Pac-12 Conference
The Pac-12 Conference is a collegiate athletic conference, that operates in the Western United States, participating in 24 sports at the NCAA Division I level. Its football teams compete in the Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS; formerly Division I-A), the highest level of college football in the nation.
 | |
| Formerly | Pacific Coast Conference (PCC, 1915–1959) Athletic Association of Western Universities (AAWU, 1959–1968) Pacific-8 (1968–1978) Pacific-10 (1978–2011) |
|---|---|
| Association | NCAA |
| Founded | 1915 (as Pacific Coast Conference) 1959 (as AAWU) |
| Commissioner | George Kliavkoff (since July 1, 2021) |
| Sports fielded |
|
| Division | Division I |
| Subdivision | FBS |
| No. of teams | 12 (10 in 2024) |
| Headquarters | San Francisco, California |
| Region | Southwest |
| Official website | pac-12 |
| Locations | |
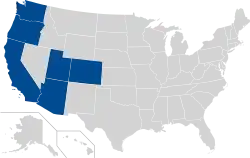 | |
The conference's 12 members are located in the states of Arizona, California, Colorado, Oregon, Utah, and Washington. They include each state's flagship public university, four additional public universities, and two private research universities.
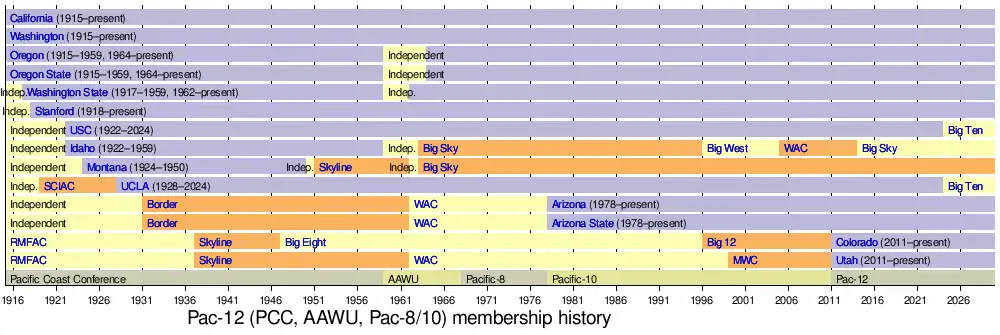
The modern Pac-12 conference formed after the disbanding of the Pacific Coast Conference (PCC), whose principal members founded the Athletic Association of Western Universities (AAWU) in 1959. The conference previously went by the names Big Five, Big Six, Pacific-8, and Pacific-10. The Pac-12 moniker was adopted in 2011 with the addition of Colorado and Utah.
Nicknamed the "Conference of Champions", the Pac-12 has won more NCAA national championships in team sports than any other conference in history. The top three schools with the most NCAA team championships are members of the Pac-12: Stanford, University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) and University of Southern California (USC), respectively. Washington's national title in women's rowing in 2017 was the 500th NCAA championship won by a Pac-12 school.[1]
On June 30, 2022, amid the broader 2021–22 NCAA conference realignment, UCLA and USC announced plans to leave the Pac-12 for the Big Ten Conference starting in 2024.[2][3]
Member schools

Full members
The Pac-12 has twelve full member institutions. Football used to be the only sport where the conference is split into two divisions, the North Division and the South Division.
The Pac-12's members are spread evenly between 3 regions, with 4 schools each in California, the Pacific Northwest, and the Four Corners region.
| Institution | Location | Founded | Joined | Type | Enrollment | Endowment | Nickname | Colors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Arizona | Tucson, Arizona | 1885 | 1978 | Public | 43,625[4] | $1.26 billion | Wildcats | |
| Arizona State University | Tempe, Arizona | 1885 | 1978 | 71,946[5] | $1.25 billion | Sun Devils | ||
| University of California, Berkeley | Berkeley, California | 1868 | 1915 | 41,910[6] | $2.92 billion | Golden Bears | ||
| University of California, Los Angeles[lower-alpha 1] | Los Angeles, California | 1919 | 1928 | Public | 45,428[7] | $3.89 billion | Bruins | |
| University of Colorado, Boulder | Boulder, Colorado | 1876 | 2011 | Public | 33,246[8] | $2.12 billion | Buffaloes | |
| University of Oregon | Eugene, Oregon | 1876 | 1915 | 22,980[9] | $1.19 billion | Ducks | ||
| Oregon State University | Corvallis, Oregon | 1868 | 1915 | 31,904[10] | $0.83 billion | Beavers | ||
| University of Southern California[lower-alpha 1] | Los Angeles, California | 1880 | 1922 | Private | 49,500[11] | $8 billion | Trojans | |
| Stanford University | Stanford, California | 1891 | 1918 | Private | 16,336[12] | $37.80 billion | Cardinal | |
| University of Utah | Salt Lake City, Utah | 1850 | 2011 | Public | 33,000[13] | $1.32 billion | Utes | |
| University of Washington | Seattle, Washington | 1861 | 1915 | 46,081 | $4.07 billion | Huskies | ||
| Washington State University | Pullman, Washington | 1890 | 1917 | 30,614 | $1.28 billion | Cougars |
- Notes
- Signed a deal in the summer of 2022 to leave the Pac-12 and join the Big Ten Conference in the 2024 academic year.
Affiliate members
The Pac-12 has three affiliate member institutions in California and one in Arkansas.
| Institution | Location | Founded | Joined | Type | Enrollment | Nickname | Colors | Pac-12 sport(s) | Primary conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| California Polytechnic State University | San Luis Obispo, California | 1901 | 1986–87 | Public | 19,777 | Mustangs | Wrestling | Big West | |
| California State University, Bakersfield[lower-alpha 1] | Bakersfield, California | 1965 | 1987–88 | 8,002 | Roadrunners | ||||
| University of Arkansas at Little Rock | Little Rock, Arkansas | 1927 | 2019–20 | 11,845 | Trojans | OVC | |||
| San Diego State University | San Diego, California | 1897 | 2005–06 | 35,578 | Aztecs | Men's soccer | Mountain West |
- Notes
- Cal State–Bakersfield initially announced it would become a men's soccer affiliate starting in 2013,[14] but never went through with those plans, accepting an invitation to become an all-sports member of the Western Athletic Conference, which sponsors men's soccer, also in 2013; it would move to the Big West Conference, which also sponsors men's soccer, in 2020. The school maintains its Pac-12 affiliation in wrestling, which neither the WAC nor the Big West sponsors.[15]
Future affiliate members
The Pac-12 women's lacrosse league will add two affiliate members, both from California, in the 2024 season (2023–24 school year). San Diego State, already a men's soccer member, will add women's lacrosse to its Pac-12 membership.[16]
| Institution | Location | Founded | Joining | Type | Enrollment | Nickname | Colors | Pac-12 sport(s) | Primary conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Diego State University | San Diego, California | 1897 | 2023–24 | Public | 35,578 | Aztecs | Women's lacrosse | Mountain West | |
| University of California, Davis (UC Davis) | Davis, California | 1908 | 40,031 | Aggies | Women's lacrosse | Big West |
Former members
No school has left the Pac-12 since its founding as the AAWU in 1959. Two members of the PCC were not invited to join the AAWU or its successors.
| Institution | Location | Founded | Joined | Left | Type | Nickname | Colors | Current conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| University of Idaho | Moscow, Idaho | 1889 | 1922 | 1959 | Public | Vandals | Big Sky | |
| University of Montana | Missoula, Montana | 1893 | 1924 | 1950 | Grizzlies |
Former affiliate members
| Institution | Location | Founded | Joined | Left | Type | Nickname | Colors | Pac-12 sport | Primary conference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boise State University | Boise, Idaho | 1932 | 1987 | 2017 | Public | Broncos | Wrestling[lower-alpha 1] | Mountain West | |
| University of California, Davis | Davis, California | 1905 | 1992 | 2010 | Aggies | Big West | |||
| University of California, Santa Barbara | Santa Barbara, California | 1909 | 2010 | 2015 | Gauchos | Men's swimming & diving[lower-alpha 2] | |||
| California Polytechnic State University | San Luis Obispo, California | 1901 | Mustangs | ||||||
| California State University, Fresno | Fresno, California | 1911 | 1986 | 1991 | Bulldogs | Wrestling[lower-alpha 3] | Mountain West | ||
| California State University, Fullerton | Fullerton, California | 1957 | 2011 | Titans | Big West | ||||
| Eastern Washington University | Cheney, Washington | 1882 | 1982 | 1990 | Eagles | Baseball | Big Sky | ||
| Gonzaga University | Spokane, Washington | 1887 | 1995 | Private | Bulldogs | West Coast | |||
| Portland State University | Portland, Oregon | 1946 | 1983 | 1998 | Public | Vikings | Wrestling | Big Sky | |
| 1998 | 2009 | ||||||||
| University of Portland | Portland, Oregon | 1901 | 1982 | 1995 | Private | Pilots | Baseball | West Coast | |
| San Jose State University | San Jose, California | 1857 | 1986 | 1988 | Public | Spartans | Wrestling | Mountain West | |
| Utah State University | Logan, Utah | 1888 | 1989 | Aggies |
- Notes
- Boise State dropped wrestling after the 2016–17 season.
- UCSB's men's swimming & diving team now competes in the Mountain Pacific Sports Federation.
- Fresno State eventually dropped wrestling after the 2005–06 season. The program was revived in 2017 and competed in the Big 12 Conference until being discontinued again after the 2020–21 season.
Facilities
| School | Football stadium | Capacity | Basketball arena | Capacity | Baseball stadium | Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | Arizona Stadium | 50,782[17] | McKale Center | 14,655[18] | Hi Corbett Field | 9,500[19] |
| Arizona State | Sun Devil Stadium | 53,599[20] | Desert Financial Arena | 14,198[21] | Phoenix Municipal Stadium | 8,775[22] |
| California | California Memorial Stadium | 62,467[23] | Haas Pavilion | 11,877[24] | Evans Diamond | 2,500[25] |
| Colorado | Folsom Field | 50,183[26] | CU Events Center | 11,064[27] | No team, dropped in 1980 | |
| Oregon | Autzen Stadium | 54,000[28] | Matthew Knight Arena | 12,346[29] | PK Park | 3,600[30] |
| Oregon State | Reser Stadium | 26,407[lower-alpha 1] | Gill Coliseum | 9,604[32] | Goss Stadium at Coleman Field | 3,248[33] |
| Stanford | Stanford Stadium | 50,424[34] | Maples Pavilion | 7,233[35] | Klein Field at Sunken Diamond | 4,000[36] |
| UCLA | Rose Bowl | 92,542[37] | Pauley Pavilion | 13,800[38][39] | Jackie Robinson Stadium | 1,820[40] |
| USC | Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum | 77,500[41] | Galen Center | 10,258[42] | Dedeaux Field | 2,500[43] |
| Utah | Rice-Eccles Stadium | 51,444[44] | Jon M. Huntsman Center | 15,000[45] | Smith's Ballpark | 15,411[46] |
| Washington | Husky Stadium | 70,083[47] | Hec Edmundson Pavilion | 10,000[48] | Husky Ballpark | 2,212[49] |
| Washington State | Martin Stadium | 32,952[50] | Beasley Coliseum | 11,671[51] | Bailey-Brayton Field | 3,500[52] |
- Capacity for the 2022 season during renovations set for completion in 2023. The future capacity has not yet been announced, but is expected to be between 34,000 and 39,000.[31]
Key personnel
| School | Athletic director | Football coach | Salary[53] | Men's basketball coach | Salary[54] | Women's basketball coach | Baseball coach | Softball coach | Volleyball coach (women, men) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | Dave Heeke | Jedd Fisch | $2,683,449 | Tommy Lloyd | $2,900,000 | Adia Barnes | Chip Hale | Caitlin Lowe | David Rubio |
| Arizona State | Ray Anderson | Shaun Aguano(interim) | $225,000 | Bobby Hurley | $2,555,000 | Natasha Adair | Willie Bloomquist | Tricia Ford | Sanja Tomasevic |
| California | Jim Knowlton | Justin Wilcox | $4,750,000 | Mark Fox | $1,575,000 | Charmin Smith | Mike Neu | Chelsea Spencer | Sam Crosson |
| Colorado | Rick George | Mike Sanford Jr.(interim) | $650,000 | Tad Boyle | $1,800,000 | JR Payne | No team | No team | Jesse Mahoney |
| Oregon | Rob Mullens | Dan Lanning | $4,850,000 | Dana Altman | $3,325,000 | Kelly Graves | Mark Wasikowski | Melyssa Lombardi | Matt Ulmer |
| Oregon State | Scott Barnes | Jonathan Smith | $3,250,000 | Wayne Tinkle | $2,500,672 | Scott Rueck | Mitch Canham | Laura Berg | Mark Barnard |
| Stanford | Bernard Muir | David Shaw | NA† | Jerod Haase | NA† | Tara VanDerveer | David Esquer | Jessica Allister | Kevin Hambly |
| UCLA | Martin Jarmond | Chip Kelly | $4,600,000 | Mick Cronin | $3,600,000 | Cori Close | John Savage | Kelly Inouye-Perez | Michael Sealy, John Speraw |
| USC | Mike Bohn | Lincoln Riley | NA† | Andy Enfield | NA† | Lindsay Gottlieb | Jason Gill | No team | Brad Keller |
| Utah | Mark Harlan | Kyle Whittingham | $6,000,000 | Craig Smith | $1,850,000 | Lynne Roberts | Gary Henderson | Amy Hogue | Beth Launiere |
| Washington | Jennifer Cohen | Kalen DeBoer | $3,100,000 | Mike Hopkins | $2,800,004 | Tina Langley | Jason Kelly | Heather Tarr | Keegan Cook |
| Washington State | Pat Chun | Jake Dickert | $2,700,000 | Kyle Smith | $1,400,000 | Kamie Ethridge | Brian Green | No team | Jen Greeny |
†Private institution not required to release coaching salaries •Salaries based on 2021–2022 academic year
Academics
Nine of the twelve member schools are members of the Association of American Universities (AAU) as of 2019, including all four California-based schools,[55] as well as at least one university in each state that has a Pac-12 member university. This is the second-highest number of AAU universities among FBS conferences (behind only the Big Ten Conference).
- University of Arizona
- University of California, Berkeley
- University of California, Los Angeles
- University of Colorado Boulder
- University of Oregon
- University of Southern California
- Stanford University
- University of Washington
- University of Utah
Additionally, these member schools are also highly ranked nationally and globally by various groups, including the Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) and Times Higher Education World University Rankings (Times).
Athletic department revenue by school
Total revenue includes ticket sales, contributions and donations, rights and licensing, student fees, school funds and all other sources including TV income, camp income, concessions, and novelties. Total expenses includes coach and staff salaries, scholarships, buildings and grounds, maintenance, utilities and rental fees, recruiting, team travel, equipment and uniforms, conference dues, and insurance.
The following table is updated to show institutional reporting to the Department of Education as shown on the DOE Equity in Athletics website for the 2013–14 academic year. The national ranking of revenue is based on 2075 institutions reporting to the Department of Education that year.
| Conf rank (2013–14) |
National rank (2013–14) |
Institution | 2013–14 Total revenue from athletics |
2013–14 Total expenses on athletics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 12 | Stanford University | $110,240,490 | $110,240,490 |
| 2 | 13 | University of Southern California | $106,528,649 | $106,528,649 |
| 3 | 19 | University of Washington | $100,275,186 | $86,097,136 |
| 4 | 22 | University of Arizona | $97,630,769 | $93,273,995 |
| 5 | 27 | University of California, Berkeley | $90,262,140 | $76,446,272 |
| 6 | 33 | University of California, Los Angeles | $86,426,780 | $86,426,780 |
| 7 | 35 | University of Oregon | $81,546,443 | $79,961,755 |
| 8 | 45 | Arizona State University | $72,775,808 | $72,599,644 |
| 9 | 55 | Oregon State University | $67,033,751 | $67,033,751 |
| 10 | 60 | University of Colorado | $64,303,098 | $64,303,098 |
| 11 | 62 | Washington State University | $60,727,273 | $60,727,273 |
| 12 | 65 | University of Utah | $59,005,590 | $57,819,434 |
Apparel
| School | Provider |
|---|---|
| Arizona | Nike |
| Arizona State | Adidas |
| California | Under Armour |
| Colorado | Nike |
| Oregon | Nike |
| Oregon State | Nike, Asics (volleyball only) |
| Stanford | Nike |
| UCLA | Jordan |
| USC | Nike |
| Utah | Under Armour |
| Washington | Adidas |
| Washington State | Nike |
History
Pacific Coast Conference
The roots of the Pac-12 Conference go back to December 2, 1915, when the Pacific Coast Conference (PCC) was founded at a meeting at the Imperial Hotel in Portland, Oregon.[56] Charter members were the University of California (now University of California, Berkeley), University of Washington, University of Oregon, and Oregon Agricultural College (now Oregon State University). The PCC began play in 1916.
One year later, Washington State College (now Washington State University) joined the league, followed by Stanford University in 1918.
In 1922, the PCC expanded to eight teams with the admission of USC and Idaho. Montana joined the Conference in 1924, and in 1928, the PCC grew to 10 members with the addition of UCLA.
For many years, the conference split into two divisions for basketball and baseball – a Southern Division comprising the four California schools and a Northern Division comprising the six schools in the Pacific Northwest.
In 1950, Montana departed to join the Mountain States Conference. The PCC continued as a nine-team league through June 1959.
AAWU (Big Five and Big Six)
Following "pay-for-play" scandals at California, USC, UCLA, and Washington, the PCC disbanded in June 1959. Ten months earlier in August 1958, these four schools agreed to form a new conference that would take effect the following summer.[57][58] When the four schools and Stanford began discussions for a new conference in 1959, retired Admiral Thomas J. Hamilton interceded and suggested the schools consider creating a national "power conference" (Hamilton had been a key player, head coach, and athletic director at Navy, and was the current athletic director at Pittsburgh). Nicknamed the "Airplane Conference,"[59][60][61] the five former PCC schools would have played with other major academically-oriented schools, including Army, Navy, Air Force, Notre Dame, Pitt, Penn State, and Syracuse.[59][62] The effort fell through when a Pentagon official vetoed the idea and the service academies backed out.[63]
On July 1, 1959, the new Athletic Association of Western Universities was launched, with California, UCLA, USC, and Washington as the four charter members.[64] Stanford joined during the first month.[58][65] Hamilton left Pittsburgh to become the first commissioner of the AAWU,[64][66] and remained for twelve years.[67] The conference also was popularly known as the Big Five from 1960 to 1962.[68] When Washington State joined in 1962,[69] the conference became informally known as the Big Six.[68][70] The new league inherited the PCC's berth in the Rose Bowl; since 1947, the PCC champion had received an automatic bid to the bowl.
Pacific-8
Oregon and Oregon State joined in the summer of 1964.[71][72][73] With their addition, the conference was known unofficially as the Pacific Athletic Conference,[74][75][76][77][78] and then the Pacific-8 (as there already was a major conference called the Big Eight). In 1968, the AAWU formally renamed itself the Pacific-8 Conference, or Pac-8 for short. The Pac-8 did not allow a second bowl team from the conference until the 1975 season;[79] in basketball, participation in the National Invitation Tournament (NIT) was not allowed until 1973.[80]
Idaho was never invited to join the AAWU;[73] the Vandals were independent for four years until the formation of the Big Sky Conference in 1963, and were independent in football until 1965.
Pacific-10

In 1978, the conference added Arizona and Arizona State from the Western Athletic Conference, becoming the Pacific-10 Conference or Pac-10. The invitations to the schools were extended in December 1976,[81] and the expansion formally announced in May 1977.[82]
In 1986, the Pac-10 began sponsoring women's athletics. Prior to this time members' women's teams competed with other large universities on the Pacific coast in either the Northern Pacific Conference or the Western Collegiate Athletic Association.
In the mid-1990s the conference expressed interest in admitting the University of Colorado and the University of Texas after the collapse of the Southwest Conference. Texas expressed an interest in joining a strong academic conference, but joined three fellow Southwest Conference schools (Texas A&M, Texas Tech, and Baylor) to merge with the Big Eight Conference to form the Big 12 Conference in 1996. Colorado elected to remain in the newly formed Big 12.[83]
Before the addition of Colorado and Utah in 2011, only the Ivy League had maintained its membership for a longer time than the Pac-10 among Division I conferences. Commissioner Larry Scott said on February 9, 2010, that the window for expansion was open for the next year as the conference began negotiations for a new television deal. Speaking on a conference call to introduce former Big 12 commissioner Kevin Weiberg as his new deputy, Scott talked about possibly adding new teams to the conference and launching a new television network.[84] Scott, the former head of the Women's Tennis Association, took over the conference in July 2009. In his first eight months on the job, he saw growing interest from the membership over the possibility of adding teams for the first time since Arizona and Arizona State joined the conference in 1978.
Pac-12
In early June 2010, there were reports that the Pac-10 was considering adding up to six teams to the conference: the University of Texas, Texas A&M University, Texas Tech University, the University of Oklahoma, Oklahoma State University, and the University of Colorado.[85]
On June 10, 2010, the University of Colorado Boulder officially accepted an invitation to join the Pac-10 Conference, effective starting with the 2012–2013 academic year.[86][87] The school later announced it would join the conference a year earlier than previously announced, in the 2011–2012 academic year.
On June 15, 2010, a deal was reached between Texas and the Big 12 Conference to keep Texas, Texas A&M, Texas Tech, Oklahoma, and Oklahoma State in the Big 12. Following Texas' decision, the other Big 12 schools that had been rumored candidates to join the Pac-10 announced they would remain in the Big 12. This deal effectively ended the Pac-10's ambition to potentially become a sixteen-team conference.[88]
On June 17, 2010, the University of Utah officially accepted an invitation to join the Pac-10 Conference, effective starting July 2011.[86] Utah was a member of the Western Athletic Conference (WAC) with Arizona and Arizona State before those two left for the Pac-10 in 1978. The Utes left an expanded WAC with seven other schools in 1999 to form the new Mountain West Conference. Utah became the first "BCS Buster" to join a BCS conference, having played in (and won) two BCS games beforehand.
On July 27, 2010, the conference unveiled a new logo and announced that the Pac-10 would be renamed the Pac-12 when Utah and Colorado formally joined in July 2011. On October 21, the Pac-12 announced that its football competition would be split into two divisions—a North Division comprising the Pacific Northwest and Bay Area schools, and a South Division comprising the Mountain Time Zone and Southern California schools. On July 1, 2011, the Pac-12 assumed its current alignment when both Colorado and Utah officially joined as full members.
On August 15, 2012, the conference debuted the Pac-12 Network. It was the third college sports conference to launch a dedicated network, and the first to completely fund and own their own network outright. Since 2014, the conference has been headquartered in San Francisco, California, with the conference moving to working remotely once the lease expires in June 2023.[89] It had been based in the nearby East Bay suburb of Walnut Creek since the late 1970s.[90]
NCAA conference realignment (2021-present)
On August 24, 2021, the Pac-12, ACC, and Big Ten announced the formation of a "historic alliance" that would bring their member institutions "together on a collaborative approach surrounding the future evolution of college athletics and scheduling."[91] The formation of this alliance between 3 of the Power Five conferences was in response to Oklahoma and Texas announcing plans to leave the Big-12 and join the SEC. The alliance included an inter-conference scheduling component for football and men's and women's basketball. In 2021, the Pac-12 paid $19.8 million to its member schools, the lowest distribution in the Power Five.[92]
On June 30, 2022, UCLA[93] and USC[94] announced their departure to the Big Ten Conference beginning in the 2024–25 academic year.
Membership timeline
The Pac-12 claims the PCC's history as its own. Not only does it maintain the automatic bid from the Rose Bowl inherited from the PCC, but the eight largest schools in the old PCC all eventually joined the new league. However, the old PCC operated under a separate charter.
The Pac-12 is one of the founding members of the Mountain Pacific Sports Federation (MPSF), a conference organized to provide competition in non-revenue Olympic sports. All-Pac-12 members participate in at least one MPSF sport (men's and women's indoor track and field both actually have enough participating Pac-12 schools for the conference to sponsor a championship, but the Pac-12 has opted not to do so). For certain sports, the Pac-12 admits certain schools as associate members.
Full members
Sponsored sports
The Pac-12 Conference sponsors championship competition in 10 men's and 13 women's NCAA-sanctioned sports, plus one men's sport that is not sanctioned by the NCAA. Four schools are associate members, each in a single men's sport.[95]
The newest sport to be sponsored by the Pac-12 is women's lacrosse, which began play in spring 2018 following the elevation of Arizona State's club team to full varsity status.[96]
| Sport | Men's | Women's |
|---|---|---|
| Baseball | 11 | – |
| Basketball | 12 | 12 |
| Beach volleyball ^ | – | 9 |
| Cross country | 9 | 12 |
| Football | 12 | – |
| Golf | 12 | 11 |
| Gymnastics | – | 8 |
| Lacrosse | – | 6 |
| Rowing † | 6 | 7 |
| Soccer | 6 | 12 |
| Softball | – | 9 |
| Swimming & Diving | 8 | 9 |
| Tennis | 8 | 11 |
| Track & Field Outdoor | 10 | 12 |
| Volleyball | – | 12 |
| Wrestling | 6 | – |
- ^ — Beach volleyball is a fully sanctioned NCAA sport which held its first national championship in the spring of 2016.[97] The Pac-12 is the second conference (after the ASUN Conference) to sponsor a championship in the sport.[98]
- † — Rowing (M) is sanctioned by the Intercollegiate Rowing Association, not by the NCAA; Rowing (W) is sanctioned by both.
Men's sponsored sports by school
Member-by-member sponsorship of the 11 men's Pac-12 sports.
| School | Baseball | Basketball | Cross Country | Football | Golf | Rowing[lower-alpha 1] | Soccer | Swimming & Diving | Tennis | Track & Field Outdoor | Wrestling | Total Pac-12 Sports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | 8 | |||||||||||
| Arizona State | 9 | |||||||||||
| California | 10 | |||||||||||
| Colorado | 5 | |||||||||||
| Oregon | 7 | |||||||||||
| Oregon State | 7 | |||||||||||
| Stanford | 11 | |||||||||||
| UCLA | 8 | |||||||||||
| USC | 7 | |||||||||||
| Utah | 6 | |||||||||||
| Washington | 9 | |||||||||||
| Washington State | 6 | |||||||||||
| Totals | 11 | 12 | 9 | 12 | 12 | 4 | 5+1[lower-alpha 3] | 6 | 9 | 10 | 3+3[lower-alpha 4] | 93+4[lower-alpha 5] |
| Affiliate Members | ||||||||||||
| Cal Poly | 1 | |||||||||||
| CSU Bakersfield | 1 | |||||||||||
| Little Rock | 1 | |||||||||||
| San Diego State | 1 | |||||||||||
Men's sports that are not sponsored by the Pac-12 but are fielded as a varsity sport at Pac-12 schools
| School | Fencing | Gymnastics | Ice Hockey | Lacrosse | Rugby[lower-alpha 1] | Sailing[lower-alpha 1] | Skiing | Track & Field Indoor | Volleyball | Water Polo | Total Sports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | MPSF | 1 | |||||||||
| Arizona State | IND | MPSF | 2 | ||||||||
| California | MPSF | PAC | MPSF | MPSF | 4 | ||||||
| Colorado | RMISA | MPSF | 2 | ||||||||
| Oregon | MPSF | 1 | |||||||||
| Oregon State | 0 | ||||||||||
| Stanford | IND[lower-alpha 2] | MPSF | PCCSC[lower-alpha 2] | MPSF | MPSF[lower-alpha 2] | MPSF | 6 | ||||
| UCLA | MPSF | MPSF | MPSF | 3 | |||||||
| USC | MPSF | MPSF | MPSF | 3 | |||||||
| Utah | ASUN[100] | RMISA | 2 | ||||||||
| Washington | MPSF | 1 | |||||||||
| Washington State | MPSF | 1 | |||||||||
| Totals | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 26 |
- Notes
- Not an NCAA-sanctioned sport.
- Stanford had announced that it would drop its men's teams in fencing, rowing, sailing, volleyball, and wrestling at the end of the 2020–21 school year,[99] but reversed course, reinstating all sports without interruption.
- Affiliate: San Diego State
- Affiliates: Cal Poly, Cal State Bakersfield, Little Rock
- Affiliate members with full varsity status.
Women's sponsored sports by school
Member-by-member sponsorship of the 13 women's Pac-12 sports.
| School | Basketball | Beach Volleyball | Cross Country | Golf | Gymnastics | Lacrosse | Rowing | Soccer | Softball | Swimming & Diving | Tennis | Track & Field Outdoor | Volleyball | Total Sports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | 11 | |||||||||||||
| Arizona State | 12 | |||||||||||||
| California | 13 | |||||||||||||
| Colorado | 8 | |||||||||||||
| Oregon | 10 | |||||||||||||
| Oregon State | 9 | |||||||||||||
| Stanford | 13 | |||||||||||||
| UCLA | 12 | |||||||||||||
| USC | 11 | |||||||||||||
| Utah | 10 | |||||||||||||
| Washington | 11 | |||||||||||||
| Washington State | 9 | |||||||||||||
| Totals | 12 | 9 | 12 | 11 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 12 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 129 |
| Future affiliate members | ||||||||||||||
| San Diego State | 1 | |||||||||||||
| UC Davis | 1 | |||||||||||||
Women's sports that are not sponsored by the Pac-12 but are fielded as a varsity sport at Pac-12 schools
| School | Acrobatics & Tumbling[lower-alpha 1] | Fencing | Field Hockey | Sailing[lower-alpha 2] | Skiing | Squash[lower-alpha 2] | Synchronized Swimming[lower-alpha 2] | Track & Field Indoor | Triathlon [lower-alpha 1] | Water Polo | Total Sports |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arizona | MPSF | IND | 2 | ||||||||
| Arizona State | MPSF | IND | MPSF | 3 | |||||||
| California | AmEast | MPSF | MPSF | 3 | |||||||
| Colorado | RMISA | MPSF | 2 | ||||||||
| Oregon | NCATA | MPSF | 2 | ||||||||
| Oregon State | MPSF | 1 | |||||||||
| Stanford | IND[lower-alpha 3] | AmEast[lower-alpha 3] | PCCSC[lower-alpha 3] | IND[lower-alpha 3] | MPSF[lower-alpha 3] | MPSF | MPSF | 7 | |||
| UCLA | MPSF | MPSF | 2 | ||||||||
| USC | MPSF | MPSF | 2 | ||||||||
| Utah | RMISA | MPSF | 2 | ||||||||
| Washington | MPSF | 1 | |||||||||
| Washington State | MPSF | 1 | |||||||||
| Totals | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 12 | 2 | 5 | 27 |
- Notes
- Part of the NCAA Emerging Sports for Women program.
- Not an NCAA-sanctioned sport.
- Stanford had announced that it would drop its women's teams in fencing, field hockey, sailing, squash, and synchronized swimming at the end of the 2020–21 school year,[99] but reversed course, reinstating all sports without interruption.
NCAA national titles
Team titles through May 25, 2022; individual titles through July 1, 2016[101]
| School | Team | Individual | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | Women | Co-ed† | Total | Men | Women | Co-ed | Total | |
| Arizona | 7 | 12 | 0 | 19 | 81 | 115 | 0 | 196[102] |
| Arizona State | 11 | 13 | 0 | 24 | 66 | 46 | 0 | 112 |
| California | 31 | 9 | 0 | 40 | 155 | 86 | 0 | 241 |
| UCLA | 76 | 43 | 0 | 119 | 166 | 103 | 0 | 269 |
| Colorado | 16 | 3 | 8 | 27 | 23 | 15 | 90 | 128 |
| Oregon | 20 | 14 | 0 | 34 | 102 | 42 | 0 | 144 |
| Oregon State | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 32 | 7 | 0 | 39 |
| USC | 85 | 25 | 0 | 111 | 319 | 72 | 0 | 391 |
| Stanford | 69 | 62 | 0 | 131 | 265 | 204 | 14 | 609[103] |
| Utah | 2 | 9 | 13 | 24 | 51[104] | 27 | 72 | 150 |
| Washington | 0 | 9 | 0 | 9 | 54 | 17 | 2 | 73 |
| Washington State | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 79 | 6 | 1 | 86 |
| Conference total | 323 | 200 | 21 | 544 | 1349 | 716 | 179 | 2244 |
† Co-ed sports include fencing (since 1990), rifle, and skiing (since 1983). Team fencing championships before 1990 and team skiing championships before 1983 were awarded as men's or women's championships and are counted here as such.
These totals do not include football national championships, which the NCAA does not officially award at the FBS level. Various polls, formulas, and other third-party systems have been used to determine national championships, not all of which are universally accepted. These totals also do not include championships prior to the inception of the NCAA.
USC claims 11 national football championships,[105] California claims 5,[106][107] Washington claims 2,[108] Stanford claims 2,[109] while Colorado and UCLA claim 1.[110][111][112][113][114]
Conference champions
- Football
- Men's basketball
- Women's basketball
- Baseball
- Softball
- Gymnastics
- Men's soccer
- Women's soccer
- Women's volleyball
Football


Rivalries
Each of the ten schools that were conference members before 2011 has its own in-state, conference rivalry. One is an intracity rivalry (UCLA-USC) and another is within the same metropolitan area (California-Stanford). Colorado and Utah, who joined in 2011, were historic rivals in the Rocky Mountain region prior to 1962 when they suspended the series. These rivalries (and the name given to the football forms) are:
- Arizona–Arizona State – The winner receives the Territorial Cup.
- California–Stanford – Known as the Big Game, the winner receives the Stanford Axe.
- Colorado–Utah – Known as the Rumble in the Rockies.
- Oregon–Oregon State – Though not officially recognized by the universities, the Platypus Trophy is awarded to the winning alumni association.
- UCLA–USC – The winner receives the Victory Bell. The two universities compete across all sports for the SoCal BMW Crosstown Cup.
- Washington–Washington State – Known as the Apple Cup, the winner receives Apple Cup trophy.
The most frequently played rivalries in the conference are between Oregon and Oregon State (124 meetings through 2020) and Big Game between Stanford and California (123 meetings). These rivalries are among the most played rivalries in college football.
The two newest members, Colorado and Utah, had a football rivalry that had been dormant since 1962 – both were conference rivals previously in the Rocky Mountain Athletic Conference (now a Division II conference) and later the now-defunct Mountain States Conference (also known as the Skyline Conference). Even after Colorado joined what became the Big 12 in 1948 (the conference was then known popularly as the Big 7 Conference), the two schools continued their football rivalry for over a decade before ending it after the 1962 season. With the two schools being placed in the same division for football starting in 2011, the rivalry was revived with their 58th meeting during the 2011 season.
All of the California schools consider each other major rivals due to the culture clash between Northern and Southern California.[115] California and UCLA have a rivalry rooted in their shared history as the top programs within the University of California system. Stanford and USC have a rivalry rooted in their shared history as the only private schools in the Pac-12. California and USC also have a long history, playing each other beginning in 1915.
The Pacific Northwest schools of Oregon, Oregon State, Washington, and Washington State all consider each other major rivals due to their proximity and long history; a sweep of the other 3 teams is known as the Northwest Championship. The Oregon–Washington rivalry is sometimes referred to as the Border War.[116]
Arizona and New Mexico have a recently renewed rivalry game, based upon when they were both members of the WAC and both states were longtime territories before being admitted as states in 1912. They played for the Kit Carson Rifle trophy, which was no longer used starting with their meeting in the 1997 Insight Bowl.[117][118]
USC and Notre Dame have an intersectional rivalry (See Notre Dame–USC rivalry). The games in odd-numbered years are played in South Bend in mid-October, while the games in even-numbered years are played in Los Angeles, usually in late November.
Stanford and Notre Dame also have an intersectional rivalry (See Notre Dame–Stanford football rivalry). The schedule of the Stanford–Notre Dame rivalry mirrors that of USC–Notre Dame. The games in even-numbered years are played at Notre Dame in mid-October, while the games in odd-numbered years are played at Stanford in late November.
The isolated rural campuses of Washington State and Idaho are eight miles (13 km) apart on the Palouse, creating a natural border war known as the Battle of the Palouse. Idaho rejoined FBS in 1996 and was a member until 2017.
Utah and BYU have a fierce rivalry nicknamed the Holy War that goes back to 1896.
Colorado also has a rivalry with in-state rival Colorado State called the Rocky Mountain Showdown.
With the NCAA permanently approving 12-game schedules in college football beginning in 2006, the Pac-10—alone among major conferences in doing so—went to a full nine-game conference schedule. Previously, the schools did not play one non-rival opponent, resulting in an eight-game conference schedule (four home games and four away). In 2010, the last season before the arrival of Colorado and Utah, the only other BCS conference that played a round-robin schedule was the Big East. The schedule consisted of one home and away game against the two schools in each region, plus the game against the primary in-state rival.
Divisions
On October 21, 2010, the Pac-10 announced the creation of divisions and a championship game in football, to be used when Colorado and Utah joined the conference effective July 1, 2011. The twelve members were split into two divisions for football only: a North Division comprising the Pacific Northwest and Bay Area schools, and a South Division comprising the Mountain Time Zone and Los Angeles schools.[119]
A nine-game conference schedule was maintained, with five games within the assigned division and four games from the opposite division. The four California teams, noted in the table in gray, still played each other every season— consequently, the four non-California teams in each division will only play one of the two California teams from the opposite division each year.
The Pac-12 Football Championship Game featured the North Division Champion against the South Division Champion for the first 11 years of its existence, with divisional champions determined based on record in all conference games (both divisional and cross-divisional). However, on May 18, 2022, the NCAA Division I Council announced that conferences would no longer be required to maintain divisions in order to hold a conference championship. As a result, later that same day, the Pac-12 announced that it would eliminate its divisions for the 2022 football season and beyond, with the championship game instead featuring the two Pac-12 teams with the highest winning percentage.[120] It was the first FBS conference to scrap its divisions as a result of this change.
| North Division | South Division |
|---|---|
| Oregon | Arizona |
| Oregon State | Arizona State |
| Washington | Colorado |
| Washington State | Utah |
| California | UCLA |
| Stanford | USC |
Bowl games
As of the 2020 college football season, the following is the selection order of bowl games with Pac-12 tie-ins. If a Pac-12 team is selected to participate in the College Football Playoff, all other bowl-eligible teams move up one spot in the order.
| Pick | Name | Location | Opposing conference |
Opposing pick |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Rose Bowl | Pasadena, California | Big Ten | 1 |
| 2 | Alamo Bowl | San Antonio, Texas | Big 12 | 2 |
| 3 | Las Vegas Bowl | Las Vegas, Nevada | SEC or Big Ten | 3(SEC)/4(Big Ten) |
| 4 | LA Bowl | Los Angeles, California | MWC | 1 |
| 5 | Holiday Bowl | San Diego, California | ACC | 4 |
| 6 | San Francisco Bowl | Santa Clara, California | Big Ten | 7 |
| 7 | Sun Bowl | El Paso, Texas | ACC | 7 |
| 8 (2020, 2023, 2024) | Independence Bowl | Shreveport, Louisiana | NCAA Division I FBS independent schools | Army in 2020 and 2024, BYU in 2023 |
Pac-12 All-Century Football Team
In honor of the 100th anniversary of the establishment of the conference, an All-Century Team was unveiled on December 2, 2015, voted on by a panel of coaches, players, and the media.[121]
- Quarterbacks: John Elway, Stanford; Marcus Mariota, Oregon; Jim Plunkett, Stanford; Andrew Luck, Stanford; Matt Leinart, USC
- Running backs: Marcus Allen, USC; O. J. Simpson, USC; Charles White, USC; Reggie Bush, USC; Mike Garrett, USC
- Wide receivers: Keyshawn Johnson, USC; Lynn Swann, USC; Marqise Lee, USC; J. J. Stokes, UCLA; Ken Margerum, Stanford
- Tight ends: Tony Gonzalez, California; Charle Young, USC;
- Offensive line: Jonathan Ogden, UCLA; Ron Yary, USC; Tony Boselli, USC; Anthony Muñoz, USC; Lincoln Kennedy, Washington; Brad Budde, USC; Randall McDaniel, Arizona State
- Defensive ends: Tedy Bruschi, Arizona; Terrell Suggs, Arizona State; Willie McGinest, USC; Andre Carter, California; Jim Jeffcoat, Arizona State
- Defensive tackles: Steve Emtman, Washington; Haloti Ngata, Oregon; Rob Waldrop, Arizona; Leonard Williams, USC; Ed White, California
- Linebackers Junior Seau, USC; Jerry Robinson, UCLA; Ricky Hunley, Arizona; Richard Wood, USC; Chris Claiborne, USC
- Cornerbacks Joey Browner, USC; Mel Renfro, Oregon; Chris McAlister, Arizona; Antoine Cason, Arizona
- Safeties: Ronnie Lott, USC ; Kenny Easley, UCLA; Troy Polamalu, USC; Mark Carrier, USC
- Kicker: Jason Hanson, Washington State
- Punter: Tom Hackett, Utah
- Returner: Reggie Bush, USC
- Coach: John McKay, USC
Note: Bold Italic notes Offensive, Defensive and Coach of the Century selections; The voting panel was made up of 119 former players, coaches and media.[122]
Men's basketball
As of 2022, Pac-12 schools have won 15 Division I national titles. This was tied with the Atlantic Coast Conference for the most of any conference. [123][124][125] Oregon won the first NCAA tournament in 1939.[126] UCLA has won 11 national titles, the most of any Division I team.[127] Arizona has won the most recent national title, winning in 1997. Stanford in 1942, Utah in 1944 & Cal in 1959 are the other NCAA champions.[128]
Rivalries in other sports
All of the intra-conference rivalries in football are carried over into other sports.
During the 1970s, UCLA and Notre Dame had an intense men's basketball rivalry. For several years, it was one of a small number of non-conference games in Division I basketball that was played twice a season (home-and-away). The most famous game in the rivalry was on January 19, 1974, when Notre Dame scored the last 12 points of the game to nip UCLA and end the Bruins' record 88-game winning streak. This rivalry is now dormant, partly because Notre Dame is no longer independent in sports other than football (now in the ACC).
In baseball, there are intense rivalries between the four southern schools. Arizona, Arizona State, and USC have long and successful histories in baseball and all have won national titles in the sport. The most intense series is widely regarded to be the "Basebrawl" series between USC and Arizona State in 1990. Arizona State swept the series and in the final game a bench clearing brawl spread quickly to the stands and made national headlines. Several were injured and riot police were called to end the fracas.
Washington and California have a longstanding rivalry in men's crew as the two traditionally dominant programs on the West Coast.
Due to the unique geographic nature of the Pac-12 teams, the teams travel in pairs for road basketball games. For example, on Thursday, February 28, 2008, USC played Arizona and UCLA played Arizona State. Two nights later the teams switched and USC played Arizona State and UCLA played Arizona. The teams are paired as follows: USC and UCLA (the L.A. teams), Arizona and Arizona State (the Arizona teams), California and Stanford (the Bay Area teams), Washington and Washington State (the Washington teams), Oregon and Oregon State (the Oregon teams), and Colorado and Utah (the Rocky Mountain teams). Usually, the games are played on Thursdays and Saturdays with a game or occasionally two on Sundays for television purposes. This pairing formula is also used in women's volleyball. To make scheduling simpler for men and women's basketball (a sport in which each conference member uses a single venue for both teams' home games), the schedule for women's basketball is the opposite of the men's schedule. For example, when the Oregon schools are hosting the men's teams from the Arizona schools, the Arizona schools host the women's teams from Oregon schools the same weekend.
This formula has made a tradition in conference play to keep track of how a team does against a particular region; and stats are kept as to how successful a team is against, for example, "the Bay Area schools" at home or away. Effective in the 2011–12 season, with the expansion into 12 teams, a 10-year rotation model has been developed to maintain the existing 18-game conference schedule. Teams remained paired with their regional rival. Each school plays its regional rival and six other teams both home and away, and the other four teams once – two at home and two away. The newest members, Colorado and Utah, are paired with each other. The single play opponents rotate every two years.[129]
Recently, Cal Poly and UCLA has grown into a competitive Men's Soccer rivalry with Cal Poly hosting UCLA in a 0–0 tie in front of a crowd of 8,717 which at the time was the 9th largest regular season, on-campus attendance in the history of college soccer.[130] The schools have played several times since however UCLA has not returned to San Luis Obispo for a Friday or Saturday game since tying Cal Poly in front of a record crowd. UCLA leads the series 6–2–2.[131]
Olympians
While the PAC-12 is known as the "Conference of Champions," for having won the most collegiate Championships than any other Conference, it could also be considered the "Conference of Olympians" for having the most athletes and medal-winners of any conference in the history of the Olympic games.
In a 2017 study by OlympStats, USA Olympians and the medals they won were counted and sorted by their college affiliations.[132][133] Stanford lead all schools with 289 athletes, 408 games, and 282 total medals won. UCLA was second, USC was third, Cal Berkeley was 4th, Harvard was 5th in each category, respectively.
Leading the country with the most participants in their respective events are, Colorado in Alpine Skiing and Cycling, Arizona State in Archery and Badminton, Stanford in Baseball, Rugby, Swimming, Tennis and Water Polo, UCLA in Basketball, Beach Volleyball, Gymnastics and Softball, USC in Athletics and Volleyball, and Utah in Freestyle Skiing.
Since 1924 a PAC-12 school has led the country in number of athlete in each and every Summer Olympic Games to date (as of this study in 2017).[133]
Commissioners
Since restarting in 1959 as the AAWU, the Pac-12 has had five commissioners:
| Name | Years | Tenure | Conference name(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thomas J. Hamilton[64] | 1959–1971 | 12 years | AAWU / Pacific-8 |
| Wiles Hallock [67][134] | 1971–1983 | 12 years | Pacific-8 / Pacific-10 |
| Thomas C. Hansen [135] | 1983–2009 | 26 years | Pacific-10 |
| Larry Scott[136] | 2009–2021 | 12 years | Pacific-10 / Pac-12 |
| George Kliavkoff | 2021–present | 1 years | Pac-12 |
See also
- Pac-12 Network
- List of American collegiate athletic stadiums and arenas
- List of U.S. colleges and universities by endowment
Notes
References
- "Washington's NCAA Championship makes Pac-12 the first to 500 NCAA titles". Pac-12. Retrieved July 9, 2017.
- "USC to Make Historic Move to Big Ten Conference in 2024". USC Athletics. Retrieved June 30, 2022.
- "UCLA to Join Big Ten Conference at Start of 2024–25 Season". UCLA. Retrieved June 30, 2022.
- "Fall 2016 Enrollment Highlights" (PDF). Fall 201 6 Enrollment Highlights University Analytics & Institutional Research. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 16, 2017. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Facts at a Glance" (PDF). ASU Facts. University Office of Institutional Analysis. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 1, 2017. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "UC Berkeley Quick Facts". Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Enrollment". UCLA. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Overall Enrollment Profile Fall 2017" (PDF). Colorado. Office of Data Analytics of the University of Colorado Boulder. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 16, 2017. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Historical Enrollment". UO Office of Institutional Research. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "OSU overall enrollment up 1.9 percent, Corvallis campus increases less than 1 percent". Oregonstate. News and Research Communications. Archived from the original on November 16, 2017. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Facts and Figures | About USC". about.usc.edu.
- "Enrollment Statistics, 2016–17". Stanford. Registrar's Office. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Term Enrollment". The Office of Budget & Institutional Analysis. Archived from the original on October 12, 2017. Retrieved November 16, 2017.
- "Pac-12 Adds CSU Bakersfield In Men's Soccer" (Press release). Pac-12 Conference. Retrieved March 19, 2012.
- "WAC Adds CSUB and UVU To Its Membership" (Press release). Western Athletic Conference. October 9, 2012. Archived from the original on October 11, 2012. Retrieved October 9, 2012.
- "Pac-12 women's lacrosse to add UC Davis and San Diego State as affiliate members" (Press release). Pac-12 Conference. May 31, 2022. Retrieved August 25, 2022.
- "2012 Arizona Football Prospectus" (PDF).
- "ArizonaWildcats.com – University of Arizona Athletics". www.arizonawildcats.com. Archived from the original on January 26, 2012. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- "Official Website of Arizona Athletics". Archived from the original on August 29, 2011. Retrieved August 29, 2011.
- "Renovated Sun Devil Stadium ready for Sept. 3 opener". AZ central. Retrieved September 18, 2016.
- "TheSunDevils.com – Arizona State University Athletics". www.thesundevils.com. Archived from the original on March 9, 2012. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- "Tempe Tourism Sports Event Planners – Tempe Tourism Office". Tempe Tourism. Archived from the original on September 15, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "California Memorial Stadium Facts at a glance". Archived from the original on May 21, 2013.
- "CalBears.com – University of California Official Athletic Site". www.calbears.com. Archived from the original on January 19, 2012. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- "CalBears.com – University of California Official Athletic Site". www.calbears.com. Archived from the original on February 23, 2012. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- "Folsom Field Home". CUBuffs.com. Archived from the original on October 20, 2010. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Coors Events Center Home". CUBuffs.com. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "- GoDucks.com – The University of Oregon Official Athletics Web Site". goducks.com. Archived from the original on September 15, 2015. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Matthew Knight Arena – Arena Network". Archived from the original on October 4, 2013.
- "2010 Baseball FAQ's" (PDF). goducks.com. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- "Oregon State mailbag: Official Reser capacity for 2022, transfers, biggest Beaver moment of 2021 - oregonlive.com". December 17, 2021.
- "Gill Coliseum". osubeavers.com. Archived from the original on May 10, 2013. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Oregon State Athletics Quick Facts". Oregon State University Athletic Department. Archived from the original on November 4, 2011. Retrieved December 25, 2011.
- "Facilities Stanford Stadium – GoStanford.com – Stanford University". gostanford.com. Archived from the original on September 15, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Facilities – GoStanford.com – Stanford University". gostanford.com. Archived from the original on April 24, 2013. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "GoStanford.com – Stanford Athletics". www.gostanford.com. Archived from the original on July 27, 2011. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- "UCLABruins.com – UCLA Athletics". www.uclabruins.com. Archived from the original on January 26, 2012. Retrieved January 22, 2012.
- Wendy Soderburg. "First glimpse of Pauley Pavilion as UCLA prepares for fall 2012 reopening". UCLA Newsroom. Archived from the original on March 18, 2014. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "UCLA Men's Basketball 2011 Media Guide". Archived from the original on May 13, 2011. Retrieved December 26, 2012.
- "UCLA Baseball to Install Additional Seats at Jackie Robinson Stadium". UCLA Bruins. UCLA Athletic Department. October 18, 2011. Archived from the original on November 19, 2012. Retrieved December 25, 2011.
- "United Airlines Field at Los Angeles Memorial Coliseum". University of Southern California Athletics. 2022.
- "USC Galen Center". usctrojans.com. Archived from the original on September 5, 2015. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "University of Southern California Official Athletic Site – Facilities". usctrojans.com. Archived from the original on November 26, 2009. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Facilities". University of Utah Athletics.
- "Huntsman Center". The University of Utah. Archived from the original on June 9, 2010. Retrieved June 26, 2010.
- "Facts and Figures: Salt Lake Bees Spring Mobile Ballpark". Salt Lake Bees. January 23, 2009. Archived from the original on June 15, 2010. Retrieved June 25, 2010.
- "Husky Stadium Facts". Archived from the original on January 25, 2013. Retrieved September 2, 2013.
- "Facilities". GoHuskies.com. Archived from the original on April 24, 2013. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Husky Ballpark". University of Washington Athletics. Archived from the original on November 19, 2012. Retrieved December 28, 2012.
- "2018 Washington State Football Media Guide" (PDF). Washington State University. p. 2.
- "Washington State Cougars Official Athletic Site". wsucougars.com. Archived from the original on April 26, 2013. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Washington State Athletics Facilities". wsucougars.com. Archived from the original on July 29, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "College Football Head Coach Salaries – USA TODAY". www.usatoday.com.
- "Men's College Basketball Coach Salaries – USA TODAY".
- "Our Members | Association of American Universities (AAU)". www.aau.edu.
- (Portland) Oregon Daily Journal, December 3, 1915. "Four Colleges Form Coast Conference at Very Secret Session"
- "Big Four loop is formed by UW, Cal, UCLA, USC". Spokesman-Review. Associated Press. August 24, 1958. p. 1, sports.
- "'Big Four' now 'Big Five'; Stanford joins new group". Eugene Register-Guard. Associated Press. July 17, 1959. p. 3B.
- Maule, Tex (February 2, 1959). "Football's jet-age secret". Sports Illustrated. Archived from the original on November 5, 2014. Retrieved November 5, 2014.
- "National grid conference is still all talk". Prescott Evening Courier. Arizona. Associated Press. January 29, 1959. p. 11.
- "Notre Dame interested in Airplane Conference". Schenectady Gazette. Associated Press. October 15, 2014. p. 24.
- Strite, Dick (January 10, 1962). "Highclimber". Eugene Register-Guard. p. 2B.
- Dunnavant, Keith. "The 50 Year Seduction." Thomas Dunne Books: New York, 2004
- "Hamilton quits at Pitt for Western loop job". St. Petersburg Times. Associated Press. June 30, 1959. p. 2C.
- "Stanford added to Western League". Milwaukee Journal. Associated Press. July 17, 1959. p. 14. Archived from the original on November 19, 2015. Retrieved November 17, 2015.
- "Just what will Tom Hamilton do?". Beaver Valley Times. Pennsylvania. UPI. July 2, 1959. p. 11.
- "Hallock gets top position in Pacific-8". Eugene Register-Guard. Associated Press. January 15, 1971. p. 3B.
- NCAA Men's Basketball Records – Division I conference alignment history (PDF copy available at NCAA.org)
- "Cougars admitted to athletic loop". Spokane Daily Chronicle. Associated Press. June 14, 1962. p. 39.
- "The Big Six still the Big Six". Eugene Register-Guard. Associated Press. June 2, 1964. p. 3B.
- Uhrhammer, Jerry (April 1, 1964). "Oregon, OSU join AAWU". Eugene Register-Guard. (Oregon). p. 1D.
- "Officials pleased by Big Six move". Spokane Daily Chronicle. (Washington). Associated Press. April 1, 1964. p. 17.
- "PCC all but revised as Oregon, Oregon State back in fold". Lewiston Morning Tribune. (Idaho). Associated Press. April 1, 1964. p. 10.
- "Not AAWU". Eugene Register-Guard. (Oregon). October 31, 1964. p. 4A.
- "Pacific Athletic Conference". Spokesman-Review. (Spokane, Washington). October 19, 1964. p. 9.
- "Western universities finally resolve Rose Bowl question". Eugene Register-Guard. (Oregon). Associated Press. June 25, 1965. p. 1C.
- "PAC standings". Eugene Register-Guard. (Oregon). November 21, 1965. p. 1B.
- "SC, UCLA roll on...but look at Bears". Spokesman-Review. (Spokane, Washington). October 17, 1966. p. 11.
- Newnham, Blaine (December 5, 1975). "Bowling 'em over". Eugene Register-Guard. (Oregon). p. 1B.
- "Nine accept NCAA bids; NIT lines up five teams". Spokesman-Review. (Spokane, Washington). Associated Press. March 2, 1972. p. 23.
- "Pacific 8 Conference invites two new tenants". Tuscaloosa News. Associated Press. December 14, 1976. p. 12.
- "Pacific-10 succeeds Pacific-8". Spokane Daily Chronicle. Associated Press. May 18, 1977. p. 39.
- Mark Wangrin – "Power brokers: How tagalong Baylor, Tech crashed the revolt" Archived February 23, 2008, at the Wayback Machine. San Antonio Express, August 14, 2005
- Ratto, Ray (August 13, 2010). "Pac-10 considers becoming Pac-12". The San Francisco Chronicle.
- Ratto, Ray (August 8, 2010). "The Pac-10's meet market". The San Francisco Chronicle.
- "University of Utah Joins Pac-10". Pacific-10 Conference. p. 4.
- "University of Colorado Joins Pac-10". Archived from the original on June 12, 2010. Retrieved June 10, 2010.
- "Texas, Oklahoma, Texas A&M, Oklahoma State stay put in Big 12 Conference". ESPN. June 14, 2010. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Going remote: Pac-12 moving out of San Francisco office". Associated Press. March 29, 2022. Retrieved March 30, 2022.
- Smith, Michael (August 19, 2013). "Pac-12 moving its headquarters to San Francisco". Sports Business Journal. Retrieved November 22, 2021.
- "Pac-12, ACC and Big Ten announce historic alliance" (Press release). Pac-12 Conference. August 24, 2021. Retrieved June 28, 2022.
The ACC, Big Ten and Pac-12 today announced an historic alliance that will bring 41 world-class institutions together on a collaborative approach surrounding the future evolution of college athletics and scheduling.
- "Pac-12 accelerates negotiations for media rights deals in wake of UCLA, USC exits". ESPN. Associated Press. July 5, 2022. Retrieved July 6, 2022.
- "UCLA to Join Big Ten Conference at Start of 2024–25 Season – UCLA". Uclabruins.com. Retrieved July 3, 2022.
- "USC to Make Historic Move to Big Ten Conference in 2024 – USC Athletics". Usctrojans.com. Retrieved July 3, 2022.
- "Pac-12". Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- "Pac-12 Adds Women's Lacrosse for 2018 Season". Lacrosse Magazine. October 23, 2015. Archived from the original on October 24, 2015. Retrieved February 6, 2016.
- "NCAA DII, DIII membership approves Sand Volleyball as 90th championship". NCAA. January 17, 2015. Retrieved April 3, 2015.
- "Pac-12 adds sand volleyball as 23rd sport". Pac-12 Conference. Retrieved July 2, 2015.
- "An open letter to the Stanford community and the Stanford Athletics family" (Press release). Stanford University. July 8, 2020. Retrieved July 8, 2020.
- "ASUN Conference Announces Formation of Men's Lacrosse League" (Press release). ASUN Conference. February 5, 2021. Retrieved February 6, 2021.
- "Championships History". Retrieved January 7, 2021.
- "University of Arizona - Individual National Championships". static.arizonawildcats.com.
- "Cardinal Athletics - Facts".
- "Skiing | Utah Athletics". Archived from the original on February 5, 2022. Retrieved March 14, 2022.
- USC Sports Information Office (2008). 2008 USC Football Media Guide (PDF). University of Southern California. pp. 119–124. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 26, 2009. Retrieved June 14, 2009.
- "CalBears.com – Traditions: Cal National Team Champions". University of California Department of Athletics. Archived from the original on July 19, 2011. Retrieved June 14, 2009.
- Benenson, Herb, ed. (2008). 2008 California Football Media Guide (PDF). Cal Media Relations Office. p. 36. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 7, 2011. Retrieved June 15, 2009.
- "UW Football National Championships". gohuskies.com. University of Washington Athletic Communications Office. Archived from the original on December 21, 2020. Retrieved December 21, 2020.
Washington officially claims two national championships in football: 1960 and 1991.
- Official 2009 NCAA Division I Football Records Book (PDF). Indianapolis: National Collegiate Athletic Association. August 2009. pp. 76–77, 81. Retrieved September 18, 2011.
- "Stanford Official Athletic Site – Traditions: Stanford Cardinal Championships". Stanford University Department of Athletics. Archived from the original on August 10, 2011. Retrieved June 16, 2009.
- Young, Jim, ed. (2009). 2009 Stanford Football Media Guide (PDF). Stanford University Athletic Communications and Media Relations Department. pp. 141, 144. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 7, 2013. Retrieved October 17, 2009.
- Dellins, Marc, ed. (2009). 2009 UCLA Football Media Guide (PDF). UCLA Sports Information Office. pp. 147, 154. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 7, 2011. Retrieved October 16, 2009.
- Dellins, Marc, ed. (2009). 2009 UCLA Football Media Guide (PDF). UCLA Sports Information Office. p. 164. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 7, 2011. Retrieved October 16, 2009.
- COLORADO FOOTBALL 1990 NATIONAL CHAMPIONS, University of Colorado Athletic Department, 2011, retrieved July 3, 2011
- Beano Cook, Longstanding West Coast rivalry, ESPN Classic.com, September 26, 2001, Accessed June 14, 2006
- Linde, Rich. "When did the Border War begin?". 4malamute.com. Archived from the original on March 23, 2012. Retrieved September 18, 2011.
- Lobos Meet Arizona for First Time in 10 Years. University of New Mexico Athletic Department, September 10, 2007. The Rifle: The two schools used to play for the Kit Carson rifle, although that custom was dropped many years ago. Kit Carson was a legendary scout in the territories of New Mexico and Arizona in the 1800s. The story goes that nearly 70 years ago former New Mexico director of athletics Roy Johnson and Arizona AD Pop McKale obtained a rifle in a trade with an Indian rumored to be Geronimo. It's not known what the administrators provided in return. McKale donated the rifle in 1938 and the score of each game was etched into the stock. The Lobos won 10 times, Arizona 21.
- UA Sports UA Breakdown. Arizona Daily Star, September 15, 2007. Arizona and New Mexico will meet tonight for the first time since the 1997 Insight Bowl. That year, before the game was played, the presidents of the two universities decided to discontinue the Kit Carson Rifle trophy out of respect for both schools' Native American communities.
- "Pac-12". Archived from the original on October 24, 2010. Retrieved September 20, 2015.
- Parks, James (May 18, 2022). "Pac-12 scraps divisions starting in the 2022 college football". si.com. Sports Illustrated. Retrieved June 8, 2022.
- "Pac-12 announces 'All-Century team'". ESPN.com. December 2, 2015. Retrieved February 8, 2016.
- Pac-12 Networks unveils Pac-12 Football All-Century Team, Pac-12 Networks, December 2, 2015
- "2013–14 Pac-12 Men's Basketball Media Guide". Pac-12 Conference. 2013. p. 14. Retrieved October 16, 2014.
- Schreiner, Michael (July 1, 2013). "Is next year's ACC the greatest basketball conference ever?". The Chronicle. Archived from the original on October 18, 2014.
- Kensler, Tom (May 24, 2012). "Counting Colorado and Utah, Pac-12 reaches 450 in NCAA titles". The Denver Post. Archived from the original on October 22, 2014.
- Titus, Mark (October 29, 2013). "2013–14 NCAA Basketball Preview: The Pac-12". Grantland.com. Archived from the original on October 25, 2014.
- Harrow, Jeremy (2008). Basketball in the Pac-10 Conference. The Rosen Publishing Group. p. 9. ISBN 9781404213852. Retrieved October 15, 2014.
- "Men's National Titles".
- "Men's Attendance Records" (PDF). NCAA Soccer. 2010. Retrieved September 18, 2021.
- "Series Records Division I" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on October 2, 2018. Retrieved October 15, 2014.
- "Pac-12 Conference produces Most U.S. Olympians in Olympic History According to Study". pac-12.com.
- "USA OLYMPIANS AND THEIR COLLEGES". OlympStats. September 21, 2017.
- "Pac-10's Hallock to step down". Lewiston Morning Tribune. Idaho. July 21, 1982. p. 2C.
- "Conference gives Hansen director's job". Eugene Register-Guard. Oregon. Associated Press. December 14, 1982. p. 1C.
- "Pac-12 announces George Kliavkoff as new commissioner". May 13, 2021.
- "Faults of P.C.C. are listed". San Jose News. United Press. January 5, 1940. p. 10.
- "Coast colleges name Atherton boss". Spokesman-Review. Spokane, Washington. Associated Press. January 6, 1940. p. 10.
- "Coast schools appoint new commissioner". Milwaukee Journal. Associated Press. September 2, 1944. p. 2, part 2. Archived from the original on November 18, 2015. Retrieved November 17, 2015.
