste Marie Pierre and Carle van Loo.[32] The painter Alexis Peyrotte added another series of medallions on the upper walls depicting floral themes, the sciences and arts. The five paintings on the vaulted ceiling were the work of François Boucher, and show the seasons and the sun beginning his journey and chasing away the night. A half-rotonda on the garden side of the room was added by Louis XV in 1773, with a painted ceiling by Lagrenée depicting Glory surrounded by his children.[33]
The room was used as a council chamber by Napoleon I, and the furnishings are from that time. The armchairs at the table for the ministers are by Marcion (1806) and the folding chairs for advisors are by Jacob-Desmalter (1808).[32]
Apartment of the Pope and of the Queen-Mothers

The apartment of the Pope, located on the first floor of the wing of the Queen Mothers and of the Gros Pavillon, takes its name from the 1804 visit of Pope Pius VII, who stayed there on his way to Paris to crown Napoleon I the Emperor of France. He stayed there again, involuntarily, under the close supervision of Napoleon from 1812 to 1814. Prior to that, beginning in the 17th century it was the residence of the Queen Mothers Marie de' Medici and Anne of Austria. It was also the home of the Grand Dauphin, the oldest son of Louis XIV. In the 18th century it was used by the daughters of Louis XV, and then by the Count of Provence, the brother of Louis XVI. During the First Empire it was used by Louis, the brother of Napoleon, and his wife Queen Hortense, the daughter of the Empress Josephine. During the reign of Louis-Philippe, it was used by his eldest son, the Duke of Orleans. During the Second Empire, it was occupied by Stephanie de Bade, the adopted niece of Napoleon I. It was restored in 1859–1861, and used thereafter for guests of high rank.[30] It was originally two apartments, which were divided or joined over the years depending upon its occupants.

The Salon de Reception was the anteroom to the bedroom of Anne of Austria, wife of Louis XIII and mother of Louis XIV. It features a gilded and sculpted ceiling divided into seven compartments, representing the sun and the known planets, along with smaller compartments for military trophies; it was created in 1558 by Ambroise Perret for the bedroom of Henry II in the pavilion des Poeles, a section of the Château that was later destroyed. Anne had it moved to the room and decorated with her own emblems, including a pelican. The wood paneling in the room is probably from the same period.[30]
The decor of the bedroom dates largely to the 1650s; it includes grotesque paintings in compartments on the ceiling, attributed to Charles Errard; richly carved wood paneling featuring oak leaves and putti; and paintings over the doors of Anne of Austria costumed as Minerva and Marie-Therese of Austria costumed as Abundance, both painted by Gilbert de Sève. The bedroom was modified in the 18th century by the addition of a new fireplace (about 1700) and sculptured borders of cascades of flowers around the mirrors added in 1784. During the Secone Empire, painted panels imitating the style of the 17th century were added above the mirrors and between the mirrors and the doors.[34]
Gallery of Diana

The Gallery of Diana, an eighty-meter (242.4 feet) long corridor now lined with bookcases, was created by Henry IV at the beginning of the 17th century as a place for the Queen to promenade. The paintings on the vaulted ceiling, painted beginning in 1605 by Ambroise Dubois and his workshop, represented scenes from the myth of Diana, goddess of the Hunt.[35] At the beginning of the 19th century, the gallery was in ruins. In 1810 Napoleon decided to turn it into a gallery devoted the achievements of his Empire. A few of the paintings still in good condition were removed and put in the Gallery of Plates. The architect Hurtault designed a new plan for the gallery, inspired by the Grand Gallery of the Louvre, featuring paintings on the ceiling illustrating the great events of Napoleon's reign. By 1814 the corridor had been rebuilt and the decorative painted frames painted by the Moench and Redouté, but the cycle of paintings on the Empire had not been started, when Napoleon fell from power.[36]
Once the monarchy was restored, King Louis XVIII had the gallery completed in a neoclassical style. A new series of the goddess Diana was done by Merry-Joseph Blondel and Abel de Pujol, using the painted frames prepared for Napoleon's cycle.[35] Paintings were also added along the corridor, illustrating the history of the French monarchy, painted in the Troubador style of the 1820s and 1830s, painted by a team of the leading academic painters. Beginning in 1853, under Napoleon III, the corridor was turned into a library and most of the paintings were removed, with the exception of a large portrait of Henry IV on horseback by Jean-Baptiste Mauzaisse. The large globe near the entrance of the gallery, placed there in 1861, came from the office of Napoleon in the Tuileries Palace.[36]
Apartments of Napoleon

In 1804 Napoleon decided that he wanted his own private suite of apartments within the Palace, separate from the old state apartments. He took over a suite of six rooms which had been created in 1786 for Louis XVI, next to the Gallery of Francis I, and had them redecorated in the Empire style.
The old apartment included a dressing room (cabinet de toilette), study, library, and bath.[37]
Emperor's bedroom
Beginning in 1808, Napoleon had his bedroom in the former dressing room of the King. From this room, using a door hidden behind the drapery to the right of the bed, Napoleon could go directly to his private library or to the offices on the ground floor.
Much of the original decor was unchanged from the time of Louis XVI; the fireplaces, the carved wooden panels sculpted by Pierre-Joseph LaPlace and the sculpture over the door by Sauvage remained as they were. The walls were painted with Imperial emblems in gold on white by Frederic-Simon Moench. The bed, made especially for the Emperor, was the summit of the Empire style; it was crowned with an imperial eagle and decorated with allegorical sculptures representing Glory, Justice, and Abundance. The Emperor had a special carpet made by Sallandrouze in the shape of the cross of the Legion of Honor; the branches of the cross alternate with symbols of military and civilian attributes.[38] The chairs near the fireplace were specially designed, with one side higher than the other, to contain the heat from the fire while allowing the occupants to see the decorations of the fireplace. The painting on the ceiling of the room was added later, after the downfall of Napoleon, by Louis XVIII. Painted by Jean-Baptiste Regnault, it is an allegory representing The clemency of the King halting justice in its course.[37]
The study was a small room designated as Napoleon's work room. In 1811 he added the camp bed, similar to the bed he used on his military campaigns, so he could rest briefly during a long night of work.
The salon of the Emperor was simply furnished and decorated. It was in this room, on the small table on display, that the Emperor signed his abdication in 1814.
Theatre

Concerts, plays and other theatrical productions were a regular part of court life at Fontainebleau. Prior to the reign of Louis XV these took place in different rooms of the palace, but during his reign a theatre was built in the Belle-Cheminée wing. It was rebuilt by the architect Gabriel, but was destroyed by a fire in 1856. It had already been judged too small for the court of Napoleon III, and a new theatre had been begun in 1854 at the far eastern end of the wing of Louis XIV. It was designed by architect Hector Lefuel in the style of Louis XVI, and was inspired by the opera theatre at the palace of Versailles and that of Marie-Antoinette at the Trianon Palace. The new theatre, with four hundred seats arranged in a parterre, two balconies and boxes in a horseshoe shape, was finished in 1856. It has the original stage machinery, and many of the original sets, including many transferred from the old theatre before the fire of 1856. [39][40]
The theatre was closed after the end of the Second Empire and was rarely used. A restoration began in 2007, funded with ten million Euros by the government of Abu-Dhabi. In exchange, the theatre was renamed for Sheik Khalifa Bin Zayed al Nahyan. It was inaugurated on 30 April 2014. The theatre can be visited, but it no longer can be used for plays because some working parts of the theater, including the stage, were not included in the restoration.[19]
Chinese Museum

The Chinese Museum, on the ground floor of the Gros Pavillon close to the pond, was among the last rooms decorated within the Chateau while it was still an imperial residence. In 1867, the Empress Eugenie had the rooms remade to display her personal collection of Asian art, which included gifts given to the Emperor by a delegation sent by the King of Siam in 1861, and other objects taken during the destruction and looting of the Old Summer Palace near Beijing by a joint British-French military expedition to China in 1860.[41][42]
The objects displayed in the antechamber include two royal palanquins given by the King of Siam, one designed for a King and the other (with curtains) for a Queen. Inside the two salons of the museum, some of the walls are covered with lacquered wood panels in black and gold, taken from 17th century Chinese screens, along with specially designed cases to display antique porcelain vases. Other objects on display include a Tibetan stupa containing a Buddha taken from the Summer Palace in China; and a royal Siamese crown given to Napoleon III. The salons are lavishly decorated with both Asian and European furnishings and art objects, including silk-covered furnishings and Second Empire sculptures by Charles Cordier and Pierre-Alexandre Schoenewerk. The room also served as a place for games and entertainment; an old bagatelle game and a mechanical piano from that period are on display.[43]
In addition to the Chinese Museum, the Empress created a small office in 1868, the Salon of Lacquerware, which also decorated with lacquered panels and Asian art objects, on the ground floor of the Louis XV wing, not far from the office of the Emperor. This was the last room decorated before the fall of the Empire, and the eventual transformation of the Chateau into a museum.[43]
Chapel of the Trinity

The Chapel of the Trinity was built at the end of the reign of Francis I to replace the old chapel of the convent of the Trinitaires. It was finished under Henry II, but was without decoration until 1608, when the painter Martin Freminet was commissioned to design frescoes for the ceiling and walls. The sculptor Barthèlemy Tremblay created the vaults of the ceiling out of stucco and sculpture.[44] The paintings of Freminet in the central vaults depict the redemption of Man, from the appearance of God to Noah at the launching of the Ark (Over the tribune) to the Annunciation. They surrounded these with smaller paintings depicting the ancestors of the Virgin Mary, the Kings of Judah, the Patriarchs announcing the coming of Christ, and the Virtues. Between 1613 and 1619 Freminet and Tremblay added paintings in stucco frames between the windows on the sides of the chapel, depicting the life of Christ.[45] Freminet died in 1619 and work did not resume until 1628.[44]
The Trinity chapel, like Sainte-Chapelle in Paris other royal chapels, had an upper section or tribune, where the King and his family sat, with a separate entrance; and a lower part, where the rest of the Court was placed. Beginning in 1628, the side chapels were decorated with iron gates and carved wood panelling, and the Florentine sculptor Francesco Bordoni began work on the marble altar. The figure to the left depicts Charlemagne, with the features of Henry II, while the figure on the right depicts Louis IX, or Saint Louis, with the features of Louis XIII, his patron. Bordoni also designed the multicolored marble pavement before the altar and the on the walls of the nave.[44] The painting of the Holy Trinity over the altar, by Jean Dubois the Elder, was added in 1642.[45] In the mid-17th century the craftsman Anthony Girault made the sculpted wooden doors of the nave. while the Jean Gobert made the doors of the tribune where the Royal family worshipped.[46]
In 1741, the royal tribune was enlarged, while ornate balconies of wrought iron were added between the royal tribune and the simpler balconies used by the musicians and those who chanted the mass. In 1779, under Louis XVI, the frescoes of Freminet illustrating the life of Christ, which had deteriorated with time, were replaced by new paintings on the same theme. The paintings were done in the same style by about a dozen painters from the Royal Academy of Painting and Sculpture.[46]
Under Napoleon, the old tabernacle of the chapel, which had been removed during the Revolution, was replaced by a new one designed by the architect Maximilien Hurtault. Beginning in 1824, the chapel underwent a program of major renovation and restoration that lasted for six years. The twelve paintings of the life of Christ were removed, as well as the gates to the side chapels. During the Second Empire, the wood panelling of side chapels was replaced. The restoration was not completed until the second half of the 20th century, when the twelve paintings, which had been scattered to different museums, were brought together again and restored in their stucco frames.[47] Between 1772 and 1774, a small organ made by François-Henri Cilquot was installed on the left side of the chapel, near the altar.[48]
On 5 September 1725, the chapel was the setting for the wedding of Louis XV and Marie Leszczynska. Napoleon III was baptized there on 4 November 1810, and Ferdinand-Philippe d'Orleans, the son of éKing Louis-Philippe, was married there to Helene de Mecklembourg Schwerin on 30 May 1837.[48]
Gardens and the park
From the time of Francis I, the palace was surrounded by formal gardens, representing the major landscaping styles of their periods; the French Renaissance garden, inspired by the Italian Renaissance gardens; the French formal garden, the favorite style of Louis XIV; and, in the 18th and 19th century, the French landscape garden, inspired by the English landscape garden.
Garden of Diana

The Garden of Diana was created during the reign of Henry IV; it was the private garden of the King and Queen, and was visible from the windows of their rooms. The fountain of Diana was originally in the center of garden, which at that time was enclosed by another wing, containing offices and later, under, Louis XIV, an orangerie. That building, and another, the former chancellery, were demolished in the 19th century, doubling the size of the garden. From the 17th until the end of the 18th century, the garden was in the Italian and then the French formal style, divided by straight paths into rectangular flower beds, flower beds, centered on the fountains, and decorated with statues, ornamental plants and citrus trees in pots. It was transformed during the reign of Napoleon I into a landscape garden in the English style, with winding paths and trees grouped into picturesque landscapes, and it was enlarged during the reign of Louis-Philippe. it was opened to the public after the downfall of Napoleon III.[49]
The fountain in the center was made by Tommaso Francini, the master Italian fountain-maker, whose work included the Medici Fountain in the Jardin du Luxembourg in Paris. The bronze statue of Diana, the goddess of the hunt, with a young deer, was made by the Keller brothers in 1684 for another royal residence, at Marly. It is a copy of an antique Roman statue, Diana of Versailles, which was given by the Pope to King Henry IV, and which is now in the Louvre. The original statue of the fountain, made by Barthelemy Prieur in 1602, can be seen in the Gallery of the Cerfs inside the palace. The sculptures of hunting dogs and deer around the fountain were made by Pierre Biard.[50]
Carp pond, English garden, grotto and spring

The large pond next to the palace, with a surface of four hectares, was made during the reign of Henry IV, and was used for boating parties by members of the Court, and as a source of fish for the table and for amusement. Descriptions of the palace in the 17th century tell of guests feeding the carp, some of which reached enormous size, and were said to be a hundred years old. The small octagonal house on an island in the center of the lake, Pavillon de l'Ètang, was added during the reign of Louis XIV, then rebuilt under Napoleon I, and is decorated with his initial.[5]
The English garden also dates back to the reign of Henry IV. In one part of the garden, known as the garden of pines, against the wing of Louis XV, is an older structure dating to Francis I; the first Renaissance-style grotto to be built in a French garden, a rustic stone structure decorated with four statues of Atlas. Under Napoleon, his architect, Maximilien Joseph Hurtault, turned this part of the garden into an English park, with winding paths and exotic trees, including the catalpa, tulip trees, the sophora, and cypress trees from Louisiana, and with a picturesque stream and antique boulders. The garden features two 17th century bronze copies of ancient Roman originals, the Borghese gladiator and the Dying Gladiator. A path leads from the garden through a curtain of trees to the spring which gave its name to the palace, next to a statue of Apollo.[5][51]
Parterre and canal

On the other side of the chateau, on the site of the garden of Francis I, Henry IV created a large formal garden, or parterre Along the axis of the parterre, he also built a grand canal 1200 meters long, similar to one at the nearby chateau of Fleury-en-Biere. Between 1660 and 1664 the chief gardener of Louis XIV, André Le Nôtre, and Louis Le Vau rebuilt the parterre on a grander scale, filling it with geometric designs and path bordered with boxwood hedges and filled with colorful flowerbeds. They also added a basin, called Les Cascades, decorated with fountains, at the head of the canal. LeNotre planted shade trees along the length of the canal, and also laid out a wide path, lined with elm trees, parallel to the canal.[5]
The fountains of Louis XIV were removed after his reign. More recently, the Cascades were decorated with works of sculpture from the 19th century. A large ornamental fountain was installed in the central basin in 1817. A bronze replica of an ancient Roman statue, "The Tiber", was placed in the round basin in 1988. It replaced an earlier statue from the 16th century which earlier had decorated the basin. Two statues of sphinxes by Mathieu Lespagnandel, from 1664, are placed near the balustrade of the grand canal.[52]
Art and decoration - the School of Fontainebleau
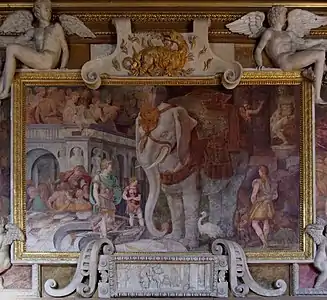 Painting by Rosso Fiorentino in the gallery of Francis I (1533–1539)
Painting by Rosso Fiorentino in the gallery of Francis I (1533–1539) Detail of stucco and woodwork in the Gallery of Francis I, by Francesco Scibec da Carpi (died c.1557)
Detail of stucco and woodwork in the Gallery of Francis I, by Francesco Scibec da Carpi (died c.1557) Diana the Huntress, School of Fontainebleau (1550–1560)
Diana the Huntress, School of Fontainebleau (1550–1560)
During the late French Renaissance, the decoration of the Palace of Fontainebleau engaged some of the finest artists and craftsmen from Italy and France, including The style of painting and decoration they created became known as the School of Fontainebleau, and covered a period from about 1530 until about 1610. It helped form the French version of Northern Mannerism.[53]
In 1531, the Florentine artist Rosso Fiorentino, having lost most of his possessions at the Sack of Rome in 1527, was invited by Francis I to work on the interior of the palace. In 1532 he was joined by another Italian artist, Francesco Primaticcio (from Bologna). Rosso died in France in 1540. On the advice of Primaticcio, Niccolò dell'Abbate (from Modena) was invited to France in 1552 by François's son Henri II. Other notable artists included:
- Juste de Juste (c.1505–1559), Franco-Italian sculptor and etcher
- Luca Penni (c.1500/1504–1556), Italian painter
- Francesco Scibec da Carpi (died c.1557), Italian furniture maker
- Benvenuto Cellini (1500–1570), Italian sculptor, goldsmith, silversmith
The works of this "first school of Fontainebleau" are characterized by the extensive use of stucco (moldings and picture frames) and frescos, and an elaborate (and often mysterious) system of allegories and mythological iconography. Renaissance decorative motifs such as grotesques, strapwork and putti are common, as well as a certain degree of eroticism. The figures are elegant and show the influence of the techniques of the Italian Mannerism of Michelangelo, Raphael and especially Parmigianino. Primaticcio was also directed to make copies of antique Roman statues for the king, thus spreading the influence of classical statuary. Many of the works of Rosso, Primaticcio and dell'Abate have not survived; parts of the Chateau were remodelled at various dates. The paintings of the group were reproduced in prints, mostly etchings, which were apparently produced initially at Fontainebleau itself, and later in Paris. These disseminated the style through France and beyond, and also record several paintings that have not survived.
From 1584 to 1594, during the Wars of Religion work inside the palace was abandoned. Upon his ascension to the throne, Henri IV undertook a renovation of the Fontainebleau buildings using a group of artists: the Flemish born Ambroise Dubois (from Antwerp) and the Parisians Toussaint Dubreuil and Martin Fréminet. They are sometimes referred to as the "second school of Fontainebleau". Their late mannerist works, many of which have been lost, continue in the use of elongated and undulating forms and crowded compositions. Many of their subjects include mythological scenes and scenes from works of fiction by the Italian Torquato Tasso and the ancient Greek novelist Heliodorus of Emesa. Second School of Fontainebleau (from 1594). The important artists of the second school were:
- Ambroise Dubois (c.1542–1614) (Flemish born)
- Toussaint Dubreuil (c.1561–1602)
- Martin Fréminet (1567–1619)
The mannerist style of the Fontainebleau school influenced French artists (with whom the Italians worked) such as the painter Jean Cousin the Elder, the sculptors Jean Goujon and Germain Pilon, and, to a lesser degree, the painter and portraitist François Clouet the son of Jean Clouet. The Fontainebleau style combined allegorical paintings in moulded plasterwork where the framing was treated as if it were leather or paper, slashed and rolled into scrolls and combined with arabesques and grotesques. Fontainebleau ideals of female beauty are Mannerist: a small neat head on a long neck, exaggeratedly long torso and limbs, small high breasts—almost a return to Late Gothic beauties. The new works at Fontainebleau were recorded in refined and detailed engravings that circulated among connoisseurs and artists. Through the engravings by the "School of Fontainebleau" this new style was transmitted to other northern European centers, Antwerp especially, and Germany, and eventually London.
While Louis XIV spent more time at Fontainebleau than any other monarch, he made most of his modifications to gardens, rather than the interiors and decor. In the 18th century, interiors underwent major change in style. Between 1750 and 1754, the architect Ange-Jacques Gabriel built a new residential wing and new apartments for Louis XV and the Queen. The most famous artists of the period, including Fraçcois Boucher, Carle Vanloo, Alexis Peyrotte and Jean-Baptiste Marie Pierre were commissioned to paint works for the Council Chamber. Louis XVI continued the decoration work, particularly in the Turkish cabinet (1777) and the game room and boudoir of the Queen, in an arabesque style. (1786–1787), up to the eve of the Revolution. Fontainebleau offers many of the best examples of interior design at the end of the Old Regime.
Napoleon I wished to continue the traditional grandeur of the monarchy, and had the palace completely refurnished. He created a new suite of rooms with the symbols and style of the Empire, and transformed the former King's bedroom into his throne room. It is the only throne room in France which is still in its original state with its original furniture. The rooms Napoleon used at Fontainebleau are among the best existing examples of the Empire style.[15]
%253B_Benvenuto_Cellini.JPG.webp) 1542 Cellini statue which would have flanked the Nymphe de Fontainebleau
1542 Cellini statue which would have flanked the Nymphe de Fontainebleau The Nymph of Fontainebleau, by Benevenuto Cellini, now in the Louvre (1542)
The Nymph of Fontainebleau, by Benevenuto Cellini, now in the Louvre (1542) 1542 Cellini statue which would have flanked the Nymphe de Fontainebleau
1542 Cellini statue which would have flanked the Nymphe de Fontainebleau
 Painting by Rosso Fiorentino in the Gallery of Francis I (1533–1539)
Painting by Rosso Fiorentino in the Gallery of Francis I (1533–1539) Allegory of painting and sculpture, by Ambroise Dubois (1543–1614)
Allegory of painting and sculpture, by Ambroise Dubois (1543–1614) Panel in the Gallery of Francis I. (Mid-16th century).
Panel in the Gallery of Francis I. (Mid-16th century). Portrait of Gabrielle d'Estrées and her sister, the Duchess of Villars, c.1594
Portrait of Gabrielle d'Estrées and her sister, the Duchess of Villars, c.1594 Master of the school of Fontainebleau, Lady at her Toilet (1585–1595) (Musée des Beaux-Arts de Dijon)
Master of the school of Fontainebleau, Lady at her Toilet (1585–1595) (Musée des Beaux-Arts de Dijon) The ceiling of the ballroom, designed by Philibert Delorme, with the symbols of Henri II and his mistress Diane de Poitiers: "HD" cyphers, three interlaced crescent moons, and Henri II's main cypher: a crowned H above a crescent moon
The ceiling of the ballroom, designed by Philibert Delorme, with the symbols of Henri II and his mistress Diane de Poitiers: "HD" cyphers, three interlaced crescent moons, and Henri II's main cypher: a crowned H above a crescent moon Decorative carved panel in the Gallery of Francis I, with his emblem, the salamander (mid 16th century).
Decorative carved panel in the Gallery of Francis I, with his emblem, the salamander (mid 16th century). The ceiling of the throne room of Napoleon I. The ceiling was originally made for Louis XIII in the 17th century, when this was his bedroom.
The ceiling of the throne room of Napoleon I. The ceiling was originally made for Louis XIII in the 17th century, when this was his bedroom. Ceiling panel in the hall of Saint Louis, built by Louis XV (18th century)
Ceiling panel in the hall of Saint Louis, built by Louis XV (18th century) Decoration over the door in the boudoir of Marie Antoinette, with her initials, (late 18th century).
Decoration over the door in the boudoir of Marie Antoinette, with her initials, (late 18th century). The bed of Marie Antoinette, ordered for her just before the French Revolution. It was used by the Empresses Josephine and Marie-Louise.
The bed of Marie Antoinette, ordered for her just before the French Revolution. It was used by the Empresses Josephine and Marie-Louise.
Museum of Napoleon I
.JPG.webp)
The Museum of Napoleon I was created in 1986 in the wing on the right side of the Court of Honor, where the apartments of the princes of the First Empire had been located. It includes a gallery of portraits of members of Napoleon's family, medals and decorations, several costumes worn during Napoleon's coronation as Emperor, and a gold leaf from the crown he wore during the coronation; a large collection of porcelain and decorative objectives from the Imperial dining table, and a cradle, toys, and other souvenirs from the Emperor's son, the King of Rome. It also has a collection of souvenirs from his military campaigns, including a recreation of his tent and its furnishings and practical items which he took with him on his campaigns.[54]
See also
- Treaty of Fontainebleau
References
Notes and citations
- "Fontainebleau". Collins Dictionary. n.d. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
- "Fontainebleau, the royal castle near Paris". Paris Digest. 2018. Retrieved 2018-09-08.
- "Palace and Park of Fontainebleau". UNESCO World Heritage Centre. United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- Salmon 2011, p. 7.
- Morel 1967, p. 28.
- Salmon 2011, p. 8.
- Salmon 2011, p. 9.
- Pérouse de Montclos 2009, p. 31.
- "Histoire de la salle de jeu de paume de Fontainebleau". Archived from the original on June 25, 2008. Retrieved March 19, 2007.
- "Cercle du jeu de paume de Fontainebleau". Archived from the original on 2014-05-17. Retrieved 2020-04-29.
- Salmon 2011, p. 10.
- Salmon 2011, p. 12.
- Мезин С.А. Взгляд из Европы: французские авторы XVIII века о Петре I. Саратов, 2003. (In Russian).
- Buvat J. Journal de la régence. T. 1. P. 269–270; Майков Л. Н. Современные рассказы... // Русский архив. 1881. Кн. 1, № 1. С. 12–13. (In Russian).
- Salmon 2011, p. 14.
- Séguin 1990, p. 26.
- Walter Bruyère-Ostells, Napoléon III et le Second Empire
- Carlier 2010, p. 37.
- "Coup de Theatre à Fontainebleau", Le Figaro, April 25, 2014.
- Le Figaro, 2 March 2015
- Salmon 2011, pp. 23–24.
- "The chapelle basse Saint-Saturnin". Palace of Fontainebleau. Archived from the original on 7 August 2017. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- "The chapelle haute Saint-Saturnin". Palace of Fontainebleau. Archived from the original on 7 July 2018. Retrieved 23 February 2016.
- Salmon 2011, p. 26.
- Carlier 2010, pp. 80–82.
- Salmon 2011, p. 31.
- Salmon 2011, p. 41.
- Carlier 2010, pp. 91–93.
- Salmon 2011, p. 42.
- Carlier 2010, p. 95.
- Salmon 2011, p. 44.
- Salmon 2011, p. 47.
- Carlier 2010, p. 96.
- Carlier 2010, pp. 110–111.
- Carlier 2010, p. 88.
- Salmon 2011, p. 95.
- Carlier 2010, p. 98.
- Salmon 2011, p. 51.
- Carlier 2010, pp. 119–120.
- Salmon 2011, p. 86.
- Salmon 2011, pp. 84–85.
- Carlier 2010, p. 121.
- Salmon 2011, p. 85.
- Salmon 2011, p. 55.
- Carlier 2010, p. 102.
- Carlier 2010, p. 104.
- Carlier 2010, p. 106.
- Salmon 2011, p. 56.
- Carlier 2010, pp. 45–46.
- Salmon 2011, p. 90.
- Salmon 2011, p. 91.
- Salmon 2011, p. 92.
- Oxford Dictionary of Art
- Salmon 2011, pp. 74–79.
Bibliography
- Allain, Yves-Marie (2006). L'art des jardins en Europe (in French). Paris: Citadelles & Mazenod. ISBN 2-85088-087-6.
- Carlier, Yves (2010). Histoire du château de Fontainebleau (in French). Paris: Editions Jean-Paul Gisserot. ISBN 978-2-75580-022-7.
- Dan, Pierre (1642). Le Trésor des merveilles de la Maison Royale de Fontainebleau. Paris: S. Cramoisy. OCLC 457360433; copy at INHA.
- Morel, Pierre (1967). Aspects de la France - Fontainebleau. Artaud.
- Pérouse de Montclos, Jean-Marie (2009). Le château de Fontainebleau (in French). Paris: Nouvelles Éditions Scala. ISBN 9782359880045.
- Salmon, Xavier (2011). Fontainebleau- Vrai demeure des rois, maison des siècles (in French). Versailles: Artlys. ISBN 978-2-85495-442-5.
- Séguin, Philippe (1990). Louis Napoléon Le Grand (in French). Paris: Bernard Grasset. ISBN 2-246-42951-X.
External links
- Official website
- World Heritage profile (in English)
- Fontainebleau Castle (in English)
- Documentary film about the Palace of Fontainebleau: Fontainebleau: A Rendezvous at the Castle (in English)
- Discover the Palace of Fontainebleau on Eurochannel
- High-resolution 360° Panoramas of the Palace of Fontainebleau | Art Atlas
- Virtual tour of the Palace of Fontainebleau provided by Google Arts & Culture
 Media related to Palace of Fontainebleau at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Palace of Fontainebleau at Wikimedia Commons
