Douro
The Douro (UK: /ˈdʊəroʊ, ˈdʊəruː/, US: /ˈdɔːruː, ˈdɔːroʊ, ˈdoʊru/,[1][2][3][4] Portuguese: [ˈdo(w)ɾu]; Spanish: Duero [ˈdweɾo]; Latin: Durius) is the highest-flow river of the Iberian Peninsula. It rises near Duruelo de la Sierra in Soria Province, central Spain, meanders south briefly then flows generally west through the north-west part of central Spain and into northern Portugal, to its mouth at Porto, the second largest city of Portugal. At its mouth it meets the Atlantic Ocean.
| Douro | |
|---|---|
_(cropped).jpg.webp) The river flowing through the Portuguese wine region, designated as a World Heritage Site. | |
.png.webp) | |
| Location | |
| Country | Spain, Portugal |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Picos de Urbión |
| • location | Sistema Ibérico, Duruelo de la Sierra, Soria, Castile and León, Spain |
| • coordinates | 42°0′38″N 2°52′49″W |
| • elevation | 2,157 m (7,077 ft) |
| Mouth | Foz do Douro |
• location | Atlantic Ocean, Porto, Greater Porto, Norte, Portugal |
• coordinates | 41°8′36″N 8°40′10″W |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 897 km (557 mi) |
| Basin size | 98,400 km2 (38,000 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Porto |
| • average | 700 m3/s (25,000 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 17,000 m3/s (600,000 cu ft/s) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | Pocinho |
| • average | 442 m3/s (15,600 cu ft/s) |
| Basin features | |
| Tributaries | |
| • left | Tera, Rituerto, Riaza, Duratón, Cega, Adaja, Tormes, Águeda, Côa, Torto, Távora, Varosa, Bestança, Paiva, Arda, Inha |
| • right | Pisuerga, Valderaduey, Esla, Sabor, Tua, Corgo, Tâmega, Sousa |
The scenic Douro railway line runs close to the river. Adjacent areas produce port (a mildly fortified wine) and other agricultural produce. A small tributary of the river has the Côa Valley Paleolithic Art site which is considered important to the archaeological pre-historic patrimony, designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Within Spain, it flows through the middle of the autonomous community of Castile and León, with the basin spanning through the northern half of the Meseta Central. The latter includes wine producing areas such as the Ribera del Duero DOP.
History
The Latin name Durius was likely a Celtic name before overwhelming Romanization of both main Iberian languages. If so the Celtic root is *dubro- (in which family of languages the final vowel sound often changes with context, as in Latin).[5] In modern Welsh, dŵr is "water," which is cognate with dour in modern Breton, dobhar in Irish and gives rise to Dover on the Dour and the other modest rivers the Dever and Deveron (Dubh Èireann) in British Isles. In Roman times, the river was personified as a god, Durius.
A folk-etymological derivation suggests that the name comes from the Portuguese or Spanish for "golden".[6][7]
The drainage basin was depopulated in the 8th century. According to Claudio Sánchez-Albornoz this was a deliberate act by Alfonso I of Asturias for the defence of his Kingdom, which led the area to be named Repoblación.
The Douro vinhateiro (vine-land) of the Douro Valley in Portugal, long devoted to vineyards, has been designated by UNESCO as a World Heritage Site. The wine was taken downriver in flat-bottom boats called rabelos, to be stored in barrels in cellars in Vila Nova de Gaia, just across the river from Porto. Nowadays port is transported there in tanker trucks.
In the 1960s and 1970s, dams with locks were built along the river, allowing river traffic into the upper regions in Spain and along the border.
In 1998, Portugal and Spain signed the Albufeira Convention, an agreement on the sharing of trans-boundary rivers to include the Douro, Tagus and Guadiana. The convention superseded an agreement on the Douro, signed in 1927, that was expanded in 1964 and 1968 to include tributaries.[8]
Geography

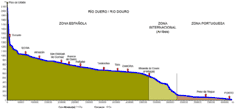
It is the third-longest river in the Iberian Peninsula after the Tagus and Ebro. Its total length is 897 kilometres (557 mi),[9] of which only sections of the Portuguese section, being below a fall/rapids line, are naturally navigable, by modest rivercraft.[10]
In its Spanish section, the Douro crosses the great Castilian meseta and meanders through five provinces of the autonomous community of Castile and León: Soria, Burgos, Valladolid, Zamora, and Salamanca, passing through the towns of Soria, Almazán, Aranda de Duero, Tordesillas, and Zamora.
The most important tributaries in this region are the Pisuerga, passing through Valladolid, and the Esla, which passes through Zamora. This region is generally semi-arid plains, with wheat and in some places, especially near Aranda de Duero, with vineyards, in the Ribera del Duero wine region. Sheep rearing is also still important.
The drainage basin borders those of Miño to the north, Ebro to the east, and Tajo to the south.[9][10]
For 112 kilometres (70 mi), the river forms part of the national border line between Spain and Portugal, in a region of narrow canyons. It formed a historical barrier to invasions, creating a cultural/linguistic divide. In these isolated areas, in which the Aldeadávila Dam impounds the river, there are protected areas: the International Douro Natural Park (on the Portuguese side) and the Arribes del Duero Natural Park (on the Zamoran margin).
The Douro fully enters Portuguese territory just after the confluence with the Águeda River; once the Douro enters Portugal, major population centres are less frequent along the river. Except for Porto and Vila Nova de Gaia at the river mouth, the only population centres of any note are Foz do Tua, Pinhão and Peso da Régua. Tributaries here are small, merging into the Douro along the canyons; the most important are Côa, Tua, Sabor, Corgo, Tavora, Paiva, Tâmega, and Sousa. None of these small, fast-flowing rivers is navigable.
Human geography

Major Spanish riverside towns include Soria, Almazán, Aranda de Duero, Tordesillas, Zamora and major Portuguese towns include Miranda do Douro, Foz Côa, Peso da Régua, Lamego, Vila Nova de Gaia, and Porto. The most populous cities along the Douro River are Valladolid and Zamora in Spain, and Porto and Vila Nova de Gaia in Portugal. The latter two are located at the mouth of the Douro at the Atlantic Ocean.
In Portugal, the Douro flows through the districts of Bragança, Guarda, Viseu, Vila Real, Aveiro and Porto. Porto is the main hub city in northern Portugal. Its historic centre has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site because of its significant architecture and history.
Economy

These reaches of the Douro have a microclimate allowing for cultivation of olives, almonds, and especially grapes, which are important for making port. The region around Pinhão and São João da Pesqueira is considered to be the centre of port, with its quintas (or farms/estates) that extend along the steep slopes of the river valleys. In the 21st century, many of these are owned by multinational, reputed wine companies.
Recently, a prosperous tourist industry has developed based on river excursions from Porto to points along the Upper Douro valley.
The Douro railway line (Linha do Douro) was completed in 1887; it connects Porto, Rio Tinto, Ermesinde, Valongo, Paredes, Penafiel, Livração, Marco de Canaveses, Régua, Tua and Pocinho.
Pocinho is near the very small city of Foz Côa, which is close to Côa Valley Paleolithic Art site. This is considered important to the archaeological pre-historic patrimony, and it has been designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Dams
Fifteen dams have been built on the Douro to regulate the water flow, generate hydroelectric power, and allow navigation through locks. Beginning at the headwaters, the first five dams are in Spain: Cuerda del Pozo, Los Rábanos, San José, Villalcampo and Castro Dams. The next five downstream are along the Portuguese-Spanish border; the first three are owned and operated by Portugal: (Miranda, Picote and Bemposta Dams), while the next two belong to Spain: (Aldeadávila and Saucelle Dams).
The Douro's last five dams are in Portugal, and allow for navigation: Pocinho, Valeira, Régua, Carrapatelo, and Crestuma–Lever dams. Vessels with a maximum length of 83 metres (272 ft) and width of 11.4 metres (37 ft) can pass through the five locks. The highest lock, at Carrapatelo Dam, has a maximum lift of 35 metres (115 ft). The waters of Pocinho lake reach 125 metres (410 ft) above sea level. Unannounced releases of water from upstream Spanish dams occasionally causes navigation issues in these locks.
Gallery
.jpg.webp) The Douro in Zamora (Spain)
The Douro in Zamora (Spain) The Pisuerga River (tributary to the Duero) in Valladolid
The Pisuerga River (tributary to the Duero) in Valladolid.jpg.webp) The Upper Douro valley where Port wine grapes grow
The Upper Douro valley where Port wine grapes grow The typical rabelo boat and Porto historical district in background
The typical rabelo boat and Porto historical district in background Port wine signs by the Douro River
Port wine signs by the Douro River Panoramic view of Oporto
Panoramic view of Oporto The river between Porto and Vila Nova de Gaia
The river between Porto and Vila Nova de Gaia The river near Régua, Portugal
The river near Régua, Portugal Douro Internacional near Miranda do Douro
Douro Internacional near Miranda do Douro Arribes del Duero near Aldeadávila
Arribes del Duero near Aldeadávila The river mouth in Porto
The river mouth in Porto.jpg.webp) Over Porto
Over Porto Douro Estuary
Douro Estuary Looking across the river mouth from Foz do Douro to Vila Nova de Gaia (Atlantic Ocean on the right)
Looking across the river mouth from Foz do Douro to Vila Nova de Gaia (Atlantic Ocean on the right) Typical almond tree, mostly seen along the river in Portugal
Typical almond tree, mostly seen along the river in Portugal
See also
- List of rivers of Portugal
- List of rivers of Spain
References
- "Douro". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). HarperCollins. Retrieved March 31, 2019.
- "Douro". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved March 31, 2019.
- "Douro" (US) and "Douro". Lexico UK English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. Archived from the original on 2020-07-30.
- "Douro". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved March 31, 2019.
- Robert Ferguson (1862). The River-names of Europe. Williams & Norgate. pp. 26–.
- Nick Timmons, Portugal (1994), p. 99: "The Douro... the Golden River (d'ouro means 'of gold')..."
- DK Eyewitness Travel Guide Portugal (2016), p. 239: "...the Douro or “Golden River” weaves its scenic path through deep-cleft gorges..."
- "Spanish-Portuguese Albufeira Convention". United Nations. Retrieved 18 February 2015.
- "Rivers in Spain". www.iberianature.com. Retrieved 12 August 2017.
- "Guide to Spain CO-CU". www.iberianature.com. Retrieved 12 August 2017.