Ranavalona I
Ranavalona I (born Rabodoandrianampoinimerina (also called Ramavo); 1778 – 16 August 1861), also known as Ranavalo-Manjaka I, was sovereign of the Kingdom of Madagascar from 1828 to 1861. After positioning herself as queen following the death of her young husband, Radama I, Ranavalona pursued a policy of isolationism and self-sufficiency, reducing economic and political ties with European powers, repelling a French attack on the coastal town of Foulpointe, and taking vigorous measures to eradicate the small but growing Malagasy Christian movement initiated under Radama I by members of the London Missionary Society. She made heavy use of the traditional practice of fanompoana (forced labor as tax payment) to complete public works projects and develop a standing army of between 20,000 and 30,000 Merina soldiers, whom she deployed to pacify outlying regions of the island and further expand the realm. The combination of regular warfare, disease, difficult forced labor and harsh trials by ordeal using a poisonous nut from the Tangena shrub resulted in a high mortality rate among both soldiers and civilians during her 33-year reign, with Madagascar's population reducing from 5 million in 1833 to 2.5 million in 1839.
| Ranavalona I | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||
| Queen of Madagascar | |||||
| Reign | 11 August 1828 – 16 August 1861 | ||||
| Coronation | 12 August 1829 | ||||
| Predecessor | Radama I | ||||
| Successor | Radama II | ||||
| Prime ministers |
| ||||
| Born | 1778 Ambatomanoina, Merina Kingdom | ||||
| Died | 16 August 1861 (aged 82–83) Manjakamiadana, Antananarivo, Merina Kingdom | ||||
| Burial | 1861/1893 (re-interred) Ambohimanga/Tomb of the Queens, Rova of Antananarivo (re-interred) | ||||
| Spouse |
| ||||
| Issue | Radama II | ||||
| |||||
| Dynasty | Hova dynasty | ||||
| Father | Prince Andriantsalamanjaka (also called Andrianavalontsalama) | ||||
| Mother | Princess Rabodonandriantompo | ||||
Although greatly obstructed by Ranavalona's policies, foreign political interests in Madagascar remained undiminished. Divisions between traditionalist and pro-European factions at the queen's court created opportunities that European intermediaries leveraged in an attempt to hasten the succession of her son, Radama II. The young prince disagreed with many of his mother's policies and was amenable to French proposals for the exploitation of the island's resources, as expressed in the Lambert Charter he concluded with a French representative in 1855. These plans were never successful, however, and Radama II did not take the throne until Ranavalona's death in 1861 at the age of 83.
Ranavalona's European contemporaries generally condemned her policies and characterized her as a tyrant at best and insane at worst. These negative characterizations persisted in Western scholarly literature until the mid-1970s. Later academic research recast Ranavalona's actions as those of a queen attempting to expand her empire while protecting Malagasy sovereignty against the encroachment of European cultural and political influence.
Early life
Princess Ramavo was born in 1778 at the royal residence at Ambatomanoina,[1] about 16 kilometers (10 mi) east of Antananarivo,[2] to Prince Andriantsalamanjaka and Princess Rabodonandriantompo.[3] When Ramavo was still a young girl, her father alerted King Andrianampoinimerina (1787–1810) to an assassination plot planned by Andrianjafy, the king's uncle, whom Andrianampoinimerina had forced from the throne at the royal city of Ambohimanga. In return for saving his life, Andrianampoinimerina betrothed Ramavo to his son, Prince Radama, whom the king designated as his heir. He furthermore declared that any child from this union would be first in the line of succession after Radama.[4]
Despite her elevated rank among the royal wives, Ramavo was not the preferred wife of Radama and did not bear him any children. Upon Andrianampoinimerina's death in 1810, Radama succeeded his father as king and followed royal custom by executing a number of potential opponents among Ramavo's relatives, an act that may have strained their relationship.[4] Unable to find satisfaction in her loveless marriage, the neglected Ramavo and other court ladies spent most days socializing and drinking rum with David Griffiths and his fellow missionaries in Griffiths' home. These visits established a deep friendship between Ramavo and Griffiths that endured for three decades.[5]
Accession to the throne
When Radama died without leaving any descendants on 27 July 1828, according to local custom, the rightful heir was Rakotobe, the eldest son of Radama's eldest sister. An intelligent and amiable young man, Rakotobe was the first pupil to have studied at the first school established by the London Missionary Society in Antananarivo on the grounds of the royal palace. Radama died in the company of two trusted courtiers who were favorable to the succession of Rakotobe. However, they hesitated to report the news of Radama's death for several days, fearing possible reprisals against them for having been involved in denouncing one of the king's rivals, whose family had a stake in the succession after Radama.[4][6] During this time, another courtier, a high-ranking military officer named Andriamamba, discovered the truth and collaborated with other powerful officers – Andriamihaja, Rainijohary and Ravalontsalama – to support Ramavo's claim to the throne.[7]

These officers hid Ramavo and one of her friends in a safe location, then secured the support of several influential power-brokers, including judges and the keepers of the sampy (royal idols). The officers then rallied the army behind Ramavo,[4][6] so that on 11 August 1828, when she declared herself the successor to Radama on the pretence that he himself had decreed it, there could be no immediate resistance. Ramavo took the throne name Ranavalona ("folded", "kept aside"), then followed royal custom by systematically capturing and putting to death her political rivals, including Rakotobe, his family, and other members of Radama's family, much as Radama had done to the queen's own family upon his succession to the throne.[4] Her coronation ceremony took place on 12 June 1829.[8]
By succeeding her husband, Ranavalona became the first female sovereign of the Kingdom of Imerina since its founding in 1540. Her rise to power occurred in a cultural milieu that favored men over women in the political sphere. In the traditional culture of Imerina, rulers were specially endowed with the power to innovate in circumvention of established norms and customs. Sovereigns often mobilized innovation through the creation of new forms of kinship, the traditional basis of the political order. Women, however, were associated with the household, a rigid kinship unit in opposition to the innovating role and power of the sovereign, and so were not viewed as suited to rule.[9] Although female rulers had once been common among the Vazimba, described in oral histories as the original inhabitants of Madagascar, this tradition ended in the central highlands with the reign of Andriamanelo (1540–1575), founder of the Kingdom of Imerina and successor to his Vazimba mother, Queen Rafohy (1530–1540).[10]
Reign

Ranavalona's 33-year reign was characterized by her effort to strengthen the domestic authority of the Kingdom of Imerina over subjugated provinces and preserve the political and cultural sovereignty of Madagascar. These policies were enacted in a context of increasing European influence within her kingdom and competing European bids for domination over the island. Early in her reign, the queen took incremental steps to distance Madagascar from the purview of European powers, first putting an end to a friendship treaty with Britain, then placing increasing restrictions on the activities of the missionaries of the London Missionary Society, who operated schools where basic education and trade skills were taught in addition to the Christian religion. In 1835 she forbade the practice of Christianity among the Malagasy population, and within a year nearly all foreigners had left her territory.[11]
Putting an end to most foreign trade relationships, the queen pursued a policy of self-reliance, made possible through frequent use of the long-standing tradition of fanompoana—forced labor in lieu of tax payments in money or goods. Ranavalona continued the wars of expansion conducted by her predecessor, Radama I, in an effort to extend her realm over the entire island, and imposed strict punishments on those who were judged as having acted in opposition to her will. Due in large part to loss of life throughout the years of military campaigns, high death rates among fanompoana workers, and harsh traditions of justice under her rule, the population of Madagascar is estimated to have declined from around 5 million to 2.5 million between 1833 and 1839, and the population of Imerina from 750,000 to 130,000 between 1829 and 1842.[12] These statistics have contributed to a strongly unfavorable view of Ranavalona's rule in historical accounts.[13]
Government

In the tradition of many of her royal Merina predecessors,[14] the queen ruled from the royal Rova compound in Antananarivo. Between 1839 and 1842, Jean Laborde built the queen a new residence called Manjakamiadana, which became the largest structure on the Rova grounds. The residence was made entirely from wood and bore most of the features of a traditional home of the Merina andriana (aristocratic class), including a central pillar (andry) to support the roof. In other ways it showcased distinctly European innovations, as it contained three floors entirely surrounded by wooden verandas and incorporated dormers in the shingled roof. The palace was eventually encased in stone in 1867 by James Cameron of the London Missionary Society during the reign of Ranavalona II. The original wooden palace of Ranavalona and virtually all other structures of the historic Rova compound were destroyed in a 1995 fire, leaving only the stone shell to mark where her palace had once stood.[15]
In many respects, Ranavalona's rule was a continuation of precedent established under Radama I. Both monarchs encouraged the introduction of new technologies and forms of knowledge from abroad, supported the establishment of an industrialized economy, and adopted measures to professionalize the army. Both viewed foreigners with ambivalence, establishing close personal relationships and drawing upon their expertise while enforcing restrictions on their activities to avert destabilizing changes to existing cultural and political systems. In addition, both contributed to the further development of a complex political bureaucracy that enabled the Merina court to govern remote provinces across an island larger than metropolitan France.[9]
Ranavalona maintained the tradition of ruling with the support of advisers drawn largely from the aristocratic class. The queen's most powerful ministers were also her consorts. Her first chief adviser was a young army officer from Namehana named Andriamihaja, who served as first minister from 1829 to 1830. Major-General Andriamihaja most likely fathered the queen's only son, Prince Rakoto (later King Radama II),[16] who was born eleven months after the death of his official father, King Radama I.[17] In the early years of Ranavalona's reign, Andriamihaja was the leader of her court's progressive faction, who favored maintaining the relations with Europe initiated under Radama. The conservative faction was led by the brothers Rainimaharo and Rainiharo, the latter being the official guardian of one of the most powerful royal sampy. These talismans were believed to embody and channel the supernatural powers of the kingship and had played a major role in the spiritual life of the Merina people since at least the 16th century reign of Ralambo. The conservative faction conspired to reduce Andriamahaja's progressive influence over the queen, and in September 1830 they managed to persuade her while highly intoxicated to sign his death warrant for charges of witchcraft and treason. He was immediately captured in his home and killed.[18][19]
Following Andriamihaja's death, the influence of Radama's old guard of progressives was eclipsed by that of conservative advisers at court, who grew ever closer to the queen, eventually resulting in Ranavalona's marriage to sampy guardian and conservative figurehead Field Marshal Rainiharo (also called Ravoninahitriniarivo) of Ilafy in 1833. Rainiharo gained initial access to the court through his father, Andriantsilavonandriana, a hova (commoner) who had exceptionally been accorded the privilege of joining King Andrianampoinimerina's inner circle of noble advisers.[16] Field Marshal Rainiharo served as the queen's First Minister from 1830 to 1832, then Prime Minister and Commander-in-Chief from 1832 to 1852. Upon Rainiharo's death, the queen wed another conservative, Field Marshal Andrianisa (also called Rainijohary), who remained Ranavalona's husband until her death in 1861. He served as Prime Minister from 1852 to 1862 before being exiled to the royal city of Ambohimanga for his part in a plot against the queen's son, Radama II.[7]
Traditionally, Merina sovereigns relied on the pronouncement of kabary (oratory) in public gatherings to communicate policy and reaffirm the relationship between sovereign and public. Due in part to her lack of experience in public speaking and politics, Ranavalona preferred to direct and inform her subordinates through letters that she dictated to missionary-educated court scribes. She strengthened her relationship with the public through occasional kabary and fulfilled the traditional role of the Merina sovereign as bestower of hasina (ancestral blessings) by enacting traditional rituals, including the fandroana (new year ritual of renewal), tributes to the royal idols, and offerings of vodiondry and jaka beef at customary occasions. Ranavalona innovated on these traditional rituals by increasing their complexity and symbolism to imbue them with added significance.[9]
Preservation and expansion of realm
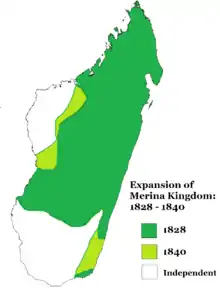
Queen Ranavalona continued the military incursions initiated under Radama I to pacify neighboring kingdoms and maintain their submission to Merina rule. These policies had a strongly negative effect on economic and population growth during her reign. Fanompoana labor among the population of Imerina could include conscription into the military, enabling the queen to raise a standing army that was estimated at 20,000 to 30,000 soldiers.[20] This army, which was sent on repeated expeditions into neighboring provinces, exacted harsh penalties against communities resistant to Merina domination. Mass executions were common, and those who were spared were commonly brought back to Imerina as slaves (andevo), and their valuables seized as booty to increase the wealth of the Crown. Approximately one million slaves entered Imerina from coastal areas between 1820 and 1853, constituting one-third of the total population in the central highlands and two-thirds of all residents in Antananarivo.[21]
According to Madagascar historian Gwyn Campbell, the number of non-Merina who died in violent conflict during the military campaigns of Ranavalona and her predecessor Radama from 1816 to 1853 was estimated at about 60,000. Additionally, a considerable proportion of the population not killed in battle in the subjugated provinces eventually died from famine as a consequence of scorched earth policies.[12] Deaths among the Merina soldiers engaged in military actions were also high, estimated at about 160,000 for the period 1820–1853. A further 25–50% of the queen's soldiers stationed in lowland areas were estimated to have died each year due to diseases such as malaria. Although prevalent in the coastal parts of the island, malaria was uncommon in the high-altitude zone around Antananarivo, and Merina soldiers possessed little natural resistance against it.[12] An average of 4,500 soldiers died each year for the greater part of Ranavalona's reign, contributing to severe depopulation in Imerina.[12]
Tangena ordeal

One of the chief measures by which Ranavalona maintained order within her realm was through the traditional practice of trial by the ordeal of tangena. A poison was extracted from the nut of the native tangena (Cerbera manghas) shrub and ingested, with the outcome determining innocence or guilt. If nobles or freemen were compelled to undergo the ordeal, the poison was typically administered to the accused only after dog and rooster stand-ins had already died from the poison's effects, while among members of the slave class (andevo), the ordeal required them to immediately ingest the poison themselves.[12] The accused would be fed the poison along with three pieces of chicken skin: if all three pieces of skin were vomited up then innocence was declared, but death or a failure to regurgitate all three pieces of skin indicated guilt.[22] According to 19th-century Malagasy historian Raombana, in the eyes of the greater populace, the tangena ordeal was believed to represent a sort of celestial justice in which the public placed their unquestioning faith, even to the point of accepting a verdict of guilt in a case of innocence as a just but unknowable divine mystery.[12]
Residents of Madagascar could accuse one another of various crimes, including theft, Christianity and especially witchcraft, for which the ordeal of tangena was routinely obligatory. On average, an estimated 20 to 50 percent of those who underwent the ordeal died. In the 1820s, the tangena ordeal caused about 1,000 deaths annually. This average rose to around 3,000 annual deaths between 1828 and 1861. In 1838, it was estimated that as many as 100,000 people—about 20 percent of the population—in Imerina had died as a result of the tangena ordeal. Although outlawed in 1863, the ordeal continued to be practised secretly in Imerina and openly in other parts of the island.[12]
Repression of Christianity

Following a visit by Radama I to Madagascar's first formal school, established in Toamasina in 1818 by members of the London Missionary Society (LMS), the king invited the first Christian artisan missionaries to the capital city to share their knowledge. Beginning in December 1820,[23] LMS missionaries established workshops in Antananarivo to teach brick-making, European carpentry and other practical skills, and developed a network of public schools where numeracy and English were taught alongside literacy using portions of the Malagasy language Bible.[24] Despite high attendance at the schools, the LMS were initially unsuccessful in converting pupils to Christianity. Near the end of Radama's reign, the king came to regard the few Malagasy who had been converted as irreverent toward royal authority. He forbade Malagasy people from being baptized or attending Christian services.[25]
Ranavalona's succession initially resulted in a relaxation of state control over Christianity. A printing press, which was imported by LMS missionaries at the end of Radama's reign, was only effectively put into operation in 1828. The press was in heaviest use during the first several years of Ranavalona's reign, when thousands of hymnals and other materials were transcribed and printed.[26] Translation of the New Testament was completed in the second year of her reign, and 3,000 copies were printed and distributed between 1829 and 1830.[27] From the beginning of her reign, Ranavalona forbade the distribution of books within the military to prevent subversion and preserve discipline. She allowed missionaries free rein in operating the printing press, however, and exempted from military service all Malagasy personnel trained to operate the press. In 1835, translation of the Old Testament was completed and the first copies were printed.[23] The freedom allowed to LMS and Malagasy Christians to print religious materials and teach religion in the state schools during the first six years of Ranavalona's reign allowed the religion to become firmly established among a small but growing group of converts in and around the capital.[23] In 1831 Ranavalona authorized Malagasy attendance at church services, administration of the sacrament, and baptism of her subjects.[28] Within a year, hundreds of Malagasies were baptized;[29] these converts were drawn from all social classes, including slaves, commoners, respected elders, court officials and even sampy guardians, who were considered the bulwarks of traditional culture.[30]
The conversion of major religious, political and social leaders sparked a backlash[30] that led Ranavalona to become increasingly wary of the political and cultural effects of Christianity, which she saw as leading the Malagasy to forsake the ancestors and their traditions.[31] In October and November 1831 the queen enacted a ban on Christian marriages, baptisms, and church services for soldiers and members of government studying in the Missionary schools,[32] and in December extended the ban on church service attendance to all Malagasy.[33] From 1832 to 1834, baptisms and church services continued, increasingly in secret.[34] During this time, several Christians each year were charged with witchcraft and exiled or made to undergo the tangena ordeal,[34] and Ranavalona requested the departure of three missionaries, retaining only those whose particular technical skills she viewed as valuable to the state.[35] In 1835, the queen attempted to shut down the press without directly targeting the LMS by banning Malagasy personnel from working at the printing house. The LMS missionaries, capitalizing on the absence of legal decrees against their own work at the press, managed to continue independently printing and distributing materials.[23]
Christianity involved a repudiation of the ancestral customs of the country, established by previous monarchs who were her ancestors. The queen's legitimacy depended entirely on her relation to her predecessors, who had given the kingdom to her. Furthermore ... she was queen because she was the descendant of the royal ancestors, who were in a mystical sense the ancestors of all the Merina. To deny her mystical power was to repudiate not only her but also the ancestors, the quintessence of good and blessings ... She was the custodian of a holy trust ... Christianity was therefore treason ... in Ranavalona's words it was "the substitution of the respect of her ancestors, Andrianampoinimerina and Radama, for the respect of the ancestor of the whites: Jesus Christ." She saw the introduction of a new religion as a political act, and there is no doubt that she was right.
Maurice Bloch, From Blessing to Violence (1986)[36]
In a kabary speech on 26 February 1835, Queen Ranavalona formally forbade the practice of Christianity among her subjects. In her discourse, she was careful to differentiate between her own people, for whom the new religion was forbidden and its practice a capital offense, and foreigners, to whom she permitted freedom of religion and conscience. She furthermore acknowledged the valuable intellectual and technological contributions that European missionaries had made to the advancement of her country, and invited them to continue working to that end on the condition that their proselytizing would cease:[37]
"To the English or French strangers: I thank you for the good that you have done in my land and my kingdom, where you have made known European wisdom and knowledge. Do not worry yourselves—I will not change the customs and rites of our ancestors. Nevertheless, whoever breaks the laws of my kingdom will be put to death—whoever he may be. I welcome all wisdom and all knowledge which are good for this country. It would be a waste of time and effort to grab the customs and rites of my ancestors. Concerning religious practice—baptism or assemblies—it is forbidden for my people who inhabit this land to take part whether on Sunday or during the week. Concerning you, foreigners, you can practice according to your own manners and customs. Nevertheless, if skilled handiwork and other practical skills exist, which can profit our people, exercise these skills that good will come. These are my instructions which I make known to you."
— Ranavalomanjaka, Kabary, February 26, 1835[37]
James Cameron and other key missionaries preferred to leave rather than remain on the island without authorization to proselytize; most of the London Missionary Society missionaries, whose primary activity was teaching Christian theology and literacy at their newly established schools using the Bible as the principal Malagasy-language text, departed the island.[38] The last two remaining missionaries chose to continue teaching practical skills in the hope that the restrictions might loosen, but one year later, after receiving indirect information that the government desired their departure, they closed the LMS mission and left Madagascar.[11]
Pursuant to the 26 February decree, those who possessed a Bible, worshiped in congregation or continued to profess adherence to Christianity were fined, jailed, manacled, subjected to trial by ordeal, or executed.[39][40] Lurid accounts of the execution and torture of Christians were reported by missionaries with informants on the island who placed emphasis on what they perceived as the savagery of the Queen's actions.[13] For instance, they reported the public execution of 15 Christian leaders near the Queen's palace who were dangled on ropes 150 feet above a rock-filled ravine before the ropes were cut upon their refusal to renounce Christianity.[40] The Andohalo cathedral was later constructed on this outcropping to commemorate early Malagasy Christians martyred at the site.[41] The precise number of Malagasy citizens put to death for religious reasons during Ranavalona's reign is difficult to state with certainty. British missionary to Madagascar W.E. Cummins (1878) places the number executed at between 60 and 80. Far more were required to undergo the tangena ordeal, condemned to hard labor, or stripped of their land and property, and many of these died. Persecution of Christians intensified in 1840, 1849 and 1857; in 1849, deemed the worst of these years by Cummins, 1,900 people were fined, jailed or otherwise punished for their Christian faith, and 18 were executed.[40]
Protection of sovereignty

Ranavalona's reign was marked by a struggle between France and Britain to increase their influence in Madagascar.[38] The French, who held several small islands off Madagascar, were interested in gaining control over the main island but this move was opposed by the British who had an interest in maintaining a secure passage to India. Ranavalona pursued a policy of self-reliance to limit the influence of foreign powers.[42]
Shortly after taking the throne, Ranavalona annulled the Anglo-Merina treaty that had been concluded between Radama and British envoys, and refused to continue receiving annual payments from Britain in exchange for adherence to the stipulations of the treaty. The most significant of these conditions was the kingdom's non-participation in the international slave trade, which had historically been a major source of revenue for the kingdoms of Imerina, Betsimisaraka, Sakalava and others across the island. One consequence of the termination of the Anglo-Merina friendship treaty was an end to the delivery of modern weaponry, which rendered the queen vulnerable to designs against her from foreign powers and pockets of local resistance.[43] This vulnerability was underscored in 1829 when a fleet of six French ships launched an unprovoked attack against the fort of Foulpointe and the nearby town of Ivondro on the eastern coast of Madagascar.[43] The queen's army successfully repelled the French at the next port, forcing the ships to Île Sainte-Marie, where they engaged a diplomatic envoy sent from Antananarivo by Ranavalona. The protracted negotiations ensured the French suffered from the malaria prevalent in coastal areas, until the increasing casualties forced the ships' withdrawal from Ranavalona's territory.[44]
It came to the Queen's attention that Frenchman Jean Laborde, who had been shipwrecked off Madagascar in 1832, was knowledgeable in the production of cannons, muskets and gunpowder. Ranavalona provided him with the labor and materials to establish factories that met the material needs of her army, thereby ending the kingdom's dependence on Europe for modern weaponry.[43]
Foreign plots

The French were eager to hasten Radama II's succession in the interest of capitalizing on the Lambert Charter, an 1855 agreement between French representative Joseph-François Lambert and Radama that could only come into effect upon the prince's succession. The charter guaranteed Lambert and his business associates first rights to the exploitation of many of the island's commodities and natural resources. According to a British account, Lambert conspired with Jean Laborde and local leaders to persuade Radama II to sign a document written in French—a language in which the prince was not fluent—which Lambert orally translated as containing only an account of the excessive pressures the Queen's policies were placing on her subjects. Radama, who was sympathetic toward the commoners and interested in easing their burden but suspicious about the letter's true purpose, reluctantly signed the document under intense pressure from the French. He was not told the letter included a request for French military intervention that could have potentially brought Madagascar under French rule. France did not however intend to take such an action without the accord of Britain, whose influence had been well-established on the island, and refused to intercede on behalf of the prince. In the meantime, Radama, who had been made to swear on the Bible not to speak of the letter to anyone, had grown concerned enough to contact a British diplomat, thereby revealing the true circumstances under which the letter had been signed. The British refused to cooperate in the French plot, and an attack was averted.[45] According to Lambert, however, the prince had indeed been an enthusiastic partner in the bid to end Ranavalona's reign, and his own true feelings about the endeavor had been misrepresented by the British diplomats.[46]
Having failed to gain the backing of a European state power to place Radama on the throne and bring the treaty into effect, Lambert decided to instigate a coup d'état independently. He traveled to Ranavalona's court in May 1857 in the company of the celebrated 19th-century Austrian globetrotter Ida Pfeiffer, who became an unwitting participant in the plot. She documented her perspective on these events in one of her late works. According to Pfeiffer, Radama and Lambert had planned to dethrone the queen on 20 June, when ministers and soldiers loyal to Radama would infiltrate the Rova grounds and declare loyalty to the prince and support for a political transition. Pfeiffer blamed the failure of the plot on Rainilaiarivony, then Commander-in-Chief of the army who reportedly had been unable to ensure the presence of soldiers in the courtyard who were loyal to Radama.[47] According to a British account, however, Radama himself was credited with warning the queen of the plot, in which his cooperation was merely a ploy to entrap the conspirators. The account claimed that Ranavalona deliberately allowed the plot to unfold almost to its conclusion in order to ascertain the loyalties of her members of government.[45] After the plot's discovery, the Europeans were largely confined to their houses on the palace grounds and prohibited from receiving visitors, until an order was issued to immediately and permanently quit the queen's territory in late July.[47]
Succession and death
While the queen had designated her son, Radama II, as her successor, Rainimaharo and the conservative faction knew of his progressive leanings and tried instead to ensure the queen's nephew, Ramboasalama, would come to power and maintain loyalties to them and their political agenda.[48] The progressive brothers Rainivoninahitriniony and Rainilaiarivony, who were the queen's co-prime minister and head of the army respectively at the time of her death, supported the succession of Radama and were able to exercise greater influence than Ramboasalama, particularly in ensuring the support of the army for the prince's claim to the throne. As Ranavalona lay on her death bed, Radama took precautions to ensure his succession would be uncontested, surrounding his residence at the Rova of Antananarivo with several hundred soldiers and sending a member of Ramboasalama's family to bring him to the Rova to swear a public oath of allegiance to the new king, to whom he submitted.[49]
On 16 August 1861, Ranavalona died in her sleep at the Manjakamiadana palace in the Rova of Antananarivo.[49] Twelve thousand zebu were slaughtered and their meat distributed to the populace in her honor, and the official mourning period lasted nine months. Her body was laid in a coffin made of silver piastres in a tomb at the royal city of Ambohimanga. During her funeral, a spark accidentally ignited a nearby barrel of gunpowder destined for use in the ceremony, causing an explosion and fire that killed a number of bystanders and destroyed three historic royal residences in the Nanjakana section of the compound where the event was held.[50] In 1897, French colonial authorities disinterred and moved the queen's body and the remains of other Merina sovereigns to the tombs at the Rova of Antananarivo in an attempt to desanctify Ambohimanga. Her bones were placed within the tomb of Queen Rasoherina.[51] Her son, Prince Rakoto, succeeded her as King Radama II.[52]
Legacy
Ranavalona's traditionalist policies were abruptly reversed under the reign of her son, King Radama II. A widespread epidemic of "spirit possession" throughout Imerina followed Radama's public conversion to Christianity and was popularly attributed to the outraged spirit of Ranavalona I.[53]
The queen's foreign contemporaries strongly condemned her policies and viewed them as the actions of a tyrant or even a madwoman, a characterization that persisted in Western historical literature until the 1970s.[9][54] Although Ranavalona has traditionally been depicted as a cruel and xenophobic tyrant, in more recent historical analyses she is commonly viewed as an astute politician who effectively protected the political and cultural sovereignty of her nation from European encroachment.[54][55] In Madagascar today, the Malagasy of the central highlands hold complex and diverse views ranging across this spectrum. Most condemn her reign, in line with negative depictions of Ranavalona in current Malagasy history textbooks; this view is most common among Malagasy Christians. Others admire her effort to preserve Malagasy traditions and independence. The majority, regardless of their feelings toward her domestic policies, consider her a remarkable figure in Malagasy history and commend her strength as a ruler in a period of tension with European powers.[54]
A fictionalized account of Ranavalona and her court appears in the novel Flashman's Lady by George MacDonald Fraser. The main character, a soldier and secret agent named Harry Paget Flashman, becomes Ranavalona's military adviser and lover.[56]
References
Citations
- Campbell (2012), p. 713
- Campbell (2012), p. 1078
- Académie malgache (1958), p. 375
- Freeman and Johns (1840), pp. 7–17
- Campbell (2012), p. 51
- Oliver (1886), pp. 42–45
- Rasoamiaramanana, Micheline (1989–1990). "Rainijohary, un homme politique meconnu (1793–1881)". Omaly Sy Anio (in French). 29–32: 287–305.
- Ellis (1838), pp. 421–422
- Berg, Gerald (1995). "Writing Ideology: Ranavalona, the Ancestral Bureaucrat". History in Africa. 22: 73–92. doi:10.2307/3171909. JSTOR 3171909. S2CID 161997570.
- Bloch (1986), p. 106
- Campbell (2012), pp. 185–186
- Campbell, Gwyn (October 1991). "The state and pre-colonial demographic history: the case of nineteenth century Madagascar". Journal of African History. 23 (3): 415–445. doi:10.1017/S0021853700031534.
- Laidler (2005)
- L'habitation à Madagascar (1898), pp. 920–923
- Frémigacci (1999), p. 427
- Ade Ajayi (1989), p. 423
- Oliver (1886), pp. 45–47
- Freeman and Johns (1840), pp. 17–22
- Prout (1863), p. 14
- Freeman and Johns (1840), p. 25
- Campbell, Gwyn (2013). "Chapter 4: Unfree labour and the significance of abolition in Madagascar c.1825–97". In Campbell, Gwyn (ed.). Abolition and Its Aftermath in the Indian Ocean, Africa and Asia. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-77078-5.
- Campbell (2012), p. 570
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), pp. 196, 208–210
- Sharp (2002), p. 43
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), p. 206
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), pp. 208–209
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), p. 196
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), p. 221
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), p. 210
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), p. 222
- Larson, Pier (1997). "Capacities and modes of thinking: Intellectual engagements and subaltern hegemony in the early history of Malagasy Christianity". The American Historical Review. 102 (4): 996–1002. doi:10.2307/2170626. JSTOR 2170626.
- Ellis (1870), p. 71
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), pp. 222–223
- Ralibera and De Taffin (1993), p. 223
- Campbell (2012), pp. 184–186
- Bloch (1986), pp. 18–19
- Koschorko (2007), p. 199
- Campbell, Gwyn (1987). "The Adoption of Autarky in Imperial Madagascar, 1820–1835". The Journal of African History. 28 (3): 395–411. doi:10.1017/S0021853700030103. S2CID 162901304.
- Oliver (1886), pp. 60–63
- Cousins, W.E. (1877–1878). "Since 1800 in Madagascar". The Sunday Magazine for Family Reading. London: Daldy, Isbister & Co. 1: 405–410.
- Andrew, Blond, Parkinson and Anderson (2008), p. 79
- Oliver (1886), p. 48
- Oliver (1886), p. 78
- Ellis (1870), p. 63
- Oliver (1886), pp. 80–85
- Pfeiffer (1861), p. 225
- Pfeiffer (1861), pp. 225–277
- Ade Ajayi (1989), p. 430
- Oliver (1886), pp. 87–88
- Ravalitera, Pela (19 July 2012). "Nampoina, des cases de ses ancêtres aux Rova" (in French). L'Express de Madagascar. Archived from the original on 27 January 2013. Retrieved 11 November 2012.
- Frémigacci (1999), pp. 174–180
- Oliver (1886), p. 89
- Cole (2001), p. 11
- Kamhi, Alison (May 2002). "Perceptions of Ranavalona I: A Malagasy Historic Figure as a Thematic Symbol of Malagasy Attitudes Toward History". Stanford Undergraduate Research Journal: 29–32.
- Sharp (2002), p. 44
- MacDonald Fraser (1977)
Bibliography
- Académie malgache. Collection de documents concernant Madagascar et les pays voisins, Volume 4, Part 4 (in French). Antananarivo: Imprimerie Moderne de l'Emyrne.
- Ade Ajayi, Jacob Festus (1989). Africa in the Nineteenth Century until the 1880s. Paris: UNESCO. ISBN 978-0-520-03917-9.
- Andrew, David; Blond, Becca; Parkinson, Tom; Anderson, Aaron (2008). Lonely Planet Madagascar & Comoros. London: Lonely Planet. ISBN 978-1-74104-608-3.
- Bloch, Maurice (1986). From blessing to violence: history and ideology in the circumcision ritual of the Merina of Madagascar. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-31404-6.
- Campbell, Gwyn (2012). David Griffiths and the Missionary "History of Madagascar". Leiden, The Netherlands: Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-20980-0.
- Cole, Jennifer (2001). Forget Colonialism?: Sacrifice and the Art of Memory in Madagascar. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-92682-0.
- Ellis, William (1838). Volume 2 of History of Madagascar: Comprising Also the Progress of the Christian Mission Established in 1818. London: Fisher, Son & Co.
- Ellis, William (1870). The Martyr Church. London: J. Snow.
- Freeman, Joseph John; Johns, David (1840). A narrative of the persecution of the Christians in Madagascar: with details of the escape of six Christian refugees now in England. Berlin: J. Snow. Retrieved 5 February 2011.
- Frémigacci, Jean (1999). "Le Rova de Tananarive: Destruction d'un lieu saint ou constitution d'une référence identitaire?". In Chrétien, Jean-Pierre (ed.). Histoire d'Afrique (in French). Paris: Editions Karthala. pp. 421–444. ISBN 978-2-86537-904-0.
- Koschorko, Klaus; Ludwig, Frieder; Delgado, Mariano (2007). A history of Christianity in Asia, Africa and Latin America, 1450–1990. Cambridge, U.K.: Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-8028-2889-7.
- Laidler, Keith (2005). Female Caligula: Ranavalona, the Mad Queen of Madagascar. London: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-470-02226-9.
- "L'habitation à Madagascar". Colonie de Madagascar: Notes, reconnaissances et explorations (in French). Vol. 4. Imprimerie Officielle de Tananarive. 1898.
- MacDonald Fraser, George (1977). Flashman's Lady. London: Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-744949-1.
- Oliver, Samuel (1886). Madagascar: An Historical and Descriptive Account of the Island and its Former Dependencies. Vol. 1. New York: Macmillan and Co.
- Pfeiffer, Ida (1861). The last travels of Ida Pfeiffer: inclusive of a visit to Madagascar. London: Harper.
- Prout, Ebenezer (1863). Madagascar: Its Mission and Its Martyrs. London: London Missionary Society.
- Raison-Jourde, Françoise (1991). Bible et pouvoir à Madagascar au XIXe siècle. Antananarivo: Karthala Editions. ISBN 978-2-86537-317-8.
- Ralibera, Daniel; De Taffin, Gabriel (1993). Madagascar et le christianisme (in French). Paris: Karthala Editions. ISBN 978-92-9028-211-2.
- Sharp, Leslie (2002). The Sacrificed Generation: Youth, History, and the Colonized Mind in Madagascar. Berkeley, CA: University of California Press. ISBN 0-520-22951-7.
- Brown, Mervyn (2016). A History of Madagascar". Markus Wiener Publishers.
- Jackson, Guida M. (1999). Women Rulers Throughout the Ages. An Illustrated Guide. ABC-CLIO.
- Wright, Jennifer (2022). I że ci (nie) odpuszczę. Najbardziej mordercze kobiety w historii (in Polish). Wydawnictwo Poznańskie.